Efficient hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over Ni-C3N4 catalysts
2024-07-04
(Press-News.org)
Utilization of biomass as the basic feedstock for the production and chemicals and energy storage has been demonstrated to be an important alternative to achieve sustainable society, which has attracted increasing interests in both academic and industrial communities for decades. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), one of the most important bio-based platform compounds, could serve as a bridge feedstock between biomass resources and chemicals. It is possible to synthesize a series of high-value added chemicals from HMF through hydrogenation, oxidative dehydrogenation, esterification, hydrolysis, and etc., due to the presence of both aldehyde and hydroxymethyl groups. Among them, the selective hydrogenolysis of HMF to 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF) as a potential liquid biofuel candidate has attracted extensive attention. As a biomass fuel, DMF can be used in internal combustion engines with higher compression ratios to improve fuel utilization efficiency as a result of its higher RON (Research octane number, 119) compared to those of commercial gasoline (90-100) and ethanol (110). In addition, DMF could be the important reactant for the direct synthesis of bio-based p-xylene (PX) by Diels-Alder reaction with ethylene. Compared to the conventional petroleum-based PX production process, such bio-based process shows high selectivity and avoids the complex separation procedure.
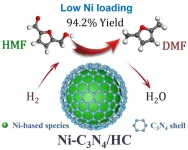
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Weimin Yang from East China University of Science and Technology and Sinopec Shanghai Research Institute of Petrochemical Technology Co., Ltd. reported the Ni-C3N4 catalyst supported on H2 activated carbon (HC) with ultra-low Ni loading for the selective hydrogenolysis of HMF to DMF. The Ni-C3N4/HC catalyst achieves DMF yield of 94.2% with high sustainability (longer than 120 h life time in fixed-bed reactor), and exhibits remarkably high productivity (12.8 mmolDMF⋅mmolNi-1 ⋅h-1) across the temperatures of 100-200 °C, outperforming the recently reported all state-of-the-art Ni, Co and Cu-based catalysts, and is also comparable to noble metal catalysts (Ru, Pd and Pt). The combination of characterizations and theoretical calculations revealed that Ni3N is the active component for the hydrogenolysis, and the C3N4 shells stabilize the Ni particles and prevent the agglomeration during the reaction. This work would advance the design of single non-noble metal catalysts for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis reactions. The results were published in Chinese Journal of Catalysis (https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(24)60017-3).
###
About the Journal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis is co-sponsored by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Chemical Society, and it is currently published by Elsevier group. This monthly journal publishes in English timely contributions of original and rigorously reviewed manuscripts covering all areas of catalysis. The journal publishes Reviews, Accounts, Communications, Articles, Highlights, Perspectives, and Viewpoints of highly scientific values that help understanding and defining of new concepts in both fundamental issues and practical applications of catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis ranks among the top one journals in Applied Chemistry with a current SCI impact factor of 15.7. The Editors-in-Chief are Profs. Can Li and Tao Zhang.
At Elsevier http://www.journals.elsevier.com/chinese-journal-of-catalysis
Manuscript submission https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjcatal
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-04
Tokyo, Japan—A research team from Japan, including scientists from Hitachi, Ltd. (TSE 6501, Hitachi), Kyushu University, RIKEN, and HREM Research Inc. (HREM), has achieved a major breakthrough in the observation of magnetic fields at unimaginably small scales. In collaboration with National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), the team used Hitachi’s atomic-resolution holography electron microscope—with a newly developed image acquisition technology and defocus correction algorithms—to visualize ...
2024-07-04
An innovative test that combines a DNA extraction system inspired by a modified 3D printer (PrintrLab) with loop-mediated isothermal molecular amplification (LAMP) could be used to detect T. cruzi infection -responsible for Chagas disease- in newborns. This is the conclusion of a proof-of-concept study conducted in the Bolivian Chaco, an endemic area for Chagas disease. The study was coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by "la Caixa" ...
2024-07-04
What types of cities exist in Europe and which are more favourable in terms of human health, environmental quality and carbon footprint? To answer these questions, a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has analysed 919 European cities. The research, published in The Lancet Planetary Health, identified four basic urban configurations on the continent: compact-high density cities, open lowrise-medium density cities, open lowrise-low density cities and green-low density cities. The results show that greener and less densely populated ...
2024-07-04
Reducing consumption of processed meat by around one-third could prevent more than 350,000 cases of diabetes in the US over 10 years, a study suggests.
Cutting US adults’ processed meat intake by 30 per cent – the equivalent of around 10 slices of bacon a week – would also lead to tens of thousands of fewer cases of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer, researchers say.
A team from the University of Edinburgh’s Global Academy of Agriculture and Food Systems together with the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, has developed ...
2024-07-04
Stem cell-based embryo models (SCBEMs) are three-dimensional biological structures that mimic aspects of early human embryo development. They can be created in the lab from stem cells, and can provide new insights into critical stages of early human development that are normally inaccessible to researchers.
Embryo model work is expected to lead to new interventions for a range of conditions, including revolutionising treatments for recurrent miscarriage, understanding developmental disorders and improving the success rate of IVF.
Although embryo models are not the same ...
2024-07-04
Tampons from several brands that potentially millions of people use each month can contain toxic metals like lead, arsenic, and cadmium, a new study led by a UC Berkeley researcher has found.
Tampons are of particular concern as a potential source of exposure to chemicals, including metals, because the skin of the vagina has a higher potential for chemical absorption than skin elsewhere on the body. In addition, the products are used by a large percentage of the population on a monthly basis—50-80% of those who menstruate use tampons—for several hours at a time.
“Despite this large potential for public health concern, very little research ...
2024-07-03
Researchers at Rice University are making strides in understanding how chromosome structures change throughout the cell’s life cycle. Their study on motorized processes that actively influence the organization of chromosomes was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
“This research provides a deeper understanding of how motorized processes shape chromosome structures and influence cellular functions,” said Peter Wolynes, study co-author and the D.R. Bullard-Welch Foundation Professor of Science. ...
2024-07-03
Rice University chemist Han Xiao has been awarded nearly $2 million from the National Institutes of Health Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award (MIRA) program for established investigators.
All organisms with few exceptions use 20 standard amino acids to build proteins. Xiao’s research aims to reprogram the genetic code to precisely manipulate biological systems by using noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) with diverse properties to help build proteins. Researchers generally use ncAAs to investigate the structure and dynamics of proteins, but Xiao wants to take that a step further.
“This innovative approach could revolutionize how ...
2024-07-03
Swedish researchers have created a questionnaire test for home use that quickly identifies high risk of heart attack. A study shows that it has the same level of accuracy as blood tests and blood pressure measurements.
The study, published in Journal of the American Heart Association, uses data from the SCAPIS population study, which is based at the University of Gothenburg, with the Swedish Heart Lung Foundation as its main sponsor.
The study was led by Göran Bergström, Professor of Clinical Physiology at Sahlgrenska Academy at the University of Gothenburg, senior ...
2024-07-03
Researchers from the Butantan Institute and collaborators are developing a more potent version of the BCG vaccine that protects against tuberculosis. While the conventional immunizer reduced infection by 90% in experiments with mice, the so-called recombinant BCG increased the protection rate to 99%. In addition, the new formulation protected the animals for a significantly longer period of time.
“BCG is the first vaccine we receive at birth, and it’s indeed effective in protecting children. But immunity against the disease tends to wane in adulthood, and as bacteria are becoming resistant to antibiotics, no ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Efficient hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over Ni-C3N4 catalysts