(Press-News.org) Whether it’s physical phenomena, share prices or climate models – many dynamic processes in our world can be described mathematically with the aid of partial differential equations. Thanks to stochastics – an area of mathematics which deals with probabilities – this is even possible when randomness plays a role in these processes. Something researchers have been working on for some decades now are so-called stochastic partial differential equations. Working together with other researchers, Dr. Markus Tempelmayr at the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster at the University of Münster has found a method which helps to solve a certain class of such equations. The results have been published in the journal Inventiones Mathematicae.
The basis for their work is a theory by Prof. Martin Hairer, recipient of the Fields Medal, developed in 2014 with international colleagues. It is seen as a great breakthrough in the research field of singular stochastic partial differential equations. “Up to then,” Markus Tempelmayr explains, “it was something of a mystery how to solve these equations. The new theory has provided a complete ‘toolbox’, so to speak, on how such equations can be tackled.”
The problem, Tempelmayr continues, is that the theory is relatively complex, with the result that applying the ‘toolbox’ and adapting it to other situations is sometimes difficult. “So, in our work, we looked at aspects of the ‘toolbox’ from a different perspective and found and proved a method which can be used more easily and flexibly.” The study, in which Markus Tempelmayr was involved as a doctoral student under Prof. Felix Otto at the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences, published in 2021 as a pre-print. Since then, several research groups have successfully applied this alternative approach in their research work.
Stochastic partial differential equations can be used to model a wide range of dynamic processes, for example the surface growth of bacteria, the evolution of thin liquid films, or interacting particle models in magnetism. However, these concrete areas of application play no role in basic research in mathematics as, irrespective of them, it is always the same class of equations which is involved. The mathematicians are concentrating on solving the equations in spite of the stochastic terms and the resulting challenges such as overlapping frequencies which lead to resonances.
Various techniques are used for this purpose. In Hairer’s theory, methods are used which result in illustrative tree diagrams. “Here, tools are applied from the fields of stochastic analysis, algebra and combinatorics,” explains Markus Tempelmayr. He and his colleagues selected, rather, an analytical approach. What interests them in particular is the question of how the solution of the equation changes if the underlying stochastic process is changed slightly.
The approach they took was not to tackle the solution of complicated stochastic partial differential equations directly, but, instead, to solve many different simpler equations and prove certain statements about them. “The solutions of the simple equations can then be combined – simply added up, so to speak – to arrive at a solution for the complicated equation which we’re actually interested in.” This knowledge is something which is used by other research groups who themselves work with other methods.
END
New mathematical proof helps to solve equations with random components
Researcher at the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics at the University of Münster finds an approach that can be used flexibly
2024-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers awarded $2.78M federal grant to improve rectal cancer treatment with artificial intelligence
2024-06-24
CLEVELAND—With a new five-year, $2.78 million grant from the National Institutes of Health and National Cancer Institute, researchers at Case Western Reserve University(CWRU), Cleveland Clinic and University Hospitals (UH) will use artificial intelligence (AI) to better treat rectal cancer patients.
The American Cancer Society estimates about 46,000 people nationally will be diagnosed this year with rectal cancer—the third most common type of cancer in the digestive system, after colon and pancreatic cancer.
By using AI, the researchers intend to derive specific metrics on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to better understand how ...
Manipulating the frequency of terahertz signals through temporal boundaries
2024-06-24
Terahertz technology could help us meet the ever-increasing demand for faster data transfer rates. However, the down-conversion of a terahertz signal to arbitrary lower frequencies is difficult. In a recent study, researchers from Japan have developed a new strategy to up- and down-convert a terahertz signal in a waveguide by dynamically modifying its conductivity using light, creating a temporal boundary. Their findings could pave the way to faster and more efficient optoelectronics and enhanced telecommunications.
As we plunge deeper into the Information Age, the demand for faster data transmission keeps soaring, accentuated by fast progress in fields like deep learning ...
Study links neighborhood violence, lung cancer progression
2024-06-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists have identified a potential driver of aggressive lung cancer tumors in patients who live in areas with high levels of violent crime. Their study found that stress responses differ between those living in neighborhoods with higher and lower levels of violent crime, and between cancerous and healthy tissues in the same individuals.
