(Press-News.org) The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) tells staff leaving for industry jobs that, despite restrictions on post-employment lobbying, they are still permitted to influence the agency, reveals an investigation by The BMJ today.
Internal emails, obtained under a freedom of information request, show how two FDA officials who worked on covid-19 vaccine approvals were proactively informed by FDA ethics staff about their ability to indirectly lobby the agency as they left for jobs with Moderna.
The record shows that since 2000 every FDA commissioner, the agency’s highest position, has gone on to work for industry.
“So, people will leave government service and can immediately start doing influence peddling and lobbying,” explained Craig Holman, a government affairs lobbyist for the organisation Public Citizen. “They can even run a lobbying campaign, as long as they don’t actually pick up the telephone and make contact with their former officials—and that’s exactly the advice that’s being given here.”
Diana Zuckerman, president of the non-profit National Center for Health Research and a decades long regulatory policy analyst, finds FDA’s proactive provision of advice on behind-the-scenes work particularly troubling. Advice given behind the scenes is precisely “what makes FDA scientists and staff valuable,” she argues.
Peter Lurie, president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest in Washington, DC, and former associate commissioner at the FDA, suspects that FDA ethics staff were simply carrying out their proper function, but he expressed concern over the perils of allowing behind-the-scenes work.
“It does seem contrary to the public interest that an ex-official would be quarterbacking activities behind the scenes, especially for a ‘particular matter’ on which they had worked,” he said. “As a practical matter, this policy likely plays out in a way that advances the interests of big pharma, as that’s where many officials head after FDA.”
The BMJ asked the FDA whether it had any concerns that proactively informing employees about their ability to work behind the scenes could be interpreted as encouraging former FDA staff indirectly to lobby the agency.
An agency spokesperson responded: “No. Working behind the scenes does not necessarily equate to direct or indirect lobbying activities. Lobbying activities are governed by the Lobbying Disclosure Act. Former employees would need to adhere to these requirements, just like any other individual or organization.”
Last month US lawmakers introduced bills to amend the law regulating restrictions on departing employees. They seek to prohibit former health sector employees from serving on the boards of manufacturers of drugs, biological products, or devices after public service. So far, none of the bills have passed.
[Ends]
END
FDA staff leaving for industry jobs given “behind the scenes” lobbying advice
Practice highlights “critical loophole” in the revolving door between the FDA and industry
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Herpes infections take major economic toll globally, new research shows
2024-07-02
Genital herpes infections and their related complications lead to billions of dollars in health care expenditures and productivity losses globally, according to the first ever global estimates of the economic costs of these conditions.
The paper, which publishes July 1st in the journal BMC Global and Public Health, calls for greater investment in prevention of herpes transmission, including concerted efforts to develop effective vaccines against this common virus.
Corresponding author Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk, PharmD, PhD, professor of pharmacotherapy, and Haeseon Lee, PharmD, research fellow in pharmacotherapy, both at the College of Pharmacy of University ...
Tax on antibiotics could help tackle threat of drug-resistance
2024-07-02
Taxing certain antibiotics could help efforts to tackle the escalating threat of antibiotic resistance in humans, according to a new study by the University of East Anglia’s Centre for Competition Policy, Loughborough University and E.CA Economics.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant global risk, causing an estimated 700,000 deaths annually. A key AMR report previously warned that if unchecked, it could endanger 10 million lives a year and result in $100 trillion in lost economic output ...
Organic material from Mars reveals the likely origin of life’s building blocks
2024-07-01
Organic material from Mars reveals the likely origin of life’s building blocks
Two samples from Mars together deliver the "smoking gun" in a new study showing the origin of Martian organic material. The study presents solid evidence for a prediction made over a decade ago by University of Copenhagen researchers that could be key to understanding how organic molecules, the foundation of life, were first formed here on Earth.
In a meteor crater on the red planet, a solitary robot is moving about. Right now it is probably collecting soil samples with a drill and a robotic arm, as it has quite ...
Light targets cells for death and triggers immune response with laser precision
2024-07-01
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new method of precisely targeting troublesome cells for death using light could unlock new understanding of and treatments for cancer and inflammatory diseases, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers report.
Inflammatory cell death, knows as necroptosis, is an important regulatory tool in the body’s arsenal against disease. However, in some diseases, the process can go haywire; for example, cancer cells are able to suppress inflammatory signals and thus escape death.
“Usually treatments for cancer use pharmacological ...
Dr. Harish Manyam revolutionizes cardiac care with innovative device
2024-07-01
Harish Manyam, MD, is on a mission to improve the lives of people with heart problems. His recent accomplishment of implanting Tennessee’s first atrial leadless pacemaker is a step toward that, marking a significant advancement in cardiac care and promising safer and more effective treatment for patients.
The leadless pacemaker, in combination with a novel subcutaneous defibrillator, forms a groundbreaking system that addresses potentially dangerous problems associated with traditional pacemakers and defibrillators.
“This is a great leap forward for the field,” said Dr. Manyam, interim chair of the Department of Medicine at the ...
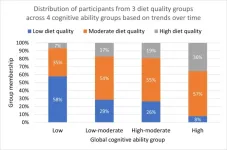
Want to stay mentally sharp longer? Eat a healthy diet now
2024-07-01
Chicago (July 1, 2024) — Eating a high-quality diet in youth and middle age could help keep your brain functioning well in your senior years, according to new preliminary findings from a study that used data collected from over 3,000 people followed for nearly seven decades.
The research adds to a growing body of evidence that a healthy diet could help ward off Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline. Whereas most previous research on the topic has focused on eating habits of people in their 60s and 70s, the new study is the first to track diet and ...
Medication choice may affect weight gain when initiating antidepressant treatment
2024-07-01
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 1 July 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization ...
Weight change across common antidepressant medications
2024-07-01
Boston, MA – New evidence comparing weight gain under eight different first-line antidepressants finds that bupropion users are 15-20% less likely to gain a clinically significant amount of weight than users of sertraline, the most common medication.
The findings are published July 2 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Antidepressants are among the most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S., with 14% of U.S. adults reporting using an antidepressant. Weight gain is a common side effect, which could affect patients’ long-term metabolic health and cause some to stop taking their prescribed treatment, leading ...
Dampening the "seeds" of hurricanes
2024-07-01
Dampening the "seeds" of hurricanes
Increased atmospheric moisture produced weaker hurricane formation
Increased atmospheric moisture may alter critical weather patterns over Africa, making it more difficult for the predecessors of many Atlantic hurricanes to form, according to a new study published this month.
The research team, led by scientists from the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR), used an innovative model that allows for higher-resolution simulations of hurricane formation than ever before. This allowed researchers to study the effects of increased regional moisture over Africa, which is the birthplace of ...
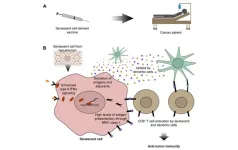
Senescent cell-derived vaccines: A new concept towards an immune response against cancer and aging?
2024-07-01
“[...] cancer immunotherapy based on tumor-associated senescent cells and other types of senescent cells may achieve exciting outcomes beyond cancer therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 1, 2024 – A new review paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 12, entitled, “Senescent cell-derived vaccines: a new concept towards an immune response against cancer and aging?”
Two recent seminal works have untangled the intricate role of tumor-associated senescent cells in cancer progression, or regression, by guiding our immune system against cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] FDA staff leaving for industry jobs given “behind the scenes” lobbying advicePractice highlights “critical loophole” in the revolving door between the FDA and industry