(Press-News.org) New recommendations for screening and treatment are based on the results of a major national study led at UCSF.
Results from a national study led by UC San Francisco informed the first guidelines at the federal level in the United States to detect and treat anal cancer precursor lesions in people with HIV to reduce the risk of developing anal cancer.
The guidelines were published on July 9 by a panel of experts in HIV care, utilizing findings from the Anal Cancer/HSIL Outcomes Research (ANCHOR) trial led by Joel M. Palefsky, MD, a professor of medicine in the UCSF Infectious Disease Division. The ANCHOR study was funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health NIH and conducted by the AIDS Malignancy Consortium.
The ANCHOR trial, conducted at 25 clinical sites around the country and published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2022, found that routine screening for and removal of precancerous anal lesions could significantly reduce the risk of anal cancer, in much the way that cervical cancer is prevented in women.
“Anal cancer is a very bad disease, and we now have the tools to significantly reduce the risk,” said Palefsky, a globally recognized expert on anal cancer. “With this new recommendation, we hope that screening for anal cancer becomes a routine procedure in the care of people with HIV.”
Risk of anal cancer is high in people with HIV
While anal cancer is rare within the general population, cases have been rising, and among people living with HIV, it is the fourth most common cancer.
For people with human papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted virus, coinfection with HIV can increase the risk of developing anal cancer. “Men with HIV who have sex with men and transgender women with HIV, are the groups at the highest risk of anal cancer,” note the new guidelines.
Anal cancer may have no symptoms in its early stages, and patients may mistake it for hemorrhoids. By the time it’s diagnosed, it may have spread.
Under the new guidelines published, if high resolution anoscopy is available, certain adults with HIV – starting at age 35 for men, and transgender women, who have sex with men; and starting at 45 for women and men who do not have sex with men – should undergo screening for anal cancer precursor lesions with laboratory testing of an anal swab sample, and a digital anorectal examination to feel for changes that might indicate the presence of a cancer.
“The screening procedure is quite simple,” Palefsky said. “If the screening test is positive, the next step of the evaluation is HRA. If an anal cancer precursor lesion is found at HRA, it is then treated to reduce the risk of progressing to cancer.”
If HRA is not available, people with HIV who are of screening age should still have an annual rectal exam and be referred for standard anoscopy if the screen is positive. Those who have pain, bleeding or masses, or who show signs of anal cancer should undergo standard anoscopy. Palefsky added that symptomatic people under 35 with HIV should also undergo standard anoscopy.
“I strongly encourage people with HIV to discuss anal cancer screening with their primary care providers,” he said.
In 1991, Palefsky established the world’s first clinic focused on prevention of anal cancer, the UCSF Anal Neoplasia Clinic Research and Education Center.
The recommendations were developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Panel on the Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in Adults and Adolescents with HIV, which is composed of experts in HIV care. The panel is a working group of the NIH Office of AIDS Research Advisory Council, in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
About UCSF Health: UCSF Health is recognized worldwide for its innovative patient care, reflecting the latest medical knowledge, advanced technologies and pioneering research. It includes the flagship UCSF Medical Center, which is a top-ranked hospital, as well as UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals, with campuses in San Francisco and Oakland; Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital; UCSF Benioff Children’s Physicians; and the UCSF Faculty Practice. These hospitals serve as the academic medical center of the University of California, San Francisco, which is world-renowned for its graduate-level health sciences education and biomedical research. UCSF Health has affiliations with hospitals and health organizations throughout the Bay Area. Visit https://www.ucsfhealth.org/. Follow UCSF Health on Facebook or on Twitter
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | Twitter.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Panel issues first guidelines to prevent anal cancer in people with HIV
2024-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Estimating rainfall intensity using surveillance audio and deep-learning
2024-07-19
Surveillance cameras generate both video and audio outputs. Unlike video images recorded, the audio can be supplemented reliably as audio sources resist background interference and lighting variability. Creating a reliable way to use these audio sources to estimate the intensity of rainfall could open a new chapter in rainfall intensity estimation.
In a study published in Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers created an audio dataset of six real-world rainfall events, named the Surveillance Audio Rainfall Intensity Dataset (SARID). ...
