(Press-News.org) About The Study: The Massachusetts statewide standing order policy was associated with a 32% increase in emergency contraceptive fills at pharmacies versus comparison states. After the policy, fills for prescription-only ulipristal more than doubled and accounted for the observed increases in fills for emergency contraceptives.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dima M. Qato, Pharm.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., email qato@usc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.11715)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the AcademyHealth 2024 Annual Research Meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.11715?guestAccessKey=f61343ad-3103-4539-a281-7597e041fd9b&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=070224
END
Changes in emergency contraceptive fills after Massachusetts’ statewide standing order
JAMA
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bacteria detected in tattoo and permanent makeup inks
2024-07-02
Washington, D.C.—Researchers have detected anaerobic and aerobic bacteria in commercial tattoo and permanent makeup inks. The findings, reported in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, demonstrate that the inks could be a source of human infections. The new study is particularly notable as it is the first to investigate the presence of anaerobic bacteria in commercial tattoo inks.
“Our findings reveal that unopened and sealed tattoo inks can harbor anaerobic bacteria, known to thrive in low-oxygen environments like ...
American Indian/Alaska Native patients less likely to undergo breast reconstruction
2024-07-02
Waltham — July 2, 2024 — American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) women with breast cancer have consistently lower rates of breast reconstruction after mastectomy compared to non-Hispanic White women, reports a paper in the July issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Despite an upward trend in reconstruction, AI/AN women continue to be less likely to undergo breast reconstruction," comments Jane Hui, MD, MS, ...
Prosocial influencers can promote societal cooperation
2024-07-02
A modeling study suggests that influential neighbors can be as effective as despotic leaders at promoting social cooperation. Prosocial behaviors can be difficult to sustain in large societies over the long term, as people give into the temptation to defect to strategies that prioritize the wellbeing of themselves and their immediate family. Stefani Crabtree and colleagues constructed a general theoretical framework to explore how cooperation could arise and be maintained in a large society. The authors explore three possible ...
SRF launches the SYNGAP1 missense account with Nordmoe family donation
2024-07-02
Mill Valley, CA – June 18, 2024 SRF has established a dedicated account to support research regarding SYNGAP1 missense variants. This account is being launched with a $10,000 donation from Dennis and Janet Nordmoe. This is a cause close to their hearts, as their granddaughter Olivia was diagnosed with SYNGAP1-Related Disorder (SRD) caused by a missense variant earlier this year.
Missense Research: Neglected to Date
“Most diagnosed SYNGAP1-Related Disorder (SRD) patients have protein truncating variants (PTV) as opposed to missense variants. Virtually all PTVs are assumed to have the ...
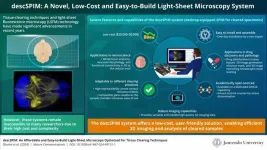
Design and development of a novel light sheet fluorescence microscope
2024-07-02
Three-dimensional (3D) imaging of organs and tissues is vital as it can provide important structural information at the cellular level. 3D imaging enables the accurate visualization of tissues and also helps in the identification of pathological conditions. However, achieving successful 3D imaging necessitates specific prerequisites, including the preparation of 'cleared' tissue samples—biological specimens rendered transparent by removing light-scattering components like lipids to ...
How to promote menstrual cups as an economic and sustainable option
2024-07-02
In recent decades, single-use plastics have pervaded modern societies, causing a significant surge in plastic pollution that exacts a heavy toll on our environment. Addressing this issue requires prioritizing sustainable alternatives to single-use plastics wherever feasible.
Disposable menstrual products are a notable contributor to plastic waste, with billions of sanitary napkins and tampons being discarded every year. Despite the availability of sustainable options like menstrual cups (MCs), consumer preference for single-use products ...
Spotted apex predator being pressured by spotted pack hunters – and it's our fault
2024-07-02
Who’s stronger? A solitary leopard or cackle of hyenas? And which is best at getting along with humans?
University of Copenhagen researchers closely studied this in a large East African natural area surrounded by rural settlements. The study demonstrates that the presence of humans has a direct impact on the competitive relationship between the two large predator species: leopards (Panthera pardus) – the iconic spotted feline and the spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) – a kleptoparasite and pack hunter known for its comical ...
True scale of carbon impact from long-distance travel revealed
2024-07-02
The reality of the climate impact of long-distance passenger travel has been revealed in new research from the University of Leeds.
Despite only accounting for less than 3% of all trips by UK residents, journeys of more than 50 miles (one way) are responsible for 70% of all passenger travel-related carbon emissions.
The disparity is even greater when international travel is singled-out: international journeys are only 0.4% of total trips but are responsible for 55% of emissions.
The new research, published today in the journal Nature Energy, also shows ...
Cutting-edge genomic test can improve care of children with cancer
2024-07-02
Whole genome sequencing has improved clinical care of some children with cancer in England by informing individual patient care.
New research from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust, Great Ormond Street Hospital, and the University of Cambridge, supports the efforts to provide genome sequencing to all children with cancer and shows how it can improve the management of care in real-time, providing more benefits than all current tests combined.
The study, published today (2 July) in Nature Medicine, ...
Drugs that kill "zombie" cells may benefit some older women, but not all, Mayo Clinic study finds
2024-07-02
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Drugs that selectively kill senescent cells may benefit otherwise healthy older women but are not a "one-size-fits-all" remedy, Mayo Clinic researchers have found. Specifically, these drugs may only benefit people with a high number of senescent cells, according to findings publishing July 2 in Nature Medicine.
Senescent cells are malfunctioning cells in the body that lapse into a state of dormancy. These cells, also known as "zombie cells," can't divide but can drive chronic inflammation and tissue dysfunction linked to aging and chronic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Changes in emergency contraceptive fills after Massachusetts’ statewide standing orderJAMA