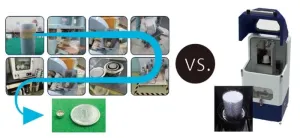
(Press-News.org) A new device can measure carbon dioxide captured in concrete more simply and in a third of the time of current methods. Researchers at the University of Tokyo worked with engineers in industry to create the boxlike device called the concrete thermal gravimetry and gas analyzer. The device heats concrete samples to almost 1,000 degrees Celsius, causing the CO2 within to be released so it can be measured. Compared to the current technique, which involves a time-consuming and complicated process of crushing concrete samples into powder for sampling, this new method is simpler, more accurate and user-friendly. The researchers hope it will contribute to CO2 trading in the future, as the concrete and cement industry work towards offsetting their emissions as part of global targets to manage greenhouse gases.
Concrete is everywhere. We live in it, walk on it, even make movies and write songs about it. Ubiquitous in modern life and even way back in ancient Rome, this sturdy and durable material is a staple for construction projects around the world. But, it is a mixed bag. On the one hand, the process of making concrete and one of its key ingredients, cement, emits a considerable amount of greenhouse gases. It is estimated that 5-8% of all CO2 emissions from human activities to date are from cement production alone. However, concrete can now be used to store CO2, through methods of carbon capture, utilization and storage.
Achieving “net zero,” whereby the amount of CO2 taken out of the atmosphere is equal to the amount released, has become a cornerstone of international policies to tackle global warming. But to do this, we need to know what creates greenhouse gases and at what levels, and how much can be removed through different techniques.
Until now, finding out how much CO2 has been successfully captured in concrete was an extensive process. A cylinder block, about 10 centimeters in diameter and 20 cm high, would be taken and crushed in a way that it couldn’t react with the air (which would affect the results). Then a complicated and long process followed to turn it into a fine, uniform powder from which a small sample was taken for chemical analysis
A new device, developed by researchers at the University of Tokyo with engineers in industry, can skip this time-consuming process. “We developed a new machine which can measure how much CO2 is fixed in concrete or cementitious material without having to crush it,” said Professor Ippei Maruyama from the Department of Architecture at the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Engineering. “Until now, there wasn’t a simple method to measure the amount of CO2 fixed in concrete, but with this device, we can shorten the time it takes to measure CO2 and increase the accuracy of the measurement.”
A specimen block is placed inside the device and then heated to 980 degrees Celsius. As the block heats up, gases including CO2 are released from the block, which can then be measured. This new process takes about one-third of the time of current methods, limiting the time the concrete can react with the air. Results showed that an accurate measurement could be taken even when CO2 was not uniformly distributed within the block.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo envisioned the concept and parts required for the device, while engineers at Rigaku Corp. then developed it. It was then verified by researchers at the University of Tokyo and Taiheiyo Consultants Co., Ltd.
“This device requires a suitably large space and special safety considerations, so for now, there are some limitations to its application,” said Maruyama. “However, after further tests, we hope to make this device commercially available, so that it can contribute to sound emissions trading in the concrete sector and support global efforts to reach carbon neutrality.”
#####
Paper: Ippei Maruyama, Koichiro Noritake, Yoshinobu Hosoi, and Haruka Takahashi. Development of a large-scale thermogravimetry and gas analyzer for determining carbon in concrete. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology. June 24th 2024. DOI: 10.3151/jact.22.383
Funding:
This study was based on the results obtained from a project (JPNP21023) commissioned by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Declaration / conflicts of interest
N/A
Useful Links
Graduate School of Engineering: https://www.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/soe
Building Material Engineering Lab: https://bme.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Research Contact:
Professor Ippei Maruyama
Department of Architecture, The University of Tokyo
Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656
Tel: 03-5841-6796
Email: i.maruyama@bme.arch.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact:
Mrs. Nicola Burghall (she/her)
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on X (formerly Twitter) at @UTokyo_News_en.
END
All-in-one method measures CO2 in concrete
New device measures greenhouse gas captured in building material quickly and easily
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Internet for billions in 100 countries with no current access and hope for transplant patients worldwide in new World Economic Forum emerging technologies report
2024-06-25
The World Economic Forum, in association with Frontiers, new Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2024, released today (25 June), shows that among technologies emerging globally, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) and High-Altitude Platform Systems (HAPS) have the potential to connect billions worldwide who currently have no internet access.
The report also highlights how advances in genetically engineering animal organs for use in human transplantation gives hope to the millions on waiting lists worldwide. Other technologies in the top ten that that could transform lives and societies ...
A new paradigm in photothermal therapy! DGIST developed “ultrasound-assisted photothermal therapy (ULTRA-PTT)” technology!
