AI matches protein interaction partners
2024-06-24
(Press-News.org)
Proteins are the building blocks of life, involved in virtually every biological process. Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular functions, and has significant implications for drug development and the treatment of diseases.
However, predicting which proteins bind together has been a challenging aspect of computational biology, primarily due to the vast diversity and complexity of protein structures. But a new study from the group of Anne-Florence Bitbol at EPFL might now change all that.
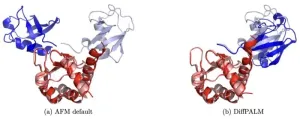
The team of scientists, including Umberto Lupo, Damiano Sgarbossa and Bitbol, has developed DiffPALM (Differentiable Pairing using Alignment-based Language Models), an AI-based approach that can significantly advance the prediction of interacting protein sequences. The study is published in PNAS.
DiffPALM leverages the power of protein language models, an advanced machine learning concept borrowed from natural language processing, to analyze and predict protein interactions among the members of two protein families with unprecedented accuracy. It uses these machine learning techniques to predict interacting protein pairs. This leads to a significant improvement over other methods that often require large, diverse datasets, and struggle with the complexity of eukaryotic protein complexes.
Another advantage of DiffPALM is its versatility, as it can work even with smaller sequence datasets and thus address rare proteins that have few homologs – proteins of different species that share common evolutionary ancestry. It relies on protein language models trained on multiple sequence alignments (MSAs), such as the MSA Transformer and AlphaFold's EvoFormer module, which allows it to understand and predict the complex interactions between proteins with a high degree of accuracy. Even more, using DiffPALM shows high promise when it comes to predicting the structure of protein complexes, which are intricate structures formed by the binding of multiple proteins, and are essential for many of the cell’s processes.
In the study, the team compared DiffPALM with traditional coevolution-based pairing methods, which study how protein sequences evolve together over time when they interact closely – changes in one protein can lead to changes in its interacting partner. This is an extremely important aspect of molecular and cell biology, which is well-captured by protein language models trained on MSAs. DiffPALM is shown to outperform traditional methods Top of Formon challenging benchmarks, demonstrating its robustness and efficiency.
The application of DiffPALM is obvious in the field of basic protein biology, but extends beyond it, as it has the potential to become a powerful tool in medical research and drug development. For instance, accurately predicting protein interactions can help understand disease mechanisms and develop targeted therapies.
The researchers have made DiffPALM freely available, hoping that the scientific community adopts it widely to further advancements in computational biology and enable researchers to explore the complexities of protein interactions.
By combining advanced machine learning techniques and efficient handling of complex biological data, DiffPALM marks a significant leap forward in computational biology. It not only enhances our understanding of protein interactions but also opens up new avenues in medical research, potentially leading to breakthroughs in disease treatment and drug development.
Reference
Umberto Lupo, Damiano Sgarbossa, Anne-Florence Bitbol. Pairing interacting protein sequences using masked language modeling. PNAS 24 June 2024. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311887121
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-24
The world of artificial intelligence (AI) has recently seen significant advancements in generative models, a type of machine-learning algorithms that “learn” patterns from set of data in order to generate new, similar sets of data. Generative models are often used for things like drawing images and natural language generation – a famous example are the models used to develop chatGPT.
Generative models have had remarkable success in various applications, from image and video generation to composing music and to language modeling. The problem ...
2024-06-24
We’ve all seen the surreal footage in nature documentaries showing hydrothermal vents on the frigid ocean floor—bellowing black plumes of super-hot water—and the life forms that cling to them. Now, a new study by UC Santa Cruz researchers suggests that lower-temperature vents, which are common across Earth's seafloor, may help to create life-supporting conditions on "ocean worlds" in our solar system.
Ocean worlds are planets and moons that have—or had in the past—a liquid ocean, often under an icy shell or within their rocky interior. In Earth's solar system, several of Jupiter's and Saturn's moons are ocean worlds, and ...
