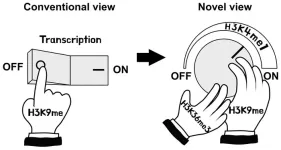
(Press-News.org) Researchers led by Kannosuke Yabe, Asuka Kamio, and Soichi Inagaki of the University of Tokyo have discovered that in thale cresses histone H3 lysine-9 (H3K9) methylation, conventionally thought to be a mark of turning off gene transcription, can also turn on gene expression via the interactions of two other proteins and histone marks. The molecular mechanisms demonstrate that rather than functioning as a simple “off switch,” H3K9 methylation is more like a “dimmer switch” that fine-tunes DNA transcription. The discovery suggests there might be similar mechanisms in other organisms, too. The findings were published in the journal Science Advances.
DNA is often called the “blueprint of biological organisms.” However, calling it the “toolbox of cells” might be more accurate because cells also need to control which genes, the basic building blocks of DNA, are transcribed, or in other words, “turned on or off.” This is epigenetics, and it involves the complex interactions of many types of proteins, such as histones. H3K9 methylation is an epigenetic mark associated with turning off DNA transcription. Even though H3K9 methylation was discovered 25 years ago, not all of its molecular mechanisms have been clarified.
“Biological systems are so complex,” says Inagaki, the principal investigator, “that it is almost impossible for us to understand exactly how life works. But we can try to understand a tiny part of it. The regulation of gene activity is fundamental to life and is connected to a lot of biological phenomena.”
The researchers chose to investigate the molecular mechanisms of gene regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana, commonly known as thale cresses. The team used a technique called chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq). This technique provides a detailed view of how proteins interact with DNA. It can be used to analyze the locations of protein modifications very precisely, making it a befitting tool to investigate histone methylation. Then, the results of H3K9 methylation’s peculiar role came in.
“At first, I did not pay attention to the results of the analysis,” Inagaki remembers, “and did not do any further research on the subject for about a year. I overlooked the finding because it was so unexpected. But one day I had a eureka moment and everything made sense in my head. After that, proving the hypothesis that H3K9 methylation had a dual role went smoothly.”
H3K9 methylation’s dual role is achieved via two other proteins, LDL2 and ASHH3. LDL2 helps to turn off genes by removing another histone mark, H3K4 methylation. ASHH3 turns the gene on by stopping LDL2 from working via a third histone mark, H3K36 methylation. The complex relationship of the 3 histone marks (H3K9, H3K4, H3K36) determines the gene’s activity.
“I’m happy that we discovered the fundamental aspect of gene regulation by H3K9 methylation, even though many studies around the function and controlling mechanisms of H3K9 methylation have been conducted in many organisms. I hope that this finding will stimulate further scientific endeavors to elucidate how gene regulation works,” Inagaki says, already thinking about future research.
END
The on-and-off affair in DNA
New research demonstrates that a process that turns off DNA transcription can, paradoxically, also turn it on
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the US Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought
2024-06-26
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the U.S. Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000246
Article Title: The water adaptation techniques atlas: A new geospatial library of solutions to water scarcity in the U.S. Southwest
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. END ...
AI generated exam answers go undetected in real-world blind test
2024-06-26
Experienced exam markers may struggle to spot answers generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), researchers have found.
The study was conducted at the University of Reading, UK, where university leaders are working to identify potential risks and opportunities of AI for research, teaching, learning, and assessment, with updated advice already issued to staff and students as a result of their findings.
The researchers are calling for the global education sector to follow the example of Reading, and others who are also forming new ...
How do our memories last a lifetime? New study offers a biological explanation
2024-06-26
Whether it’s a first-time visit to a zoo or when we learned to ride a bicycle, we have memories from our childhoods kept well into adult years. But what explains how these memories last nearly an entire lifetime?
