(Press-News.org) This pivotal study explores the genetic orchestration of bud dormancy in woody perennials, a survival strategy crucial for enduring harsh climates. It focuses on the PmDAM6 gene, revealing its regulatory effects on lipid metabolism and phytohormone dynamics within dormant meristems, which dictate the plant's seasonal transition from rest to growth.
Plant dormancy's genetic mechanisms are vital for enhancing agricultural resilience and productivity. The interaction between lipid metabolism and hormone regulation significantly influences dormancy phases, essential for plant survival under varying climatic conditions. Exploring these biological challenges through genetic research is crucial for devising innovative strategies to ensure crop adaptability and sustainability.
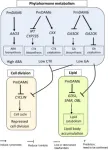
Researchers at Kyoto University have made significant strides in understanding plant dormancy, a critical adaptation for woody perennials. In a study (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae102) published on April 9, 2024, in Horticulture Research, they reveal the intricate regulatory role of the PmDAM6 gene on lipid body accumulation and phytohormone metabolism in the dormant vegetative meristem, offering new insights into the genetic control of this vital process.
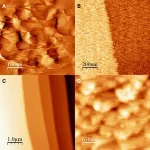
The study underscores the role of the Prunus mume DAM6 gene in managing lipid accumulation and phytohormone balance within dormant vegetative meristems. Enhanced DAM6 expression resulted in increased lipid bodies and reduced cell division by downregulating genes involved in lipid catabolism and the cell cycle. This genetic modulation also altered phytohormone levels, notably increasing abscisic acid while decreasing cytokinin and gibberellin. These findings indicate a complex regulatory network where lipid metabolism and hormone adjustments converge to manage dormancy. Transmission electron microscopy provided detailed visual evidence of DAM6's cellular impact, highlighting its potential as a target for enhancing plant adaptability and dormancy management.
Dr. Hisayo Yamane, the study's lead author, states, "Modulating DAM6 not only deepens our understanding of dormancy mechanisms but also catalyzes the development of strategies to enhance crop adaptation to changing climates, potentially revolutionizing agricultural practices."
Manipulating the DAM6 gene could transform agricultural practices by allowing precise control over dormancy periods, optimizing growth cycles, and enhancing crop resilience against environmental stresses. This breakthrough opens new avenues for breeding programs focused on improving food security amid global climate change challenges.
###
References
DOI
10.1093/hr/uhae102
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1093/hr/uhae102
Funding information
This research was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan (Grant-in-Aid KAKENHI Nos. 18H02198 and 21H02186) to HY.
About Horticulture Research
Horticulture Research is an open access journal of Nanjing Agricultural University and ranked number one in the Horticulture category of the Journal Citation Reports ™ from Clarivate, 2022. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence articles and letters to the editor related to all major horticultural plants and disciplines, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, evolution, genetics, inter-species interactions, physiology, and the origination and domestication of crops.
END
From winter's rest to spring's bloom: PmDAM6 gene steers plant bud dormancy
2024-07-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
From kale to carotenoid powerhouse: a breakthrough in plant nutrition
2024-07-09
A recent study has identified a crucial regulatory mechanism in Chinese kale, potentially revolutionizing its nutritional profile. By manipulating the BoaBZR1.1 transcription factor, researchers significantly enhanced carotenoid levels, crucial antioxidants for human health. This advancement opens pathways for improving vegetable nutrition through genetic engineering.
Carotenoids, vital antioxidants in plants, are integral for human health, enhancing immunity and preventing diseases. However, many vegetables, including Chinese kale, naturally exhibit low carotenoid levels. To address this nutritional gap, scientists are exploring genetic ...
CMU, Meta announce research collaboration aimed at making computer-based tasks and gaming accessible to people with different motor abilities via wearable sensing technology
2024-07-09
PITTSBURGH - As part of a larger commitment to developing equitable technology, Carnegie Mellon University and Meta announce a collaborative project to make computer-based tasks accessible to more people. This project focuses on using wearable sensing technology to enable people with different motor abilities to perform everyday tasks and enjoy gaming in digital and mixed reality environments.
