(Press-News.org) It reads. It talks. It collates mountains of data and recommends business decisions. Today’s artificial intelligence might seem more human than ever. However, AI still has several critical shortcomings.
“As impressive as ChatGPT and all these current AI technologies are, in terms of interacting with the physical world, they’re still very limited. Even in things they do, like solve math problems and write essays, they take billions and billions of training examples before they can do them well, " explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) NeuroAI Scholar Kyle Daruwalla.
Daruwalla has been searching for new, unconventional ways to design AI that can overcome such computational obstacles. And he might have just found one.
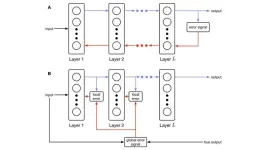
The key was moving data. Nowadays, most of modern computing’s energy consumption comes from bouncing data around. In artificial neural networks, which are made up of billions of connections, data can have a very long way to go. So, to find a solution, Daruwalla looked for inspiration in one of the most computationally powerful and energy-efficient machines in existence—the human brain.
Daruwalla designed a new way for AI algorithms to move and process data much more efficiently, based on how our brains take in new information. The design allows individual AI “neurons” to receive feedback and adjust on the fly rather than wait for a whole circuit to update simultaneously. This way, data doesn’t have to travel as far and gets processed in real time.
“In our brains, our connections are changing and adjusting all the time,” Daruwalla says. “It’s not like you pause everything, adjust, and then resume being you.”
The new machine-learning model provides evidence for a yet unproven theory that correlates working memory with learning and academic performance. Working memory is the cognitive system that enables us to stay on task while recalling stored knowledge and experiences.
“There have been theories in neuroscience of how working memory circuits could help facilitate learning. But there isn’t something as concrete as our rule that actually ties these two together. And so that was one of the nice things we stumbled into here. The theory led out to a rule where adjusting each synapse individually necessitated this working memory sitting alongside it, " says Daruwalla.
Daruwalla’s design may help pioneer a new generation of AI that learns like we do. That would not only make AI more efficient and accessible—it would also be somewhat of a full-circle moment for neuroAI. Neuroscience has been feeding AI valuable data since long before ChatGPT uttered its first digital syllable. Soon, it seems, AI may return the favor.
END
Can AI learn like us?
2024-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
2024-06-20
Changing climate will make home feel like somewhere else
Interactive app shows how climate change will make places around the world feel like they are closer to the equator
FROSTBURG, MD (June 20, 2024)—The impacts of climate change are being felt all over the world, but how will it impact how your hometown feels? An interactive web application from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science allows users to search 40,581 places and 5,323 metro areas around the globe to match the expected future climate in each city with the current climate of another location, ...
Newly discovered dinosaur boasts big, blade-like horns
2024-06-20
What do you get when you cross Norse mythology with a 78-million-year-old ancestor to the Triceratops? Answer: Lokiceratops rangiformis, a plant-eating dinosaur with a very fancy set of horns.
The new dinosaur was identified and named by Colorado State University affiliate faculty member Joseph Sertich and University of Utah Professor Mark Loewen. The dinosaur’s name, announced today in the scientific journal PeerJ, translates roughly to “Loki’s horned face that looks like a caribou.”
Loewen and Sertich, co-lead authors of the PeerJ study, dubbed the new species Lokiceratops (lo-Kee-sare-a-tops) ...
Exploring the relationship between civilians and military organizations through an experiment in Japan
2024-06-20
In democracies where civilian control is followed, the power to make crucial decisions, like those of national security, is mainly exercised by elected officials, allowing the citizens who elect them to influence such decisions indirectly. This role can give people a sense of participation in matters of national importance, potentially associated with their political trust. The military, in such cases, advises and helps these elected leaders in serving the nation, rather than assuming leadership itself. A balance between civilians and military organizations is, therefore, crucial for any democracy to thrive, and it is pointed out that civilian control is a requisite of democracy.
Existing ...
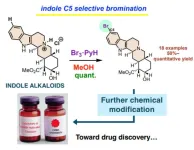
A simple, fast, and versatile method for selective bromination of indole alkaloids
2024-06-20
Indolo[2,3-a]quinolizidine is a common structural motif in various natural products. Its molecular structure contains the indole ring, a functional group in tryptophan. Tryptophan, an essential amino acid, is required for the production and maintenance of our body’s proteins, muscles, enzymes, and neurotransmitters. Many natural products are derived from it. Over 3,000 monoterpene indole alkaloids (MTIAs), which are natural products consisting of indole rings, have been found in plants, and some of them have been used as medicines. For example, vinblastine has been used as an anticancer drug, and reserpine is used to treat high blood pressure.
The ...
Removal of ovaries before menopause associated with reduced white matter in brain
2024-06-20
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – June 20, 2024 – Women who have their ovaries removed before menopause, particularly before the age of 40, have reduced white matter integrity in multiple regions of the brain later in life. White matter refers to the nerve fibers that connect neurons in different areas of the brain.
The findings appear online today in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We know that having both ovaries removed before natural menopause causes abrupt endocrine dysfunction, which increases ...
Fewer good gut bacteria increase the risk of serious infection
2024-06-20
The composition of the intestinal flora can predict the chances of developing serious infections such as pneumonia. Researchers from Amsterdam UMC and the University of Turku, Finland, followed more than 10,000 people for 6 years. More than 600 people who had less healthy intestinal flora developed a serious infection, with this leading in some cases to death. The results of the study are published today in The Lancet Microbe.
The 602 people who were hospitalised due to an infection showed at the start of the study that they had fewer butyrate-producing ...
Sweat health monitor measures levels of disease markers
2024-06-20
PULLMAN, Wash. -- A wearable health monitor developed by Washington State University researchers can reliably measure levels of important biochemicals in sweat during physical exercise.
The 3D-printed monitor could someday provide a simple and non-invasive way to track health conditions and diagnose common diseases, such as diabetes, gout, kidney disease or heart disease.
Reporting in the journal, ACS Sensors, the researchers were able to accurately monitor the levels of volunteers’ glucose, lactate ...
Scientists devise algorithm to engineer improved enzymes
2024-06-20
Scientists have prototyped a new method for “rationally engineering” enzymes to deliver improved performance. They have devised an algorithm, which takes into account an enzyme’s evolutionary history, to flag where mutations could be introduced with a high likelihood of delivering functional improvements.
Their work – published today in leading journal Nature Communications – could have significant, wide-ranging impacts across a suite of industries, from food production to human ...
We may soon be able to detect cancer with AI
2024-06-20
A new paper in Biology Methods & Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that it may soon be possible for doctors to use artificial intelligence (AI) to detect and diagnose cancer in patients, allowing for earlier treatment. Cancer remains one of the most challenging human diseases, with over 19 million cases and 10 million deaths annually. The evolutionary nature of cancer makes it difficult to treat late-stage tumours.
Genetic information is encoded in DNA by patterns of the four bases—denoted by A, T, G and C—that make ...
Rate of cannabis use disorder during pregnancy increased over 20% after cannabis legalization in Canada
2024-06-20
In October 2018, Canada enacted the Cannabis Act in Canada (CAC), which legalised the non-medical use of cannabis. A new study has found that the rate of cannabis-related disorders diagnosed among pregnant women in the Canadian province of Québec increased by more than 20% after the enactment of the CAC, while rates for all other drug- and alcohol-related disorders remained stable. The study is published today in the scientific journal Addiction.
This study measured changes to the monthly rates of diagnosed cannabis-related disorders (CRDs) in the pregnant population in Québec. Since 2010 the monthly average number of CRDs has increased consistently, ...