(Press-News.org) Being nursed by a single parent could be an evolutionary strategy to curb the spread of harmful microbes in mammals, according to a novel theory developed by mathematicians.
The rainforests of Malaysia are home to the only known case of a wild male mammal that produces milk. The Dayak fruit bat is a vanishingly rare case of male milk production, despite the fact that the potential for breastfeeding remains in place in most male mammals.
In the 1970s, evolutionary theorists posited that the near absence of lactation in males, even though offspring could benefit from the extra nutrition provided, could be attributed to the uncertainty of paternity: As male mammals can’t be sure they are the biological father, this reduces their evolutionary drive to invest heavily in offspring care, including breastfeeding.
Now, mathematicians from the University of York have suggested a complementary perspective. Their hypothesis, published in Nature Communications, suggests that the reason male mammals don’t breastfeed might be driven by the rich community of microbes that lives in breast milk and which plays an important part in establishing the gut microbiome of the infant.
The theory demonstrates how the transmission of the milk microbiome from both parents would allow harmful microbes to spread through mammalian populations. Maternal-only lactation stops this as restricting transmission of the milk microbiome to females in effect acts as a sieve, retaining just the microbes with beneficial effects.
One of the authors of the study, Dr George Constable from the Department of Mathematics at the University of York, said: “We became fascinated with this topic when we read about Azara's owl monkeys. They turn previous assumptions about why males don’t breastfeed upside down because they are the most devoted dads in the primate world: They do 80–90% of childcare and only hand their babies back to their female partners for nursing.
“When both parents are involved in feeding, the chance of a microbe being passed along and getting an initial foothold in a population is essentially doubled. So our theory suggests selection against the transmission of harmful microbes through mammary milk could be an additional selection pressure against male lactation.”
First author of the study, Dr Brennen Fagan working at the Leverhulme Centre for Anthropocene Biodiversity and the Mathematics Department at the University of York, added: “Breast milk is a living substance and it plays a key role in establishing the gut microbiome of mammals, which is a complex ecosystem of bacteria, viruses and fungi, along with their genetic material. This ecosystem plays a crucial role in health including by helping to protect animals against disease, helping to digest food and in many other ways we are only just discovering.
“While microbes are not inherently harmful or beneficial; it’s their presence and abundance that dictate the overall health of this internal community. A “wrong actor” at the early point of an animal’s life could change the microbiome at a pivotal moment.”
The mathematical model highlights the advantage of getting fed by just one parent, but the researchers say it makes evolutionary sense for this to be the mother because there has already been an inevitable transmission of microbes during birth and perhaps also in the womb.
Dr Constable added: “This theory fits with a pattern of strategies mammals have adopted in an evolutionary bid to limit the spread of potentially harmful elements. Notably, in humans mitochondrial DNA is exclusively passed down from the mother. This mechanism serves as a natural filter, maintaining genetic integrity by suppressing the proliferation of detrimental mutations. Additionally, the prevalence of monogamous relationships among certain species has been suggested as an adaptive response aimed at minimising the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).”
The researchers caution that their hypothesis is not intended as the basis for any judgements about the different ways of feeding human infants.
Dr Fagan added: “Our model is very much focused on the long-term evolution of the animal kingdom. The model does not tell us about individual families making individual choices on how to safely feed their children, especially not for humans in the modern world.
“Our hypothesis fills a gap in evolutionary theory and is concerned with selection pressures on mammals at population level and over very long periods of time spanning multiple generations.”
Maternal transmission as a microbial symbiont sieve, and the absence of lactation in male mammals is published in Nature Communications.
END
New mathematical model sheds light on the absence of breastfeeding in male mammals
Being nursed by a single parent could be an evolutionary strategy to curb the spread of harmful microbes in mammals, according to a novel theory developed by mathematicians.
2024-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ammonites went out with a diverse bang—and not a long, slow fizzle—in the Late Cretaceous
2024-06-27
Los Angeles, CA (June 27, 2024) —A new study published in the journal Nature Communications led by paleontologists at the University of Bristol along with a team of international researchers, including Dr. Austin Hendy, Curator of Invertebrate Paleontology at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, finds that instead of fizzling out ahead of their extinction, ammonoids were still going strong across the globe in the Late Cretaceous. Made possible by museum collections, the new study compared their diversity across the globe just prior to extinction, unearthing the complex evolutionary history ...
Cleveland Clinic launches wellness and diet coaching app featuring state-of-the-art food and fitness tracking, support and education
2024-06-27
Embargoed until 4am EDT Cleveland, OH (Thursday, June 27, 2024) – Cleveland Clinic and app developer FitNow, Inc. have launched the Cleveland Clinic Diet app, which offers health and diet advice built upon evidence-based nutrition science and clinical success, paired with a comprehensive food and fitness tracker.
