(Press-News.org) On June 25, China’s Chang’e-6 (CE-6) lunar probe is set to return to Earth, carrying the first surface samples collected from the farside of the Moon. In anticipation of this historic event, scientists from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences are publishing their predictions for the unique materials that may be found in the CE-6 samples in the journal The Innovation.
Based on the geological characteristics of the probe’s landing site, the researchers anticipate that the returned surface samples will consist of 2.5-million-year-old volcanic rock combined with small amounts of material generated by nearby meteorite strikes. There is also the possibility that evidence of distant impacts will be found in the samples.
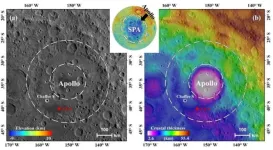
“There are significant differences between the farside and the nearside of the Moon in terms of lunar crustal thickness, volcanic activity, composition, etc., especially considering that CE-6 landed on the South Polar-Aitkin (SPA) basin, the special terrane of the Moon,” says first author Zongyu Yue, a geologist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. “The CE-6 samples, being the first obtained from the farside of the Moon, are expected to answer one of the most fundamental scientific questions in lunar science research: what geologic activity is responsible for the differences between the two sides?”
Nearly 3 weeks ago, on June 2, CE-6 landed in the Apollo Crater, located at the edge of the largest depression on the Moon known as the SPA basin. The probe used core drilling and surface scooping to collect rocks and minerals that are likely to contain traces of early meteorite impacts. The data will reveal how far ejecta from early collisions spread across the Moon and whether there are any differences compared to what’s been recorded on the asymmetrical nearside.
“My greatest hope is that the CE-6 samples contain some impact melts (fragments generated when smaller bodies crashing into the Moon) from the Apollo Crater and the SPA basin, which can provide crucial constraints on the early impact flux of the Moon,” says Yue. “Once this information is obtained, it will not only help clarify the role of early lunar meteorite impacts on the Moon’s evolution, but also be of great significance in analyzing the early impact history of the inner solar system.”
With 10 successful lunar sample return missions conducted on the nearside of the Moon, the CE-6 lunar probe samples represent the first collected from the farside of the Moon. Researchers expect their analysis in the coming months and years to contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of lunar evolution.
###
The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Key Research Programs of IGGCAS.
The Innovation, Yue et al.: “Geological context of Chang’e-6 landing area and implications for sample analysis.”
The Innovation (@The_InnovationJ), published by Cell Press in partnership with members of the Youth Innovation Promotion Association (YIPA), a part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, is a new broad-scope, open access journal publishing basic and applied research that impacts and benefits society. Visit https://www.cell.com/the-innovation. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
Geologists expect Chang’e-6 lunar surface samples to contain volcanic rock and impact ejecta
2024-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New security loophole allows spying on internet users visiting websites and watching videos
2024-06-24
Internet users leave many traces on websites and online services. Measures such as firewalls, VPN connections and browser privacy modes are in place to ensure a certain level of data protection. However, a newly discovered security loophole allows bypassing all of these protective measures: Computer scientists from the Institute of Applied Information Processing and Communication Technology (IAIK) at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) were able to track users' online activities in detail simply by monitoring fluctuations in the speed of their internet connection. No malicious code is required to exploit this vulnerability, ...
Comparison of no-test telehealth and in-person medication abortion
2024-06-24
About The Study: This prospective, observational study found that medication abortion obtained following no-test telehealth screening and mailing of medications was associated with similar rates of complete abortion compared with in-person care with ultrasonography and met prespecified criteria for noninferiority, with a low prevalence of adverse events.
Quote from corresponding author Lauren J. Ralph, Ph.D., M.P.H.:
“This is a prospective, observational study comparing patients who received medication abortion care remotely and without ultrasound to those who went in person to a facility and got an ultrasound. Using data from patient surveys and their medical record, we found ...
