(Press-News.org) Solid-state batteries have several advantages: they can store more energy and are safer than batteries with liquid electrolytes. However, they do not last as long and their capacity decreases with each charge cycle. But it doesn't have to stay that way: Researchers are already on the trail of the causes. In the journal ACS Energy Letters, a team from HZB and Justus-Liebig-Universität, Giessen, presents a new method for precisely monitoring electrochemical reactions during the operation of a solid-state battery using photoelectron spectroscopy at BESSY II. The results help to improve battery materials and design.
Solid-state batteries use a solid ion conductor between the battery electrodes instead of a liquid electrolyte, which allows lithium to be transported during charging and discharging. This has advantages including increased safety during operation and generally higher capacity. However, the lifetime of solid-state batteries is still very limited. This is because decomposition products and interphases form at the interfaces between the electrolyte and the electrode, which hinders the transport of the lithium ions and leads to consumption of active lithium so that the capacity of the batteries decreases with each charge cycle.
What happens during operation?
Now a team led by HZB researchers Dr. Elmar Kataev and Prof. Marcus Bär has developed a new approach to analyse the electrochemical reactions at the interface between solid electrolyte and electrode with high temporal resolution. Kataev explains the research question: "Under what conditions and at what voltage do such reactions occur, and how does the chemical composition of these intermediate phases evolve during cell operation?"
Best candidate LiPSCl examined
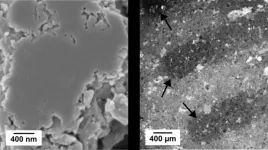
For the study, they analysed samples of the solid electrolyte Li6PS5Cl, a material that is considered the best candidate for solid-state batteries as it possesses high ionic conductivity. They worked closely with the team of battery expert Professor Jürgen Janek from the Justus Liebig University Giessen (JLU Giessen). An extremely thin layer of nickel (30 atomic layers or 6 nanometres) served as the working electrode. A film of lithium was pressed onto the other side of the Li6PS5Cl pellet to act as a counter electrode.
Hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy HAXPES
In order to analyse the interfacial reactions and the formation of an interlayer (SEI) in real time and as a function of the applied voltage, Kataev used the method of hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) exploiting the analytical capabilities of the Energy Materials In-situ Laboratory Berlin (EMIL) at BESSY II: X-rays hit the sample, exciting the atoms there and the reaction products can be identified from the photoelectrons emitted as a function of the applied cell voltage and time. The results showed that the decomposition reactions were only partially reversible.
Outlook: Examination of different battery materials
"We demonstrate that it is possible to use an ultra-thin current collector to study the electrochemical reactions at the buried interfaces using surface characterisation methods," says Kataev. The HZB team has already received inquiries from research groups in Germany and abroad that are also interested in this characterization approach. As a next step, the HZB team wants to extend this approach and also investigate batteries with composite polymer electrolytes and a variety of anode and cathode materials.
END
BESSY II shows how solid-state batteries degrade
Electrochemical reactions in solid state batteries can be precisely monitored during operation unsing hard X-ray photoelectronspectroscopy at BESSY II
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers show promising material for solar energy gets its curious boost from entropy
2024-07-10
Solar energy is critical for a clean-energy future. Traditionally, solar energy is harvested using silicon – the same semiconductor material used in everyday electronic devices. But silicon solar panels have drawbacks: for instance, they’re expensive and hard to mount on curved surfaces.
Researchers have developed alternative materials for solar-energy harvesting to solve such shortcomings. Among the most promising of these are called “organic” semiconductors, carbon-based semiconductors that are Earth-abundant, cheaper and environmentally friendly.
“They can potentially lower the production cost for solar panels because these ...
Faculty physicians to establish new community "health village" at Mondawmin Mall
2024-07-10
University of Maryland Faculty Physicians has entered into an agreement to lease 17,000 square feet of space at The Village at Mondawmin, which would establish a new community "health village," University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, and Faculty Practice President William F. Regine, MD, announced today. It is part of a larger effort to work in partnership with the West Baltimore community to develop and implement health care delivery based on neighborhood needs and to improve patient access to healthcare.
