The time it takes a person to decide can predict their preference
Behavioral and computational study shows that human social preferences can be inferred from decision speed alone
2024-06-20
(Press-News.org) Researchers led by Sophie Bavard at the University of Hamburg, Germany, found that people can infer hidden social preferences by observing how fast others make social decisions. Publishing June 20th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, the study shows that when someone knows the options being considered by another person, and they know how long it takes them to reach their decisions, they can use this information to predict the other person’s preference, even if they do not know what the actual choices were.
How do we know what someone’s social preferences or beliefs are when they are so often hidden and unspoken? While past studies have focused on observing another’s choices, the new study takes a deeper look by examining both choices and decision time. The researchers asked participants to play the Dictator Game in which a so-called dictator must choose between two options to determine how much they will give away or keep for themselves. After playing the part of the dictator, the participants were asked to observe other dictators and predict the preferred give/take proportions. The amount of information provided to the participants varied; sometimes they knew the decisions, sometimes the decision time, sometimes both, and sometimes neither.
The researchers hypothesized that even without knowing the decisions, if they could see the options and know the decision speed, participants would be able to predict the preferences. A computational modeling analysis showed that in theory, dictator behavior could be predicted from decision times alone using a reinforcement learning model. But do people naturally internalize this type of mathematical model when observing others? The answer was yes; the participants learned the dictator’s preferences when all they knew were the options and the decision times, although their predictions were best when they also knew the actual decisions. This indicates that time was used when decisions were not available, which expands our knowledge about decision making in social contexts.
The authors add, “Our findings challenge the conventional belief that choices alone are the only piece of information one can use to understand others' social preferences. By incorporating response times into models of how people learn from each other, we can make more accurate predictions of human behavior, as response times provide a continuous measure that reveals the strength of these preferences, offering a more detailed perspective.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002686
Citation: Bavard S, Stuchlý E, Konovalov A, Gluth S (2024) Humans can infer social preferences from decision speed alone. PLoS Biol 22(6): e3002686. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002686
Author Countries: Germany, United Kingdom
Funding: SG is supported by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (Grant agreement No. 948545, https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/948545). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-20
A devastating hurricane transformed a monkey society by changing the pros and cons of interacting with others, new research shows.
Hurricane Maria hit Puerto Rico in 2017, killing more than 3,000 people. It also destroyed 63% of vegetation on Cayo Santiago (also known as Monkey Island), which is home to a population of rhesus macaques.
Even now, tree cover remains far below pre-hurricane levels and – in this hot part of the world – that makes shade a scarce and precious resource for the macaques.
The new study, led by the universities of Pennsylvania and Exeter and published in the journal Science, shows the storm ...
2024-06-20
Researchers widely observe yet seldom publish about same-sex sexual behavior in primates and other mammals - often because it is perceived to be rare
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304885
Article Title: Same-sex sexual behaviour among mammals is widely observed, yet seldomly reported: Evidence from an online expert survey
Author Countries: Canada, USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
2024-06-20
Chimpanzees appear to consume plants with medicinal properties to treat their ailments, according to a study publishing on June 20 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Elodie Freymann from the University of Oxford, UK, and colleagues.
Many plants produce compounds that have medicinal effects on humans and other animals. Wild chimpanzees eat a variety of plant matter, including some that is nutritionally poor but may treat or lessen the symptoms of illness. However, it is hard to determine whether chimpanzees self-medicate, by intentionally seeking out plants with properties that help their specific ailments, or passively consume plants ...
2024-06-20
Hydrogen is a promising chemical and energy vector to decarbonize our society. Unlike conventional fuels, hydrogen utilization as a fuel does not generate carbon dioxide in return. Unfortunately, today, most of the hydrogen that is produced in our society comes from methane, a fossil fuel. It does so in a process (methane reforming) that leads to substantial carbon dioxide emissions. Therefore, the production of green hydrogen requires scalable alternatives to this process.
Water electrolysis offers a path to generate green hydrogen which can be ...
2024-06-20
Supermassive black holes pose unanswered questions for astronomers around the world, not least “How do they grow so big?” Now, an international team of astronomers, including researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, has discovered a powerful rotating, magnetic wind that they believe is helping a galaxy’s central supermassive black hole to grow. The swirling wind, revealed with the help of the ALMA telescope in nearby galaxy ESO320-G030, suggests that similar processes are involved both in black hole growth and the birth of stars.
Most galaxies, including our own Milky Way have a supermassive black hole at their centre. How ...
2024-06-20
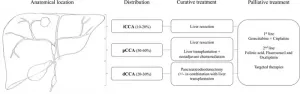
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a rare progressive liver disease that damages bile ducts and significantly increases the risk of bile duct cancer, particularly a type called cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). This cancer is aggressive, and curative surgery is uncommon. Liver transplantation is a potential treatment option for some PSC-CCA patients, especially if the cancer is caught early. Early diagnosis is essential for successful treatment.
PSC can affect people of all ages but primarily strikes men in their 30s and 40s. It is often accompanied by inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The disease can progress to liver failure and increase the risk of colorectal cancer ...
2024-06-20
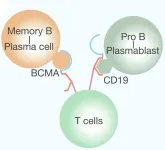
This study is led by Professor Junnian Zheng and Ming Shi from the Cancer Institute of Xuzhou Medical University, together with the team of Professor Guiyun Cui and Wei Zhang from the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University. The team reported for the first time using BCMA-CD19 bispecific CAR T cells for treating relapsed/refractory CIDP.
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an uncommon condition with sudden onset symptoms, including nerve damage affecting movement, sensation, speech, breathing, and heart rate. ...
2024-06-20
Advances in organoids and embryonic models of human development have the potential to prompt social and existential questions—e.g., what defines human individuality? However, bioethicist Insoo Hyun of Harvard Medical School and the Museum of Science in Boston says that these models have the potential to strengthen rather than weaken the concept of human individuality when considered within the philosophical frameworks of “personhood” and sentience. In a commentary publishing June 20 in the journal Cell, Hyun argues that despite huge advances, we are a long way off from developing technologies that would ...
2024-06-20
Last year on a Friday evening, chemical biology researcher Josh Smalley was in the lab when he received a call inviting him to appear on the 14th and latest season of The Great British Bake Off. Starting as one of a group of 12 amateur bakers, Smalley made it all the way to the final round, where the top 3 contestants compete for the winning spot. In an essay published in the journal Cell Chemical Biology on June 20, Smalley describes the overlap between chemistry and baking and how his training in one ...
2024-06-20
Scientists have discovered a new cause of why people who lack a specific blood group are genetically predisposed to be overweight or obese.
A team of international researchers, led by the University of Exeter, discovered that people with a genetic variant that disables the SMIM1 gene have higher body weight because they expend less energy when at rest.
SMIM1 was only identified 10 years ago, whilst searching for the gene encoding a specific blood group, known as Vel. One in 5,000 people lack both copies of the gene, making them Vel-negative. The findings from the new research suggest that this group is also more likely to be overweight, a conclusion ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The time it takes a person to decide can predict their preference
Behavioral and computational study shows that human social preferences can be inferred from decision speed alone