2024-06-25
□ Professor Jin-ho Chang’s research team from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST (President Kun-woo Lee) developed “Ultrasound-assisted photothermal therapy (ULTRA-PTT)” technology that significantly enhances the performance of conventional photothermal therapy. This technology was developed in collaboration with Senior Researcher Hye-min Kim from the Advanced Photonics Research Institute at GIST (President Ki-chul Lim) using the team’s proprietary “ultrasound-induced optical clearing” technology.
□ Phototherapy, using light, ...
Nanowires create elite warriors to enhance T cell therapy
2024-06-25
Adoptive T-cell therapy has revolutionized medicine. A patient’s T-cells — a type of white blood cell that is part of the body’s immune system — are extracted and modified in a lab and then infused back into the body, to seek and destroy infection, or cancer cells.
Now Georgia Tech bioengineer Ankur Singh and his research team have developed a method to improve this pioneering immunotherapy.
Their solution involves using nanowires to deliver therapeutic ...
Plant-sourced nitrate proves positive to human health
2024-06-25
Plant-sourced nitrate proves positive to human health
New research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has found that nitrate from plant sources is associated with a lower risk of mortality while nitrate from other sources such as animal-based foods, processed meat and tap water, is linked to a higher risk of mortality.
Nitrate, a compound found in vegetables, meat, and drinking water, has been the subject of debate due to its potential impact on health. Emerging evidence suggests that dietary nitrate may play a role in preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD), dementia, and ...
DGIST-POSTECH joint research team developed next-generation impact-resistant stretchable electronic component
2024-06-25
□ Professor Kyung-In Jang’s research team from the Department of Robotics and Mechatronics Engineering at DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee) has succeeded in developing a highly stable stretchable electronic device, which overcomes the mechanical limitations of conventional inorganic materials and enhances their stretchability and durability. In collaboration with Professor Taeho Park’s team from the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH (President Seong-Keun Kim), the research team has developed a stretchable hybrid polymer and applied it to electronic devices, enabling them to operate stably even under deformation ...
Robots help put brakes on inflammatory diseases
2024-06-25
Fully automated diagnostic techniques, including liquid handling robots, are poised to improve the lives of millions of people living with inflammatory diseases worldwide.
A landmark WEHI study has revealed new methods in detecting necroptosis, a key factor in many inflammatory diseases like psoriasis, arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
The findings mark a huge leap forward in our ability to diagnose necroptosis accurately. They also offer practical methods that can be easily reproduced in hospitals worldwide, giving hope for new ways to treat inflammatory diseases.
At a glance
Necroptosis is a form of cell death, one of the body’s natural ...
Chronic loneliness may increase stroke risk among older adults
2024-06-25
Embargoed for release: Monday, June 24, 7:30 PM ET
Key points:
In a study of loneliness and stroke risk over time among adults ages 50+, those who experienced chronic loneliness had a 56% higher risk of stroke than those who consistently reported not being lonely.
Those who experienced situational loneliness did not have an elevated risk of stroke—suggesting that the impact of loneliness on stroke risk occurs over the longer term.
Boston, MA—Chronic loneliness may significantly raise older adults’ risk of stroke, according to a new study led by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
“Loneliness is increasingly considered a ...
Risk of Parkinson’s more than double for people with anxiety
2024-06-25
The risk of developing Parkinson’s is at least twice as high in people with anxiety compared to those without, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in the British Journal of General Practice, investigated whether there was a link between people over the age of 50 who had recently developed anxiety and a later diagnosis of Parkinson’s.
The team used UK primary care data between 2008 and 2018 and assessed 109,435 patients who had developed anxiety after the age of 50 and compared them to 878,256 matched ...
European countries differ in their drinking styles – what is yours?
2024-06-25
A new study of drinking patterns across Europe from 2000 to 2019 shows that drinking occurs in stable, beverage-specific clusters that seem to be partly determined by geography. The study was published today by the scientific journal Addiction.
The study identified six drinking patterns in Europe in 2019:
Wine-drinking countries: France, Greece, Italy, Portugal, and Sweden. Characterized by the highest consumption of wine, lowest consumption of beer and spirits, and lowest overall alcohol consumption.
High beer/low spirit drinking ...
Children born underweight are at increased risk of disease if they develop obesity
2024-06-25
Scientists at the University of Copenhagen discover a link between birthweight and the risk of health complications from obesity during childhood. The findings highlight the need for prevention and treatment approaches for children with obesity who were born with a lower birth weight.
Hundreds of millions of people live with obesity, which is normally measured as a higher-than-optimal body mass index (BMI). While an elevated BMI increases the risk of a range of cardiometabolic diseases and is responsible for around five million deaths a year according to the World Health Organization, not everyone is equally at risk.
Scientists at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] All-in-one method measures CO2 in concreteNew device measures greenhouse gas captured in building material quickly and easily