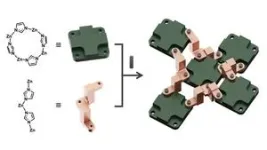
(Press-News.org) NORMAN, OKLA. – Bin Wang, a professor in the School of Sustainable Chemical, Biological and Materials Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, has received a Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Research Award from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Wang was selected for his contributions to computational catalysis and physical chemistry.
The Bessel Award is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research to foster collaborative relationships between international academics and German researchers. The award includes a grant that supports up to 12 months of study in Germany.
In his research, Wang uses simulations to understand materials at the atomic level, providing insights into materials that can be used to accelerate chemical reactions. He will work with the Sustainable Materials Computational Materials Design department of the Max Planck Institute to use a machine learning approach to study solid-liquid interfacial chemistry. Wang says that because simulations of the solid-liquid interface include so much complexity, accurate simulation can be challenging. Machine learning techniques can help improve those simulations.
According to Wang, the collaboration could not come at a better time. Recently, OU’s School of Sustainable Chemical, Biological and Materials Engineering added “sustainable” to its name. “When people think about chemical engineering, the perception is that it’s all about oil and gas chemistry and operation,” he said. “That’s the reason [the school] changed the name, to show that our research and education is very broad and to achieve a sustainable future.”
This April, the Max Planck Institute for Iron Research did something similar, becoming the Max Planck Institute for Sustainable Materials.
“This really reflects what’s happening in the field right now. People are looking to sustainability and the challenges associated with it,” said Wang.
Wang has received numerous accolades during the span of his career, including an Early Career Award from the U.S. Department of Energy. He has been recognized as an Emerging Investigator by the Royal Society of Chemistry’s Catalysis Science & Technology and an Influential Researcher by the American Chemical Society’s Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
END
Bin Wang receives Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Research Award
2024-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Decline in UK coronary heart disease rates offset by rise in other cardiovascular conditions
2024-06-27
Rates of coronary heart disease in the UK have declined by about 30% over the past two decades, but this has been offset by rising rates of other conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels, finds a study in The BMJ today.
What’s more, improvements in rates of coronary heart disease almost exclusively appeared to benefit the over 60s, with little or no improvement in younger or more deprived groups, the results show.
As such, the researchers say future prevention strategies might need to consider a broader spectrum ...
Specialist weight-loss services in England unable to keep up with spiralling demand
2024-06-27
One in six integrated care boards (ICBs) in England have stopped accepting new patients for specialist weight management services as their referral numbers spiral out of control, an investigation by The BMJ has found.
ICBs are responsible for planning health services for their local population. At least seven out of 42 ICBs across the country - covering Manchester, Bristol, Suffolk, Leicester, Essex, and much of Yorkshire - have had to close a specialist (tier 3) weight management service list in their area, with many warning that demand is far exceeding capacity, reports Elisabeth Mahase.
Experts have said the rise in obesity and the demand for weight-loss injections may be fuelling ...
Cardiovascular health could be biggest risk factor for future dementia rates
2024-06-27
Dementia risk factors associated with cardiovascular health may have increased over time compared to factors such as smoking and having less education, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in The Lancet Public Health, explored how the prevalence of dementia risk factors had changed over time and how this could impact rates of dementia in the future.
It is estimated that there are currently 944,000 people living with dementia in the UK and 52% of the UK public – 34.5 million ...
New study shows alcohol rehabilitation and abstinence reduce the risk of alcohol-associated cancers
2024-06-27
June 26, 2024 (Toronto, Canada) – A new study conducted by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH), Bordeaux University Hospital, France, and the World Health Organization (WHO) has found that individuals with alcohol dependence who undergo rehabilitation or maintain abstinence experience significantly lower risks of developing alcohol-associated cancers. The article, entitled Alcohol rehabilitation and cancer risk: a nationwide hospital cohort study in France was published today in Lancet Public Health. It is the largest of its kind to provide evidence linking reduced ...
Early childhood problems linked to persistent school absenteeism
2024-06-27
University of Leeds news
Children who are not considered “school ready” by their teachers are more than twice as likely to become persistently absent at some point in their education, according to a new study led by the University of Leeds.
Researchers analysed data for 62,598 children aged 5-13 from across the Bradford district and compared it with school absence records between the academic years 2012/2013 and 2019/2020 to identify associations between early childhood problems and absenteeism.
The team from the School of Psychology and the Born in Bradford Centre for Applied Education Research found ...
Use of glucose monitors by people not living with diabetes needs more regulation
2024-06-27
A new narrative review1 led by researchers at UCL and Birmingham Children’s Hospital has found there is a lack of evidence to demonstrate the effective use of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in people not living with diabetes (PNLD).
In the study, published in Diabetic Medicine, researchers conclude there is currently little published evidence on how accurate CGMs are in measuring blood glucose levels in PNLD, nor sufficient evidence of what the health benefits or utility ...
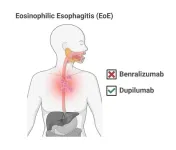
Two studies shows mixed progress against EoE
2024-06-27
Despite high hopes, a drug that wipes out the namesake cell type associated with the disease eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) doesn’t make patients feel better and doesn’t reverse tissue damage in their throats.
Meanwhile, data show that a different drug that had previously been approved for use in adults and teens with EoE is also safe and effective for children under 12 who weigh at least 15 kg (about 33 pounds).
The results of these clinical trials—plus an accompanying editorial—appear in the June 17, 2024, edition of The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Together, these trials provide exciting advances in our understanding of, and treatment options for, ...
Specific bacteria in your gut are involved in compulsive eating and obesity
2024-06-27
Vienna, Austria: An international team of researchers has identified specific bacteria in the gut that are associated with both mice and humans developing an addiction to food that can lead to obesity. They have also identified bacteria that play a beneficial role in preventing food addiction.
The research is presented today (Thursday) at the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) Forum 2024 and is published simultaneously in the journal Gut [1,2].
Professor Elena Martín-García, from the Laboratory of Neuropharmacology-NeuroPhar in the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences at the Universitat ...
More than a quarter of ‘healthy’ over-60s have heart valve disease, according to new research
2024-06-27
Almost 4,500 healthy and symptom-free over-60s were examined, with 28pc found to have heart valve disease
Age was found to be strongly associated with an increased incidence of significant heart valve disease
Study lays the foundation for more research into the potential role of screening in the elderly population
Peer-reviewed – Prospective Cohort Study - People
The sheer scale of undiagnosed heart valve disease in our ageing population has been revealed for the first ...
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet - June 2024
2024-06-26
BLOOD CANCER
Sylvester Expert Endorses FDA’s Recent Cancer Drug Approval
Mikkael Sekeres, M.D., chief of the Division of Hematology at Sylvester, who specializes in treating leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), expressed his support for the Food and Drug Administration’s recent approval of the drug imetelstat. The drug, a telomerase inhibitor, treats cancer-related anemia in patients with lower-risk MDS. “With approval of imetelstat to treat myelodysplastic syndromes, we finally have another approach ...