The app provides individualized guided support with the input of Cleveland Clinic health experts to help users make sustainable changes to their lifestyle and dietary habits for better health and well-being.
“We know that health is about far more than just weight. ...
Light-controlled artificial maple seeds could monitor the environment even in hard-to-reach locations
2024-06-27
Researchers from Tampere University, Finland, and the University of Pittsburgh, USA, have developed a tiny robot replicating the aerial dance of falling maple seeds. In the future, this robot could be used for real-time environmental monitoring or delivery of small samples even in inaccessible terrain such as deserts, mountains or cliffs, or the open sea. This technology could be a game changer for fields such as search-and-rescue, endangered species studies, or infrastructure monitoring.
At Tampere University, Professor Hao Zeng and Doctoral Researcher Jianfeng Yang ...
Patients receiving protocol exceptions to participate in targeted therapy trial experienced similar outcomes as eligible participants
2024-06-27
Bottom Line: Patients with treatment-refractory cancers who received eligibility and testing waivers to participate in a large basket/umbrella oncology trial had similar rates of clinical benefit and adverse events as patients who participated in the trial without waivers.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Hans Gelderblom, MD, senior author of the study and chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center in the Netherlands
Background: Eligibility requirements ...
Magic mushrooms are the most-used psychedelic drug
2024-06-27
Psilocybin mushrooms are the psychedelic substance most often used in the U.S., with its popularity outpacing other psychedelic drugs such as MDMA (known as ecstasy), according to a new RAND report.
Based on a new national survey, researchers found that about 12% of respondents reported using psilocybin at some point over their lives and 3.1% reported using the substance over the past year. An estimated 8 million American adults used psilocybin in 2023.
Psychedelic substances such as psilocybin mushrooms and MDMA long have been touted as holding promise for treating various mental ...
Diagnostic stewardship approach to C. diff reduces unnecessary testing
2024-06-27
Arlington, Va. — June 27, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) describes the outcome of a new approach to testing for Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) guided by the principles of diagnostic stewardship. At Memorial Healthcare System in Hollywood, Fla., revised rules for when C. diff tests could be ordered helped to reduce inappropriate testing by 20%, which in turn can help rein in the overtreatment of patients.
C. diff is a common and potentially dangerous gastrointestinal pathogen, often linked to healthcare-associated infections ...
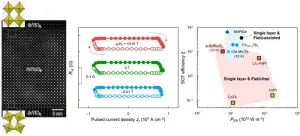
Materials research revolutionized by a small change
2024-06-27
Like the flutter of a butterfly's wings, sometimes small and minute changes can lead to big and unexpected results and changes in our lives. Recently, a team of researchers at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) made a very small change to develop a material called “spin-orbit torque (SOT),” which is a hot topic in next-generation DRAM memory.
This research team, led by Professor Daesu Lee and Yongjoo Jo, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Physics and Professor Si-Young ...
How scientists build rotatory machines with molecules
2024-06-27
Machines have evolved to meet the demands of daily life and industrial use, with molecular-scale devices often exhibiting improved functionalities and mechanical movements. However, mastering the control of mechanics within solid-state molecular structures remains a significant challenge.
Researchers at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), South Korea have made a groundbreaking discovery that could pave the way for revolutionary advancements in data storage and beyond. Led by Professor Wonyoung Choe in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST), a team of scientists has developed zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) that mimic intricate machines. These molecular-scale ...
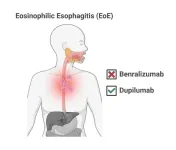
Two studies show mixed progress against EoE
2024-06-27
Despite high hopes, a drug that wipes out the namesake cell type associated with the disease eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) doesn’t make patients feel better and doesn’t reverse tissue damage in their throats.
Meanwhile, data show that a different drug that had previously been approved for use in adults and teens with EoE is also safe and effective for children under 12 who weigh at least 15 kg (about 33 pounds).
The results of these clinical trials—plus an accompanying editorial—appear in the June 17, 2024, edition of The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Together, these ...
Why the harsh Snowball Earth kick-started our earliest multicellular ancestors: new study
2024-06-27
For a billion years, single-celled eukaryotes ruled the planet. Then around 700 million years ago during Snowball Earth — a geologic era when glaciers may have stretched as far as the Equator — a new creature burst into existence: the multicellular organism.
Why did multicellularity arise? Solving that mystery may help pinpoint life on other planets and explain the vast diversity and complexity seen on Earth today, from sea sponges to redwoods to human society.
Common wisdom holds that oxygen levels had to hit a certain threshold ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] New mathematical model sheds light on the absence of breastfeeding in male mammalsBeing nursed by a single parent could be an evolutionary strategy to curb the spread of harmful microbes in mammals, according to a novel theory developed by mathematicians.