(Press-News.org)
“FDG-PET is generally considered as a useful metabolic evaluation tool, while it is also thought to have an emerging role for assessment of systemic therapy response.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 15, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Comparison of FDG-PET/CT and CT for evaluation of tumor response to nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy and prognosis prediction in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma.”
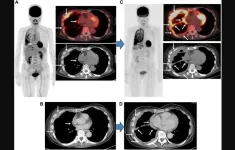
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive neoplasm and affected patients have low survival rates. In this new retrospective study, researchers Kazuhiro Kitajima, Kozo Kuribayashi, Toshiyuki Minami, Hiroyuki Yokoyama, Akifumi Nakamura, Masaki Hashimoto, Takashi Kijima, Seiki Hasegawa, Hayato Kaida, and Koichiro Yamakado from Hyogo Medical University and Kindai University Faculty of Medicine examined the effectiveness of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) criteria, i.e., immunotherapy-modified PET response criteria in solid tumors (imPERCIST), with morphological computed tomography (CT) criteria, i.e., modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (mRECIST), to evaluate patients with unresectable MPM undergoing nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy as first-line treatment regarding response and prognosis prediction.
“Results for malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) patients following first-line treatment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab obtained with immunotherapy-modified PERCIST (imPERCIST), shown by [18F] (FDG-PET/CT), and modified RECIST (mRECIST), shown by CT, were compared for response evaluation and prognosis prediction.”
Twenty-six patients (23 males, 3 females; median 73.5 years) with histologically proven MPM and no curative surgery received nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy. FDG-PET/CT and diagnostic CT scanning at the baseline, and after 2–4 cycles (2 in three, 3 in 17, 4 in six patients) were performed. Therapeutic response findings evaluated using imPERCIST and mRECIST were compared. PFS and OS analyses were done using log-rank and Cox methods.
Results: imPERCIST indicated nine progressive metabolic disease (PMD), eight stable metabolic disease (SMD), four partial metabolic response (PMR), and five complete metabolic response (CMR) cases. mRECIST showed nine with progressive disease (PD), nine stable disease (SD), seven partial response (PR), and one complete response (CR). Although high concordance was noted (κ = 0.827), imPERCIST correctly judged a greater percentage with CMR (15.4%). Following a median 10.0 months, 15 patients showed progression and eight died from MPM. With both, progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly longer in patients without progression (CMR/PMR/SMD, CR/PR/SD, respectively) as compared to PMD/PD patients (imPERCIST p < 0.0001 and p = 0.015, respectively; mRECIST p < 0.0001 and p = 0.015, respectively).
“For unresectable MPM patient examinations, FDG-PET and CT provide accurate findings for evaluating tumor response and also prognosis prediction following first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab immunotherapy (approximately three cycles).”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28594
Correspondence to: Kazuhiro Kitajima
Email: kazu10041976@yahoo.co.jp
Keywords: mesothelioma; immunotherapy; FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose); PET-CT (positron emission tomography-computed tomography); immunotherapy-modified PERCIST (positron emission tomography response criteria in solid tumors)
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Reddit
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
A new UBC study published recently in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) has unveiled insights into how microscopic organisms such as marine plankton move through water with different density layers.
Researchers Gwynn Elfring and Vaseem Shaik found that density layers, created by variations in temperature or salinity, influence the swimming direction and speed of tiny particles navigating a liquid.
Pushers and pullers
“There are two different types of microscopic swimmers – ...
UTICA, NY – The president of SUNY Polytechnic Institute (SUNY Poly), Dr. Winston “Wole” Soboyejo, and postdoctoral researcher, Dr. Tabiri Kwayie Asumadu, have published a revolutionary new paper titled, "Robust Macroscale Superlubricity on Carbon-Coated Metallic Surfaces." This paper explores an innovative approach to reducing friction on metallic surfaces – a significant advancement that could have major real-world impacts.
The study shows that superlubricity – a state with virtually no friction that was once believed to only be achievable at nanoscale – can now be maintained at macroscale for extended time ...
HOUSTON - (July 15, 2024) - As parents, teachers and pet owners can attest, rewards play a huge role in shaping behaviors in humans and animals. Rewards – whether as edible treats, gifts, words of appreciation or praise, fame or monetary benefits – act as positive reinforcement for the associated behavior. While this correlation between reward and future choice has been used as a well-established paradigm in neuroscience research for well over a century, not much is known about the neural process underlying it, namely how the brain encodes, ...
Waltham — July 15, 2024 — The strengths of academic psychiatry departments and the fast-growing private telehealth sector are complementary, according to a Perspective article published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer. Justin A. Chen, MD, MPH, a psychiatrist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City, and colleagues reviewed literature on provision of outpatient mental health care in the United States. They concluded that academic psychiatry departments and telehealth companies could mutually benefit from strategic collaboration.
Academic medical centers struggle to ...
Researchers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have finally confirmed what models have previously predicted: An exoplanet has differences between its eternal morning and eternal evening atmosphere. WASP-39 b, a giant planet with a diameter 1.3 times greater than Jupiter, but similar mass to Saturn that orbits a star about 700 light-years away from Earth, is tidally locked to its parent star. This means it has a constant dayside and a constant nightside—one side of the planet is always exposed to its star, while the other is always shrouded in darkness.
Using Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared ...
AMES, Iowa – As highly pathogenic avian influenza has spread in dairy herds across the U.S., the virus is being detected in raw milk. A new study by a broad team of researchers at Iowa State University’s College of Veterinary Medicine helps explain why.
Sialic acid, a sugar molecule found on the surface of some animal cells, acts as a receptor for influenza. Without sialic acid providing an entry point to attach, invade and infect, a flu virus is unlikely to find a potential host hospitable.
Before the recent HPAI outbreak ...
Humans make nearly 35,000 decisions every day, from whether it’s safe to cross the road to what to have for lunch. Every decision involves weighing the options, remembering similar past scenarios, and feeling reasonably confident about the right choice. What may seem like a snap decision actually comes from gathering evidence from the surrounding environment. And often the same person makes different decisions in the same scenarios at different times.
Neural networks do the opposite, making the same decisions each time. Now, Georgia Tech researchers in Associate Professor Dobromir Rahnev’s lab are ...
Janusz Wojtusiak, Professor, Health Administration and Policy, College of Public Health, is set to receive funding for the project: “An Artificial Intelligence Solution to Social Isolation and Longlines of Caregivers of People with Dementia.”
Wojtusiak and his graduate student Ghaida Alsadah will lay the foundation for a large study aimed at utilizing AI methods to address social isolation and loneliness among people who care for those with Alzheimer’s Disease and those suffering from dementia.
Addressing ...
Images
A new camera could prevent companies from collecting embarrassing and identifiable photos and videos from devices like smart home cameras and robotic vacuums. It's called PrivacyLens and was made by University of Michigan engineers.
PrivacyLens uses both a standard video camera and a heat-sensing camera to spot people in images from their body temperature. The person's likeness is then completely replaced by a generic stick figure, whose movements mirror those of the person it stands in for. The accurately animated stick figure allows a device relying on the ...
Astronomers have created the most detailed weather report so far for two distant worlds beyond our own solar system.
The international study – the first of its kind – reveals the extreme atmospheric conditions on the celestial objects, which are swathed in swirling clouds of hot sand amid temperatures of 950C.
Using NASA’s powerful James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), researchers set out to capture the weather on a pair of brown dwarfs – cosmic bodies that are bigger than planets but smaller than stars.
These brown dwarfs, named collectively ...