The findings are detailed in the journal Cancer Research Communications.
The study was designed to address the higher incidence of lung cancer in Black men than in white men, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign ...
Philadelphia social entrepreneurs address root causes of community violence
2024-06-24
PHILADELPHIA, June 24, 2024 — About 80% of an individual’s modifiable health contributors are determined by social and economic factors.[1] Exposure to violence can have detrimental health implications contributing to toxic stress and trauma, mental health illness, substance abuse and an increased risk for heart disease[2].
The American Heart Association, which marked 100 years of service saving lives earlier this month, has distributed $480,000 from the Association’s Bernard J. Tyson Impact Fund to four social ...
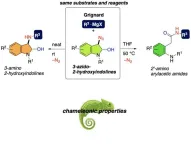
Choosing outcomes: new switchable process for synthesizing 3-aminoindolines and 2’-aminoarylacetic acids from same substrate
2024-06-24
Aniline or nitrogen-containing organic molecules like 3-aniline-substituted indoles commonly found in natural products have shown promising results as pharmaceutical contenders. The same goes for moieties such as 2-aminoaryl acetic acid scaffold which forms the fundamental structural motif of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as diclofenac which inhibits COX-2 to relieve pain and inflammation. While there are several ways of synthesizing these molecules individually using different starting materials, can we produce them ...
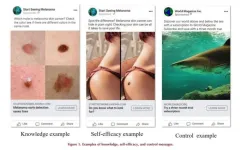
Doing a skin check? Confidence is key & social media ads may help
2024-06-24
It’s summer and time to enjoy the sunshine. But it’s also important to do so safely. Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States—and it’s most commonly caused by sun exposure. Research has shown that skin self-awareness and regular skin self-examinations are strongly linked to better treatment outcomes if you receive a skin cancer diagnosis.
As part of an effort to identify effective interventions to increase skin self-examinations and decrease melanoma deaths, faculty ...
Researchers engineer AI path to prevent power outages
2024-06-24
University of Texas at Dallas researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that could help electrical grids prevent power outages by automatically rerouting electricity in milliseconds.
The UT Dallas researchers, who collaborated with engineers at the University at Buffalo in New York, demonstrated the automated system in a study published online June 4 in Nature Communications.
The approach is an early example of “self-healing grid” technology, which uses AI to detect and repair problems such as outages ...
International collaboration lays the foundation for future AI for materials
2024-06-24
Artificial intelligence (AI) is accelerating the development of new materials. A prerequisite for AI in materials research is large-scale use and exchange of data on materials, which is facilitated by a broad international standard. A major international collaboration now presents an extended version of the OPTIMADE standard.
New technologies in areas such as energy and sustainability involving for example batteries, solar cells, LED lighting and biodegradable materials require new materials. Many researchers around the world are working to create materials that have not existed before. But there are major challenges in creating materials ...
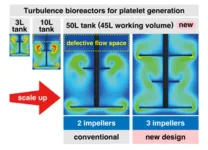
Refining turbulent flow to scale up iPS cell-based platelet manufacturing
2024-06-24
iPS cell-derived expandable immortalized megakaryocyte progenitor cell lines (imMKCLs) represent a renewable means to produce large amounts of platelets ex vivo for transfusion. Despite generating 100 billion (1011) competent iPS cell-derived platelets using a 10-L tank system previously by recreating turbulent flow with optimal turbulent energy and shear stress, true industrial-scale manufacturing is necessary for a consistent supply of transfusable platelets for patients with thrombocytopenia and other platelet disorders. As such, the team began this study by developing a 50 L good manufacturing practices (GMP) grade, single-use United States Pharmacopoeia ...
Can acupuncture lessen hot flashes and other side effects of anti-hormonal breast cancer therapy?
2024-06-24
In a pooled analysis of three clinical trials, acupuncture significantly reduced hot flashes and other hormonal side effects of endocrine therapy taken by women with breast cancer. The analysis of data from the United States, China, and South Korea is published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Endocrine therapy, which blocks hormone signaling that drives some forms of breast cancer, can be a life-saving treatment, but up to 80% of patients who take it experience hot flashes—a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
[Press-News.org] New mathematical proof helps to solve equations with random componentsResearcher at the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics at the University of Münster finds an approach that can be used flexibly