(Press-News.org) Study shows how materials change as they are stressed and relaxed.
Like people, materials evolve over time. They also behave differently when they are stressed and relaxed. Scientists looking to measure the dynamics of how materials change have developed a new technique that leverages X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy (XPCS), artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
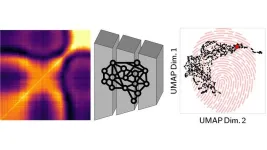
This technique creates “fingerprints” of different materials that can be read and analyzed by a neural network to yield new information that scientists previously could not access. A neural network is a computer model that makes decisions in a manner similar to the human brain.
In a new study by researchers in the Advanced Photon Source (APS) and Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM) at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, scientists have paired XPCS with an unsupervised machine learning algorithm, a form of neural network that requires no expert training. The algorithm teaches itself to recognize patterns hidden within arrangements of X-rays scattered by a colloid — a group of particles suspended in solution. The APS and CNM are DOE Office of Science user facilities.
“The goal of the AI is just to treat the scattering patterns as regular images or pictures and digest them to figure out what are the repeating patterns. The AI is a pattern recognition expert.” — James (Jay) Horwath, Argonne National Laboratory
“The way we understand how materials move and change over time is by collecting X-ray scattering data,” said Argonne postdoctoral researcher James (Jay) Horwath, the first author of the study.
These patterns are too complicated for scientists to detect without the aid of AI. “As we’re shining the X-ray beam, the patterns are so diverse and so complicated that it becomes difficult even for experts to understand what any of them mean,” Horwath said.
For researchers to better understand what they are studying, they have to condense all the data into fingerprints that carry only the most essential information about the sample. “You can think of it like having the material’s genome, it has all the information necessary to reconstruct the entire picture,” Horwath said.
The project is called Artificial Intelligence for Non-Equilibrium Relaxation Dynamics, or AI-NERD. The fingerprints are created by using a technique called an autoencoder. An autoencoder is a type of neural network that transforms the original image data into the fingerprint — called a latent representation by scientists — and that also includes a decoder algorithm used to go from the latent representation back to the full image.
The goal of the researchers was to try to create a map of the material’s fingerprints, clustering together fingerprints with similar characteristics into neighborhoods. By looking holistically at the features of the various fingerprint neighborhoods on the map, the researchers were able to better understand how the materials were structured and how they evolved over time as they were stressed and relaxed.
AI, simply put, has good general pattern recognition capabilities, making it able to efficiently categorize the different X-ray images and sort them into the map. “The goal of the AI is just to treat the scattering patterns as regular images or pictures and digest them to figure out what are the repeating patterns,” Horwath said. “The AI is a pattern recognition expert.”
Using AI to understand scattering data will be especially important as the upgraded APS comes online. The improved facility will generate 500 times brighter X-ray beams than the original APS. “The data we get from the upgraded APS will need the power of AI to sort through it,” Horwath said.
The theory group at CNM collaborated with the computational group in Argonne’s X-ray Science division to perform molecular simulations of the polymer dynamics demonstrated by XPCS and going forward synthetically generate data for training AI workflows like the AI-NERD.
A paper based on the study appeared in Nature Communications. The study was funded through an Argonne laboratory-directed research and development grant.
Authors of the study include Argonne’s James (Jay) Horwath, Xiao-Min Lin, Hongrui He, Qingteng Zhang, Eric Dufresne, Miaoqi Chu, Subramanian Sankaranaryanan, Wei Chen, Suresh Narayanan and Mathew Cherukara. Chen and He have joint appointments at the University of Chicago, and Sankaranaryanan has a joint appointment at the University of Illinois Chicago.
About Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials
The Center for Nanoscale Materials is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE’s Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge, Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit https://science.osti.gov/User-Facilities/User-Facilities-at-a-Glance.
About the Advanced Photon Source
The U. S. Department of Energy Office of Science’s Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the world’s most productive X-ray light source facilities. The APS provides high-brightness X-ray beams to a diverse community of researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. These X-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation’s economic, technological, and physical well-being. Each year, more than 5,000 researchers use the APS to produce over 2,000 publications detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other X-ray light source research facility. APS scientists and engineers innovate technology that is at the heart of advancing accelerator and light-source operations. This includes the insertion devices that produce extreme-brightness X-rays prized by researchers, lenses that focus the X-rays down to a few nanometers, instrumentation that maximizes the way the X-rays interact with samples being studied, and software that gathers and manages the massive quantity of data resulting from discovery research at the APS.
This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology by conducting leading-edge basic and applied research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.
END
Scientists develop new artificial intelligence method to create material ‘fingerprints’
Algorithm can teach itself to recognize patterns in materials
2024-07-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sun-like stars found orbiting hidden companions
2024-07-16
Most stars in our universe come in pairs. While our own Sun is a loner, many stars like our Sun orbit similar stars, while a host of other exotic pairings between stars and cosmic orbs pepper the universe. Black holes, for example, are often found orbiting each other. One pairing that has proved to be quite rare is that between a Sun-like star and a type of dead star called a neutron star.
