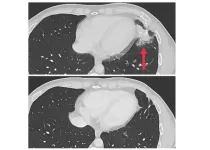
(Press-News.org) Early findings from a small clinical trial provide evidence that a new cellular immunotherapy approach may be effective in treating metastatic solid tumors. In the trial, researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) genetically engineered normal white blood cells, known as lymphocytes, from each patient to produce receptors that recognize and attack their specific cancer cells. These initial findings are from people with metastatic colorectal cancer who had already undergone multiple earlier treatments. The personalized immunotherapy shrank tumors in several patients and was able to keep the tumors from regrowing for up to seven months. The findings were published July 11, 2024, in Nature Medicine.
One form of cellular immunotherapy, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has already been shown to be effective against some blood cancers, and another, called tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy, has proven to be effective against metastatic melanoma. However, to date, a cellular therapy that’s effective against any other solid cancers has been elusive, according to Steven A. Rosenberg, M.D., Ph.D., of NCI’s Center for Cancer Research (CCR), who co-led the study with Maria Parkhurst, Ph.D., of CCR’s Surgery Branch.
“The fact that we can take a growing metastatic solid cancer and get it to regress shows that the new cellular immunotherapy approach has promise,” Dr. Rosenberg said. “However, it’s important to understand that these findings are preliminary and that the approach needs to be further refined and tested in more types of solid cancers.”
The new approach overcomes two challenges in cellular immunotherapy: how to produce large numbers of T cells that can recognize cancer cells specifically, and how to boost the ability of modified T cells to multiply once they’ve been returned to the patient.
For each patient in the study, Dr. Rosenberg and his colleagues collected lymphocytes present in the patient’s tumors. They then used sophisticated molecular characterization techniques to identify and isolate receptors on those lymphocytes, called T-cell receptors, that recognized specific changes in each patient’s tumor. After genetically sequencing those receptors, they then used a retrovirus to insert the genes for the receptor into normal lymphocytes collected from each patient’s circulating blood.
The genetically modified lymphocytes were then multiplied into the hundreds of millions in the laboratory and infused back into the patients, where they expressed the tumor-specific T-cell receptors and continued to multiply.
“By taking the natural T-cell receptors that are present in a very small number of cells and putting them into normal lymphocytes for which we have enormous numbers—a million in every thimbleful of blood—we can generate as many cancer-fighting cells as we want,” Dr. Rosenberg explained.
As part of a larger phase 2 trial, seven patients with metastatic colon cancer were treated with the experimental personalized cellular immunotherapy. All seven received several doses of the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab before the cell therapy and another immunotherapy drug called IL-2 afterward. Three patients had substantial shrinkage of metastatic tumors in the liver, lung, and lymph nodes that lasted for four to seven months. The median time to disease progression was 4.6 months.
Dr. Rosenberg noted that, of the three patients who responded to the treatment, two had received T-cell receptors derived from cytotoxic T cells, which are primarily responsible for killing diseased cells. Dr. Rosenberg said his research team is exploring how to put the T cell receptors into subtypes of normal lymphocytes to improve their reactivity.
Colon cancer is just one of many solid tumors the researchers are studying. The trial is still ongoing and includes patients with different types of solid cancers.
“It's just the very beginning of converting normal lymphocytes into cells capable of treating the common solid cancers,” Dr. Rosenberg said. “What this study shows is that it's possible. Once you know it’s possible, you work to improve it.”
###
About the National Cancer Institute (NCI): NCI leads the National Cancer Program and NIH’s efforts to dramatically reduce the prevalence of cancer and improve the lives of people with cancer. NCI supports a wide range of cancer research and training extramurally through grants and contracts. NCI’s intramural research program conducts innovative, transdisciplinary basic, translational, clinical, and epidemiological research on the causes of cancer, avenues for prevention, risk prediction, early detection, and treatment, including research at the NIH Clinical Center—the world’s largest research hospital. Learn more about the intramural research done in NCI’s Center for Cancer Research. For more information about cancer, please visit the NCI website at cancer.gov or call NCI’s contact center at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit nih.gov.
END
Immunotherapy approach shows potential in some people with metastatic solid tumors
NIH researchers achieved tumor shrinkage in three of seven patients with colorectal cancers
2024-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neighborhood impact on children's well-being shifted during COVID-19 pandemic, ECHO study suggests
2024-07-11
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted daily life and has raised concerns about its impact on children’s well-being. A new study from the NIH Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes Program (ECHO) sheds light on how a neighborhood’s physical and social environment influenced a child’s well-being before and during the pandemic.
According to an analysis of ECHO Cohort data, the neighborhood environment was less likely to be associated with child well-being during the ...