A new study in the journal Science Advances, conducted by a team of international researchers, has uncovered a biological explanation for long-term memories. It centers on the discovery of the role of a molecule, KIBRA, that serves as a “glue” to other molecules, thereby solidifying memory formation.
“Previous efforts to understand ...
Mechanical computer relies on kirigami cubes, not electronics
2024-06-26
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a kirigami-inspired mechanical computer that uses a complex structure of rigid, interconnected polymer cubes to store, retrieve and erase data without relying on electronic components. The system also includes a reversible feature that allows users to control when data editing is permitted and when data should be locked in place.
Mechanical computers are computers that operate using mechanical components rather than electronic ones. Historically, these mechanical components have been things like levers or gears. However, mechanical computers can also be made using structures that are multistable, meaning ...
Acting for a common goal with humanoid robots
2024-06-26
Genova (Italy), 26 June 2024 – Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) have demonstrated that under specific conditions, humans can treat robots as co-authors of the results of their actions. The condition that enables this phenomenon is that a robot behaves in a human-like, social manner. Engaging in gaze contact and participating in a common emotional experience, such as watching a movie, are the key. The study was published in Science Robotics and paves the way for understanding and designing the optimal circumstances for humans and robots to collaborate in the same environment.
The ...
Time-compression in electron microscopy
2024-06-26
Scientists at the University of Konstanz in Germany have advanced ultrafast electron microscopy to unprecedented time resolution. Reporting in Science Advances, the research team presents a method for the all-optical control, compression, and characterization of electron pulses within a transmission electron microscope using terahertz light. Additionally, the researchers have discovered substantial anti-correlations in the time domain for two-electron and three-electron states, providing deeper insight into the quantum physics of ...
First case of Down syndrome in Neandertals documented in new study
2024-06-26
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A new study published by an international multidisciplinary team of researchers including faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York, documents the first case of Down syndrome in Neandertals and reveals that they were capable of providing altruistic care and support for a vulnerable member of their social group.
The research, led by anthropologists at the University of Alcalá and the University of Valencia in Spain, studied the skeletal remains of a Neandertal child, whom they affectionately named “Tina”, found at Cova Negra, a cave in Valencia, Spain long known for yielding important Neandertal discoveries.
“The ...
Future risk of coral bleaching set to intensify globally
2024-06-26
An international team of researchers led by the University of Adelaide has projected future marine heatwaves will cause coral reefs to be at severe risk of bleaching for longer periods than previously seen.
Through climate modelling and supercomputing, the researchers discovered that extended bleaching events may significantly disrupt coral spawning.
“We found that coral bleaching will start earlier in the year and last longer than previously thought,” said lead author Dr Camille Mellin, from the University of Adelaide’s Environment Institute.
“Our results show that by 2080, coral bleaching will tend to start in spring, rather than late summer, which ...
The science of procrastination
2024-06-26
Procrastination, the deliberate but detrimental deferring of tasks, has many forms. Sahiti Chebolu of the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics uses a precise mathematical framework to understand its different patterns and their underlying reasons. Her insights could help tailor individual strategies to tackle the issue.
“Why did I not do this when I still had the time?” – Whether it is filing taxes, meeting a deadline at work, or cleaning the apartment before a family visit, most of us have already wondered why we tend to put off certain tasks, even in the face of unpleasant consequences. Why do we make decisions that are harmful to us – against our better ...
Saudi women’s quest for change enabled them earn citizenship rights
2024-06-26
Saudi women have obtained their citizenship rights through their own struggle and there is little truth in the widely held idea in the West that their role in the fight for their freedom has been negligible.
The finding is part of a new research in the journal Diogenes authored by Zahia Salhi, a professor at Sharjah University’s College of Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences. The University of Cambridge Press has also posted Prof. Salhi’s research online.
“Far from being passive victims of their society, Saudi women are active agents ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] The on-and-off affair in DNANew research demonstrates that a process that turns off DNA transcription can, paradoxically, also turn it on