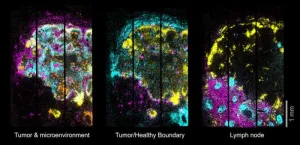
3D maps of diseased tissues at subcellular precision
2024-06-24
An open-source platform developed by researchers in Nikolaus Rajewsky’s lab at the Max Delbrück Center creates molecular maps from patient tissue samples with subcellular precision, enabling detailed study and potentially enhancing routine clinical pathology. The study was published in “Cell.”
Researchers in the Systems Biology Lab of Professor Nikolaus Rajewsky have developed a spatial transcriptomics platform, called Open-ST, that enables scientists to reconstruct gene expression in cells within a tissue in three ...
Estimated effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine against COVID-19
2024-06-24
About The Study: The findings of this case-control study reaffirm current recommendations for broad age-based use of annually updated COVID-19 vaccines given that (1) the BNT162b2 XBB vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech; 2023-2024 formulation) provided statistically significant additional protection against a range of COVID-19 outcomes and (2) older versions of COVID-19 vaccines offered little, if any, long-term protection, including against hospital admission, regardless of the number or type of prior doses received.
Corresponding Author: To contact the ...
New study shows medication abortion without ultrasound to be safe
2024-06-24
Researchers compared patients who received care remotely to those who got ultrasounds and found no differences in outcomes.
Medication abortion patients who receive pills by mail without first getting an ultrasound do just as well as those who are examined and given the drugs in person, new research from UC San Francisco has found.
The study, which appears June 24 in JAMA, adds to evidence from UCSF’s Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health (ANSIRH) program that using telehealth for medication abortion is safe and effective.
Although the ...
New approach accurately identifies medications most toxic to the liver
2024-06-24
The current method for assessing medication-related liver injury is not providing an accurate picture of some medications’ toxicity—or lack thereof—to the liver, according to a new study led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Classification of a medication’s potential to damage the liver, termed “hepatotoxicity,” has been historically determined by counting individual reported cases of acute liver injury (ALI). Instead, the researchers used real-world health care data to measure rates of ALI within a population and uncovered that some medications’ levels of danger to the liver ...
Study reveals new opportunities to develop cancer treatments
2024-06-24
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have uncovered new potential therapeutic targets for cancer and new insights into existing cancer drug targets, expanding the breadth of possibilities for treating this disease. Using a comprehensive approach that included integrating proteomics, genomics and epigenomics data from 10 cancer types, the team identified protein and small protein or peptide targets in cancer tissues and validated many of them experimentally as promising candidates for therapeutic strategies. The study appeared in Cell.
“Experience ...
Bezos Center for Sustainable Protein launches at Imperial with $30M funding
2024-06-24
Bezos Earth Fund grant establishes new Centre at Imperial to transform global food systems from environmentally damaging to innovative by creating sustainable solutions.
Imperial’s Bezos Centre for Sustainable Protein, launched today, will develop innovative and evidence-based solutions through the design, delivery, and commercialisation of alternative food products that are economically and environmentally friendly, nutritious, affordable, and tasty.
The Centre, spanning across seven Imperial academic departments, will advance research into precision fermentation, cultivated meat, bioprocessing and automation, ...
Star clusters observed within a galaxy in the early Universe for the first time
2024-06-24
The history of how stars and galaxies came to be and evolved into the present day remains among the most challenging astrophysical questions to solve yet, but new research brings us closer to understanding it.
In a new study by an international team led by Dr. Angela Adamo at Stockholm University, new insights about young galaxies during the Epoch of Reionization have been revealed. Observations with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) of the galaxy Cosmic Gems arc (SPT0615-JD) have confirmed that the light of the galaxy was emitted 460 million years after ...
How much oxygen do very premature babies need after birth?
2024-06-24
Giving very premature babies high concentrations of oxygen soon after birth may reduce the risk of death by 50 percent, compared to lower levels of oxygen says new research led by University of Sydney researchers.
When premature babies are born, they sometimes need help breathing because their lungs haven’t finished developing. To help babies during this process, doctors may give them extra oxygen through a breathing mask or breathing tube.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, examined clinical trial data and outcomes of ...