Meta’s research in electromyography uses sensors placed on the skin to measure the electrical signals the user generates through muscles in their wrist, which are translated into input signals for various devices. While Meta has already ...
Detecting defects in tomorrow’s technology
2024-07-09
Silicon computer chips have served us well for more than half a century. The tiniest features on chips currently sold are approximately 3 nanometers — a startlingly small size given that a human hair is roughly 80,000 nanometers wide. Reducing the size of features on chips will help us meet our endless need for more memory and processing power in the palm of our hand. But the limit of what can be achieved with standard materials and processes is near.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are applying their expertise in ...
It takes a cool microscope and antifreeze to really look at ice
2024-07-09
Ice in nature is surrounded by liquid most of the time, and therefore it is key to understand how ice and liquid interact. A Kobe University and Institute for Molecular Science study could now for the first time directly observe the precise shape of ice at the interface between ice and liquid – by using antifreeze and a refrigerated microscope.
When we slide on ice, when snowflakes form, when we lick ice cream, the surface of the ice is always covered with liquid water, and understanding the interaction between the ...
First local extinction in the US due to sea level rise
2024-07-09
The United States has lost its only stand of the massive Key Largo tree cactus in what researchers believe is the first local extinction of a species caused by sea level rise in the country.
The Key Largo tree cactus (Pilosocereus millspaughii) still grows on a few scattered islands in the Caribbean, including northern Cuba and parts of the Bahamas. In the United States, it was restricted to a single population in the Florida Keys, first discovered in 1992 and monitored intermittently since.
Salt water intrusion from rising seas, soil depletion from hurricanes and high tides, and herbivory by mammals had put significant pressure ...
Empowering Ugandan female youth with self-esteem, self-efficacy, and gratitude using Transcendental Meditation
2024-07-09
A peer-reviewed study published today in Health Care for Women International found that the Transcendental Meditation® (TM®) technique can empower the lives of female youth living under conditions of poverty in the city slums of Kampala, Uganda. Outcomes include increased self-esteem, self-efficacy, and gratitude; and decreased tiredness, worry, and excessive alcohol use. TM helped these young women improve their mental and physical health, as well as their relations with family and community members.
“The ...
Brian Wachtel is promoted to Chief Development Officer at NFCR
2024-07-09
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) proudly announces the promotion of Brian Wachtel to Chief Development Officer. Brian will continue his responsibilities as the Executive Director, and his expanded role will further enhance his leadership within the organization.
Brian joined the National Foundation for Cancer Research in September 2016 as the Director of Corporate Partnerships & Special Events. In that capacity, he was in charge of organizing and expanding NFCR’s community outreach events. One of his important ...
Digital self-harm surges among U.S. teens from 2016 to 2021
2024-07-09
Adolescents worldwide have embraced social media and online platforms for self-expression and to explore their identity. This freedom, however, can lead to risky behaviors, especially with limited adult supervision. For example, digital self-harm is a recent, emerging trend where individuals anonymously post or share hurtful content about themselves online. This behavior can be mistaken for mistreatment by others, yet the perpetrator and victim are the same person.
First identified in 2010, digital self-harm has not received the same amount of scholarly scrutiny as other forms of self-directed abuse and has not been widely addressed by adults ...
UTSA joins new consortium dedicated to nuclear security and nonproliferation
2024-07-09
The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) has joined one of two newly established university consortia committed to nuclear security and nonproliferation. The consortia were awarded $50 million in cooperative agreements by the Office of Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation in the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (DOE NNSA).
“The pressing challenges of nuclear security and nonproliferation require a concerted effort from experts across the country,” said JoAnn Browning, UTSA interim vice president for research. ...
Diabetes increases the risk of failure in spinal fusion procedures
2024-07-09
A new study from orthopaedic researchers at The University of Toledo has found lumbar spinal fusion procedures are far more likely to fail in individuals with diabetes.
“We’ve known for a long time that diabetic patients are at high risk of infection from any surgery, including spinal fusion,” said Dr. Hossein Elgafy, a professor of orthopaedics in the College of Medicine and Life Sciences and chief of spine surgery at UTMC. “More recently, however, physicians have taken a closer look at the high ...