Now, astronomers led by Caltech's Kareem El-Badry have uncovered what appear to be 21 neutron stars in orbit around stars like our Sun. Neutron stars are dense burned-out ...
Roles of PEDF in exercise-induced suppression of senescence and its impact on lung pathology in mice
2024-07-16
“[...] the present results strongly suggest the potential of PEDF as a myokine linking exercise training to the suppression of senescence.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 16, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 13, entitled, “Roles of pigment epithelium-derived factor in exercise-induced suppression of senescence and its impact on lung pathology in mice.”
Senescent cells contribute ...
HER2-low and HER2-zero in breast cancer between prognosis, prediction and entity
2024-07-16
“[...] we found an independent positive prognostic effect of HER2-low compared to HER2-zero in early breast cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 16, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “HER2-low and HER2-zero in breast cancer between prognosis, prediction and entity.”
In this new editorial, researchers Marcus Schmidt, Hans-Anton Lehr, and Katrin Almstedt from the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University discuss HER2 in breast cancer. HER2 is a well-established prognostic and predictive factor in breast ...
How to assess a general-purpose AI model’s reliability before it’s deployed
2024-07-16
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Foundation models are massive deep-learning models that have been pretrained on an enormous amount of general-purpose, unlabeled data. They can be applied to a variety of tasks, like generating images or answering customer questions.
But these models, which serve as the backbone for powerful artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E, can offer up incorrect or misleading information. In a safety-critical situation, such as a pedestrian approaching a self-driving car, these mistakes could have serious consequences.
To help prevent such mistakes, researchers from MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab developed a technique to estimate the reliability ...
Advancing quantum research – DOE inks MOU with Department of Defense
2024-07-16
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) announce a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to coordinate efforts to move the needle on quantum computing.
“Realizing practical quantum computers has the potential to dramatically accelerate the pace of discovery across the science and technology landscape,” said Ceren Susut, DOE Associate Director of Science for the Advanced Scientific Computing Research program. “The Office of Science is proud to bring decades of experience in fundamental science for quantum ...
Transporting precious cargo using the body’s own delivery system
2024-07-16
Each cell in the body has its own unique delivery system that scientists are working on harnessing to move revolutionary biological drugs — molecules like proteins, RNA and combinations of the two — to specific diseased parts of the body.
A new study from Northwestern University hijacked the transit system and sent tiny, virus-sized containers to effectively deliver an engineered protein to its target cell and trigger a change in the cell’s gene expression. The success came from encouraging engineered proteins to move toward a specific cell membrane structure that the researchers found increased a protein’s likelihood of latching onto the container.
Published ...
SwRI, UTD jointly fund project to evaluate space sensor in unique facility
2024-07-16
SAN ANTONIO — July 16, 2024 — Researchers from Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and The University of Texas at Dallas (UTD) are collaborating to evaluate a next-generation sensor designed to measure neutral gas velocities in the Earth’s upper atmosphere. The project, led by SwRI’s Dr. Joo Hwang and UTD’s Dr. Phillip Anderson, is supported by a grant from the new SwRI/UTD Seed Projects for Research, INnovation, and Technology (SPRINT) Program. Another SPRINT project is researching domestic lithium independence, looking at ...
Nature-based solutions to disaster risk from climate change are cost effective, UMmass Amherst study confirms
2024-07-16
AMHERST, Mass. – A new global assessment of scientific literature led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst finds that nature-based solutions (NbS) are an economically effective method to mitigate risks from a range of disasters—from floods and hurricanes to heatwaves and landslides—which are only expected to intensify as Earth continues to warm.
NbS are interventions where an ecosystem is either preserved, sustainably managed or restored to provide benefits to society and to nature. For instance, they can mitigate risk from a natural disaster, or facilitate climate mitigation and adaptation. NbS ...
Decline in global adolescent fertility rates is counteracted by increasing teen births in Sub-Saharan Africa
2024-07-16
July 16, 2024-- A new report from Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and the Columbia Aging Center with colleagues from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health highlights a troubling trend: while global adolescent fertility rates have significantly declined, sub-Saharan Africa is experiencing an increase in teen births. This region's share of global adolescent births surged from 12 percent in 1950 to 47 percent in 2020 and is projected to reach a clear majority – a full 67 percent - by ...
Apps and AI could help personalize depression diagnosis and treatment
2024-07-16
New research at the University of Illinois Chicago is testing whether digital tools can help predict which patients with depression will benefit from specific treatments and help deliver those treatments to them on demand.
Two new grants awarding over $10 million to UIC will help Dr. Jun Ma and colleagues in the College of Medicine investigate the use of a smartphone app, an AI voice assistant and other technologies to diagnose and treat depression.
The researchers hope these tools will both broaden access to psychiatric care and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Scientists develop new artificial intelligence method to create material ‘fingerprints’Algorithm can teach itself to recognize patterns in materials