The Faculty Practice group of ...
Pitch perfect: match the message to the idea's newness, study finds
2024-07-10
In a study examining styles of pitching ideas to audiences, researchers found that pitches promoting radical ideas are better received when framed in concrete and explanatory ‘how’ terms, while progressive ideas do better with abstract ‘why’ style of pitches.
Previous research found that professional audiences, like investors, prefer concrete pitches with how-style explanations, while lay audiences such as students and crowdfunders respond better to ‘why’ style pitches for abstract ideas.
Professor Simone Ferriani, Professor of Entrepreneurship at Bayes Business School (formerly ...
MSU study reveals rapid growth, persistent challenges in telemedicine adoption among US hospitals
2024-07-10
EAST LANSING, Mich. – A new study led by Michigan State University researchers shows a significant increase in telemedicine services offered by U.S. hospitals from 2017 to 2022, while also highlighting persistent barriers to its full implementation.
The comprehensive analysis of telemedicine adoption in U.S. hospitals during these years reveals both significant progress and ongoing challenges in the health care sector’s digital transformation. The study, published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, found that the percentage of hospitals offering at least one form of telemedicine ...
Cirrhosis affects twice as many transgender adults as cisgender adults
2024-07-10
LOS ANGELES — Cirrhosis is chronic, progressive end-stage liver disease that occurs when scar tissue prevents the liver from functioning normally. Studies have shown that two of the leading causes of cirrhosis — alcohol use disorder and viral hepatitis — occur more frequently in transgender individuals, but there has been little research examining if these risk factors translate into greater incidences of cirrhosis among transgender patients.
A new study from Keck Medicine ...
Astronomers find the nearest massive black hole, a missing link in massive black hole formation
2024-07-10
Omega Centauri is a spectacular collection of about ten million stars, visible as a smudge in the night sky from Southern latitudes. Through a small telescope, it looks no different from other so-called globular clusters: a spherical collection of stars, so dense towards the centre that it becomes impossible to distinguish individual stars. But now a new study, led by Maximilian Häberle (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy), confirms what astronomers had been suspecting for some time: Omega Centauri contains a central black hole. The black hole appears to be the “missing link” between its stellar and ...
Telehealth availability for mental health care during and after the COVID-19 public health emergency
2024-07-10
About The Study: Based on this longitudinal cohort study of 1,001 mental health treatment facilities, telehealth availability has declined since the public health emergency end with respect to scope and modality of services, suggesting targeted policies may be necessary to sustain telehealth access.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ryan K. McBain, Ph.D., M.P.H., email rmcbain@mail.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.20853)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Mobile media content exposure and toddlers’ responses to attention prompts and behavioral requests
2024-07-10
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that use of touch-screen, engaging, tablet games by toddlers may inhibit early social-communicative interactions.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dimitri A. Christakis, M.D., M.P.H., email dimitri.christakis@seattlechildrens.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.18492)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# ...
The molecule that could alleviate stroke-related brain injury
2024-07-10
A newly developed molecule, LK-2, could inform new therapies for stroke-related brain injury, finds scientists at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids).
An ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, depriving the brain cells of oxygen and nutrients. Without timely treatment, brain cells can die, resulting in permanent damage to the brain and its functions. Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, affecting millions every year.
An international study published in Nature co-led by Dr. Lu-Yang Wang, a Senior Scientist in the ...
Scientists discover a cause of lupus and a possible way to reverse it
2024-07-10
· Lupus is an autoimmune disease affecting more than 1.5 million people in the U.S.
· Until now, the causes of this disease remained unclear
· Scientists are working to expand research into novel treatment
CHICAGO --- Northwestern Medicine and Brigham and Women’s Hospital scientists have discovered a molecular defect that promotes the pathologic immune response in systemic lupus erythematosus (known as lupus) and show that reversing this defect may potentially reverse the disease.
Lupus affects more than 1.5 million ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
[Press-News.org] BESSY II shows how solid-state batteries degradeElectrochemical reactions in solid state batteries can be precisely monitored during operation unsing hard X-ray photoelectronspectroscopy at BESSY II