2024-06-24
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
TAMPA, Fla. (June 24, 2024) – Mindfulness – focusing on the present moment – can improve sleep, reduce stress and improve overall health. A new University of South Florida-led study helps explain why.
Researchers studied 144 nurses over two weeks to see how well they could stay focused on the present and how often they fixated on negative thoughts. The nurses completed surveys three times a day and reported their sleep quality the following morning.
The findings shed light on how mindfulness relates to emotion ...
2024-06-24
The first issue of JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology, under new Editor-in-Chief Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, SM, FACC, publishes today, ushering in a new era of one of the world’s leading scholarly journals.
“I envision JACC, with all its strengths, as a transformative platform for building community, elevating strong science, influencing clinical practice, supporting career development, and improving patient outcomes.” Krumholz said in his Editor’s Page. “JACC and its group of journals can play a pivotal role in serving our community and shaping the future.”
Under his editorship, JACC will be guided by ...
2024-06-24
Using an instrument on the 4.1-meter Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope, researchers obtained the first astronomical spectrum using skipper charge-coupled devices (CCDs).
The results were presented on June 16 at the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation meeting in Japan by Edgar Marrufo Villalpando, a physics PhD candidate at the University of Chicago and a Fermilab DOE Graduate Instrumentation Research Award Fellow.
“This is a major milestone for skipper-CCD technology,” said Alex Drlica-Wagner, a cosmologist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi ...
2024-06-24
Researchers at the University of Toronto have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing.
The technology opens the door to new applications, including systematically interrogating the functions of parts of genes and correcting splicing deficiencies that underlie numerous diseases and disorders.
“Almost all human genes produce RNA transcripts that undergo the process of splicing, whereby coding segments, called exons, are joined together and non-coding segments, called introns, are removed and typically degraded,” said Jack Daiyang Li, first author on the study and PhD student ...
2024-06-24
Oak Brook, IL – The Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening (SLAS) will launch NexusXp, its new interactive pavilion at SLAS2025 to showcase collaborative and integrated lab automation scenarios. NexusXp combines Nexus, the Latin word for link or connection where multiple elements meet, with the modern “Xp” to signify the “Xperience” of making that critical link or connection. Through this new pavilion, SLAS will demonstrate how automation integration transforms research and enables scientific breakthroughs.
“NexusXp is an exclusive event or attendee ...
2024-06-24
AMES, Iowa – A Google Cloud video takes you inside a company data center in
southwest Iowa’s Council Bluffs.
There you are, in the middle of a long, industrial corridor. You slowly move past rack after rack after rack of the computer servers that are, Google says, “helping to keep the internet humming 24/7.”
Part of that hum is the power that keeps those data centers up and running.
“Think about when you use your computer,” said Matthew ...
2024-06-24
LAWRENCE — Many people are familiar with oncogenes — genes long known to be involved in cancers in humans, such as the gene “Src.”
What’s less widely understood is that oncogenes didn’t evolve just to cause cancer in species, but rather to control events of normal growth and differentiation.
“As an organism grows from a single fertilized egg to form all the different tissue types, these oncogenes, including Src, evolved to control these normal events,” said Erik Lundquist, professor of molecular ...
2024-06-24
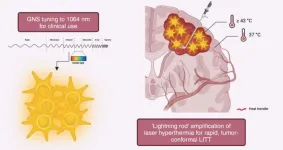
“Gold nanostars amplify brain-tumor selective laser interstitial thermal therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 24, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 14, 2024, entitled, “Leveraging gold nanostars for precision laser interstitial thermal therapy.”
In this new editorial, researchers Aden P. Haskell-Mendoza, Ethan S. Srinivasan, Tuan Vo-Dinh and Peter E. Fecci from Duke University discuss laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT). Over the past decade, LITT has become an important tool for the neurosurgical treatment of a variety of intracranial pathologies, including focal epilepsies, vascular malformations, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] AI matches protein interaction partners