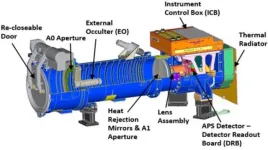
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON – The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s (NRL) Compact Coronagraph (CCOR) was launched June 25, on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) from NASA – Kennedy Space Center to detect and characterize coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
The NOAA sponsored NRL to design, integrate, and test CCOR, a small space telescope that will create an artificial eclipse of the sun and image the solar corona, which is the outer layer of the sun’s atmosphere.
“CMEs are the explosive release of mass and energy from the solar surface and are a primary driver of space weather and play a central role in understanding the conditions in the Earth’s magnetosphere, ionosphere, and thermosphere,” said Arnaud Thernisien, a research physicist from the Advanced Sensor Technology Section within the Space Science Division. “The instrument will be used by NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center and the Department of Defense to detect CMEs and will provide an early warning of possible magnetic storms surrounding Earth.”
NRL’s CCOR is the nation’s first operational coronagraph. Operational means that the instrument is tailored to provide low latency observations of the corona, and has some resilience to radiation induced space weather effects. The GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite has a Solar Pointing Platform that is dedicated to host solar pointed instruments for space weather monitoring.
“Watching NRL’s CCOR launch into space on the NOAA GOES-U is a testament to our collaborative space efforts and joint capabilities,” said NRL Commanding Officer, Capt. Jesse Black. “I am proud to be a part of an organization dedicated to innovation, and our commitment to scientific progress and national security. The science is important to orbital tracking, radio communications, and navigation that affect the operation of ships and aircraft, utilization of the near-space and space environment of the Earth, and the fundamental understanding of natural radiation and geophysical phenomena.”
The CCOR design has been adapted for the Space Weather Follow On Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite, set to launch in 2025, and the Vigil space weather satellite, an international space weather mission led by the European Space Agency (ESA) to launch later in this decade.
About the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
NRL is a scientific and engineering command dedicated to research that drives innovative advances for the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps from the seafloor to space and in the information domain. NRL is located in Washington, D.C. with major field sites in Stennis Space Center, Mississippi; Key West, Florida; Monterey, California, and employs approximately 3,000 civilian scientists, engineers and support personnel.
For more information, contact NRL Corporate Communications at (202) 480-3746 or nrlpao@us.navy.mil.
END
NRL CCOR launches on the GOES-U NOAA satellite to monitor space weather
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows how liver damage from stress and aging might be reversible
2024-06-26
DURHAM, N.C. – While the liver is one of the body’s most resilient organs, it is still vulnerable to the ravages of stress and aging, leading to disease, severe scarring and failure. A Duke Health research team now might have found a way to turn back time and restore the liver.
In experiments using mice and liver tissue from humans, the researchers identified how the aging process prompts certain liver cells to die off. They were then able to reverse the process in the animals with an investigational drug.
The finding, which ...
Bone stem cells with IFITM5 mutation get caught in a loop leading to osteogenesis imperfecta type V
2024-06-26
A study conducted by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions reveals the molecular events leading to osteogenesis imperfecta type V, a form of brittle bone disease caused by a mutation in the gene IFITM5.
The mutation blocks the normal development of bone stem cells into mature cells, which would form healthy bones. Instead, the mutation leads to the formation of bones that are extremely brittle. Children with this disorder have recurrent fractures, bone deformities, chronic pain and other complications. ...
Tai Chi reduces risk of inflammatory disease, treats insomnia among breast cancer survivors
2024-06-26
New research led by UCLA Health confirms that both Tai Chi and cognitive behavioral therapy can reduce insomnia in breast cancer survivors but also may provide additional health benefits by reducing inflammation and bolstering anti-viral defenses.
Chronic insomnia is one of the most prominent symptoms experienced among cancer survivors and poses significant health concerns, including the risk of inflammatory disease that could increase the risk of cancer recurrence.
About 30% of breast cancer survivors are reported to have insomnia, which is twice the rate of the general population. While previous research has shown cognitive behavioral therapy and mind-body ...
Technology presented for measuring carbon in media, advertising and generative AI
2024-06-26
Measuring energy consumption derived from digital activity from a scientific point of view is the challenge faced by Hiili, S.L., a company recently formed and driven by two researchers from the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), Ángel and Rubén Cuevas Rumín, from the Telematics Engineering Department. Specifically, they develop technological solutions that combine Internet measurement techniques and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to make an accurate estimate of the energy consumption of a company's ...
Do people who exercise more have a lower risk of ALS?
2024-06-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Moderate levels of physical activity and fitness may be linked to a reduced risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) later in life, according to a new study published in the June 26, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study only found an association between physical activity and risk of ALS in male participants, not female participants.
ALS is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. People with ALS lose the ability to initiate ...
Could preventative drug be effective in people with migraine and rebound headache?
2024-06-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A drug used to prevent migraine may also be effective in people with migraine who experience rebound headaches, according to a new study published in the June 26, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
People with chronic migraine who overused pain medication had fewer monthly migraine and headache days and fewer days using pain medication when taking the migraine prevention drug atogepant.
“There is a high prevalence of pain medication ...
Pathologists awarded grant from American Society of Hematology
2024-06-26
Dr. Zhen Mei, a clinical pathologist, and Dr. Vivian Chang, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist, both at UCLA Health, have been awarded $30,000 from the American Society of Hematology to revise blood cell ranges for people with Duffy-null Associated Neutrophil Count, which is also known as Duffy-negative.
Those who are Duffy-negative, estimated to be two out of three people identifying as Black in the U.S., lack Duffy antigens on the surface of their red blood cells as a mechanism to resist malaria. This helps provide protection but ...
Revolutionizing ovarian cancer treatment with adaptive PARP inhibitor therapy
2024-06-26
TAMPA, Fla. — Ovarian cancer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage, presents significant treatment challenges because patients tend to develop resistance to conventional therapies quickly. Despite aggressive treatment, recurrence rates remain high, and managing this disease effectively requires innovative approaches. Poly-adenosine ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have emerged as a treatment option, targeting specific DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. However, their use is often limited ...
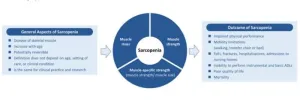
Global consensus for sarcopenia
2024-06-26
“[...] the development of a global conceptual definition of sarcopenia signifies a new dawn for this muscle disease.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 26, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Global consensus for sarcopenia.”
In this new editorial, researchers Ben Kirk, Peggy M. Cawthon, and Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft from the University of Melbourne and Western Health discuss the global societal issue of skeletal muscle loss and weakness, termed Sarcopenia. Low muscle ...
Ocean’s loss of oxygen caused massive Jurassic extinction. Could it happen again?
2024-06-26
DURHAM, NC – Researchers have discovered a clue in Italian limestone that helps explain a mass extinction of marine life millions of years ago, and may provide warnings about how oxygen depletion and climate change could impact today’s oceans.
“This event, and events like it, are the best analogs we have in Earth's past for what is to come in the next decades and centuries,” said Michael A. Kipp, an earth and climate science assistant professor at Duke University. Kipp co-authored a study published June 24 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that measures oxygen loss ...