(Press-News.org)
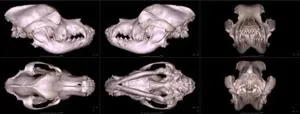
The ELTE Eötvös Loránd University is home to the skulls of more than 150 dog breeds and other animals. To make this unique collection accessible to all, researchers digitised the skulls of 431 dogs, cats and wild relatives. The database can be used for educational and research purposes.
Tibor Csörgő, a researcher at ELTE, has been collecting animal skulls for decades to teach anatomy to biologists. The shape of the skull varies considerably between species and breeds, especially in dogs, where, for example, greyhounds have long skulls and the now popular French bulldogs have rounded skulls.
A skull biobank could be a valuable resource for education, medicine and evolutionary research.
For example, Zsolt László Garamszegi, Director of the HUN-REN Institute of Ecological Research, together with ethologists from ELTE and Niclas Kolm from Stockholm University, have based their findings in part on this collection, which shows that modern dog breeds bred in the last 200 years have larger brains than those with ancient origin, due to altered selection effects. The researchers wanted to make this unique collection of skulls available to all.
VIDEOABSTRACT: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wE5elULOfWk
Similar research previously required researchers to visit collections in person. Today, however, it is possible to digitise skulls so that anyone can conduct studies at their desk, even on another continent. The digitisation was carried out by Kálmán Czeibert, a veterinary neuroanatomist in collaboration with Ádám Csóka, Tamás Donkó and Örs Petneházy, imaging specialists from the Medicopus Nonprofit Ltd. research unit, using a medical high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scanner.
In total, 431 skulls were digitised, representing 152 dog breeds, 9 cat breeds and 12 of their wild relatives, including wolves, jackals, coyotes, a leopard and a serval.
The database was published in the journal Scientific Data. According to the study's corresponding author, Enikő Kubinyi, head of the MTA-ELTE Lendület Companion Animal and ELTE NAP Canine Brain research groups, "the digital skull database can be used for comparative anatomical and evolutionary studies, in the education of veterinarians and biologists, and even for the development of machine learning algorithms for automated species identification and veterinary diagnostics". The researchers have also produced a video to illustrate the database, which can be viewed here.
Original article: Czeibert, K., Nagy, G., Csörgő, T., Donkó, T., Petneházy, Ö., Csóka, Á., Garamszegi, L. Z., Kolm, N., Kubinyi, E. (2024) High-resolution computed tomographic (HRCT) image series from 413 canid and 18 felid skulls. Scientific Data, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03572-x
END
Overcoming Historical Barriers
Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, has traditionally been limited to surface-level nanofabrication due to the challenges posed by existing lithographic techniques. Available methods either fail to penetrate the wafer surface without causing alterations or are limited by the micron-scale resolution of laser lithography within Si. In the spirit of Richard Feynman's famous dictum, 'There's plenty of room at the bottom', ...
Preeclampsia (PE) is a significant contributor to the increase in maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide, with particularly alarming numbers in the United States, where it affects about 2–8% of pregnancies, resulting in premature birth with associated morbidities for their infants as well. A new study by researchers at UCLA Health finds that early detection of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) packaged in vesicles may offer the opportunity to predict preeclampsia in pregnant people before clinical symptoms manifest.
The study, led by Dr. Sherin U. Devaskar, MD, executive chair of the Department of Pediatrics ...
Researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed low-cost micro-sized silicon anodes from recycled photovoltaic waste using a novel electrolyte design.
Their pioneering work, published in Nature Sustainability on July 16, offers a path to more sustainable, low-cost, and high-energy-density batteries that could transform energy storage systems for electric vehicles and renewable energy applications.
Silicon anodes are favored for their ability to substantially increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries compared to traditional graphite anodes but are hindered by significant volume ...
Billions of dollars in foreign aid could be spent more effectively if international poverty statistics were more accurate, according to new research led by King's College London.
Dr Michail Moatsos, a research fellow in the Department of International Development, says current methods for calculating the international poverty line lead to a skewed picture of how poverty is distributed across the world – and this is hampering attempts to eradicate it.
“Currently, international donors cannot prioritise their funds based on the best possible information and therefore funnel those funds to those most in need around the world. A $2.15 per day poverty line affords very different ...
Scientists from RMIT University have led a world-first study on common food aromas that may help explain why astronauts report that meals taste bland in space and struggle to eat their normal nutritional intake.
This research, which is published in the International Journal of Food Science and Technology, has broader implications for improving the diets of isolated people, including nursing home residents, by personalising aromas to enhance the flavour of their food.
Previous research has shown that aroma plays a big role in the flavour of food.
The team in this study tested how people perceived vanilla and almond extracts and lemon essential oil changed from normal environments on ...
Britain, prepare for deep depression: storms ruin tea.
A new study reveals that Storm Ciaran cut an invisible path of mayhem across southern Britain last autumn, destroying any possibility that 20 million people could have a proper cup of tea at breakfast.
The storm's record-breaking low pressure meant the boiling point of water was below the crucial 100 degrees Celsius required for a decent cuppa, meteorologists at the University of Reading have discovered.
In a study published today [Tuesday, 16 July] in the journal Weather, the scientists reported that water in Reading was boiling at just 98°C.
During the storm on the morning of November 2, ...
With the rapid development of AI technology, voice-controlled smart speakers are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience and ability to control compatible home devices. Despite the rise in use, smart speakers often do not have screens and little-to-none of the visual information feedback common to manually operated devices. This aspect complicates their usability, thus providing room for research and subsequent improvement.
As such, a research team led by Dr. Toshihisa Doi, a lecturer at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology, recruited 39 young adults (22 males and ...
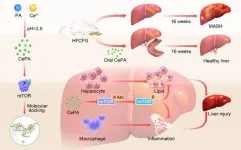
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is one of the most common chronic liver diseases, primarily caused by metabolic disorders and systemic inflammatory responses. Although the incidence of MASH is gradually increasing, there is a lack of effective drugs and methods for its treatment, thus limiting therapeutic options for MASH. Professor Liu Lei's team has long focused on the treatment and molecular mechanisms of liver-related diseases. Due to cerium's significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, as well as its hepatophilicity and good biosafety, it shows great potential ...
Krishna Reddy, MD, MS, a physician-investigator at the Medical Practice Evaluation Center and the Tobacco Research and Treatment Center at Massachusetts General Hospital and an Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, is the senior author of a recently published paper in Journal of the International AIDS Society: Tobacco Smoking, Smoking Cessation and Life Expectancy Among People with HIV on Antiretroviral Therapy in South Africa: A Simulation Modelling Study.
What Question Were You Investigating in this Study?
Now that more people with HIV in South Africa are on antiretroviral therapy (medicines to treat ...
If a man and a woman each suffer a heart attack, you may assume the symptoms and diagnoses should be the same.
That’s not always the case. While men are more likely to show the more “typical” signs of a heart attack — chest pains, shortness of breath — women are more likely to experience pain in their necks or symptoms that feel like heartburn or nausea. An angiogram that shows a blockage in male blood vessels may not show occlusion in a woman’s smaller vessels, and these differences can lead ...