Neurobiologist Sung Soo Kim receives 2024 Scholar Award from McKnight Foundation
2024-07-11
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Birds migrating. Your cat, returning home from a day of roaming. Bees taking pollen to their hives. You, finding yourself back home without actually remembering the drive from work. Animal navigation is a fundamental behavior, so innate that most of the time we don’t notice that we’re doing it. And yet, so many times a day we (and the animals around us) unerringly find our ways to our target locations whether they be old haunts or new venues, from different directions and even in the dark.
How do we do it? That’s the question UC Santa Barbara neurobiologist Sung Soo Kim seeks to ...
Charting an equitable future for DNA and ancient DNA research in Africa
2024-07-11
CLEVELAND AND NAIROBI — July 11, 2024 — Today, the American Journal of Human Genetics published a perspective piece on the need for an equitable and inclusive future for DNA and ancient DNA (aDNA) research in Africa. The paper, coauthored by an international team of 36 scientists from Africa, North America, Asia, Australia, and Europe, was led by Dr. Elizabeth (Ebeth) Sawchuk of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History and Dr. Kendra Sirak of Harvard University.
DNA from ancient and living African peoples is critical for researchers studying our species’ evolution and population ...
Introducing co-cultures: When co-habiting animal species share culture
2024-07-11
Cooperative hunting, resource sharing, and using the same signals to communicate the same information—these are all examples of cultural sharing that have been observed between distinct animal species. In an opinion piece published June 19 in the journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution, researchers introduce the term “co-culture” to describe cultural sharing between animal species. These relationships are mutual and go beyond one species watching and mimicking another species’ behavior—in co-cultures, both species influence each other in substantial ways.
“Co-culture challenges the notion ...
Study finds health risks in switching ships from diesel to ammonia fuel
2024-07-11
As container ships the size of city blocks cross the oceans to deliver cargo, their huge diesel engines emit large quantities of air pollutants that drive climate change and have human health impacts. It has been estimated that maritime shipping accounts for almost 3 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions and the industry’s negative impacts on air quality cause about 100,000 premature deaths each year.
Decarbonizing shipping to reduce these detrimental effects is a goal of the International Maritime Organization, ...
Seeing inside Alzheimer’s disease brain
2024-07-11
Scientists investigating Alzheimer’s disease have determined the structure of molecules within a human brain for the very first time.
Published today in Nature, the study describes how scientists used cryo-electron tomography, guided by fluorescence microscopy, to explore deep inside an Alzheimer’s disease donor brain.
This gave 3-dimensional maps in which they could observe proteins, the molecular building blocks of life a million-times smaller than a grain of rice, within the brain.
The study zoomed in on two proteins that cause dementia– ‘β-amyloid’, a protein that forms microscopic ...
Nanoplastics and ‘forever chemicals’ disrupt molecular structures, functionality
2024-07-11
EL PASO, Texas (July 11, 2024) – Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso have made significant inroads in understanding how nanoplastics and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — commonly known as forever chemicals — disrupt biomolecular structure and function. The work shows that the compounds can alter proteins found in human breast milk and infant formulas — potentially causing developmental issues downstream.
Nanoplastics and forever chemicals are manmade compounds present throughout the environment; a series of recent studies have linked them to numerous ...
Quadrupolar nuclei measured for the first time by zero-field NMR
2024-07-11
What is the structure of a particular molecule? And how do molecules interact with each other? Researchers interested in those questions frequently use nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to find answers. In NMR, a powerful external magnetic field is employed to align the spins of atomic nuclei, which are then induced to rotate by an oscillating weak magnetic field generated by coils. A change in voltage as a result can be converted to measurable frequencies. Based on this, researchers can identify the molecular structures while also revealing ...
UT Arlington research contributes $226 million to U.S. economy
2024-07-11
A new report shows that research projects at The University of Texas at Arlington contributed one quarter of a billion dollars—$226.4 million, to be exact—to the national economy through 797 vendor contracts and subcontracts between 2018 and 2022. Of those contracts, 111 were from small businesses and 87 from minority- or woman-owned businesses.
“Research coming from UT Arlington faculty and students not only helps solve some of society’s most vexing problems, but it is also an important economic driver for business development,” said Kate C. Miller, vice president for research and innovation at UTA. “This report makes clear that UTA research ...
Researchers develop a way to make lifesaving phages accessible, transportable and much easier to use
2024-07-11
The great promise of bacteriophages is that they naturally destroy bacteria, often in situations where antibiotics fail.
Until now, though, there has been no way to access them quickly and efficiently, especially in emergency cases of antibiotic resistant infections.
Researchers at McMaster University, working with a colleague from Université Laval, have developed a simple new way to store, identify, and share phages, making them more accessible to patients who need them.
“Bacteriophages ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
[Press-News.org] Immunotherapy approach shows potential in some people with metastatic solid tumorsNIH researchers achieved tumor shrinkage in three of seven patients with colorectal cancers