Targeting factors for chemoprevention and cancer interception to tackle mesothelioma
2024-07-19
BUFFALO, NY- July 19, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on May 23, 2024, entitled, “Targeting inflammatory factors for chemoprevention and cancer interception to tackle malignant mesothelioma.”
In this perspective, researchers Joseph R. Testa, Yuwaraj Kadariya, and Joseph S. Friedberg from Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, identify potential targets for mesothelioma prevention. Mesothelioma, an incurable cancer of the mesothelial lining, ...
New snake discovery rewrites history, points to North America’s role in snake evolution
2024-07-19
A new species of fossil snake unearthed in Wyoming is rewriting our understanding of snake evolution. The discovery, based on four remarkably well-preserved specimens found curled together in a burrow, reveals a new species named Hibernophis breithaupti. This snake lived in North America 34 million years ago and sheds light on the origin and diversification of boas and pythons.
Hibernophis breithaupti has unique anatomical features, in part because the specimens are articulated—meaning they were found all in one piece with the bones still arranged in the proper order—which is unusual for fossil snakes. Researchers believe it may be ...
Large and unequal life expectancy declines in India during COVID-19
2024-07-19
The international study, co-authored by the Department of Sociology and the Leverhulme Centre for Demographic Science’s Dr Aashish Gupta and Professor Ridhi Kashyap, reveals that life expectancy in India suffered large and unequal declines during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Overall, mortality across India was 17% higher in 2020 compared to 2019, implying 1.19 million excess deaths in India. This extrapolated estimate is about eight times higher than the official number of COVID-19 deaths in India, and 1.5 times higher than the World Health Organization’s estimates.
Ridhi ...
A study of 156,000 UK residents found that urban residents score the lowest in social and economic satisfaction and well-being
2024-07-19
A new study conducted by the Centre for Urban Mental Health at the University of Amsterdam finds that, in a sample of 156,000 UK residents aged 40 and up, urban living is linked to lower levels of well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction. Urban residents also exhibit greater psychological inequality. The study identifies a ‘Goldilocks zone’ between cities and rural areas, where the highest satisfaction and most equal scores are observed.
The percentage of people living in cities has surged from 10% in the 1910s to a projected 68% by 2050. This shift means ...
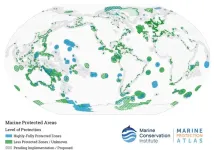
Global study by Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology demonstrates benefit of marine protected areas to recreational fisheries
2024-07-19
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are having a positive spillover effect, producing more “trophy-size” fish just outside of the fully protected areas, and the effect is growing stronger over time. That’s according to research led by University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa scientists at the Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) published today in Science Advances. The research provides the first global assessment of the benefits of MPAs. “Trophy-size” refers to fish that are exceptionally long or heavy and are considered a rare, ...
Researchers clarify how soft materials fail under stress
2024-07-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Understanding how soft materials fail under stress is critical for solving engineering challenges as disparate as pharmaceutical technology and landslide prevention. A new study linking a spectrum of soft material behaviors — previously thought to be unrelated — led researchers to identify a new parameter they call the brittility factor, which allows them to simplify soft material failure behavior. This will ultimately help engineers design better materials that meet future challenges.
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign chemical and biomolecular engineering professor Simon Rogers and graduate student Krutarth Kamani specialize ...
Revolutionizing the abilities of adaptive radar with AI
2024-07-19
DURHAM, N.C. – The world around us is constantly being flash photographed by adaptive radar systems. From salt flats to mountains and everything in between, adaptive radar is used to detect, locate and track moving objects. Just because human eyes can’t see these ultra-high frequency (UHF) ranges doesn’t mean they’re not taking pictures.
Although adaptive radar systems have been around since World War II, they’ve hit a fundamental performance wall in the past couple of decades. But with the help of modern AI approaches and lessons learned from computer vision, researchers at Duke University have broken through that wall, and they want to bring everyone ...
Plastic waste can now be converted to electronic devices
2024-07-19
University of Delaware and Argonne National Laboratory have come up with a chemical reaction that can convert Styrofoam into a high-value conducting polymer known as PEDOT:PSS. In a new paper published in JACS Au, the study demonstrates how upgraded plastic waste can be successfully incorporated into functional electronic devices, including silicon-based hybrid solar cells and organic electrochemical transistors.
The research group of corresponding author Laure Kayser, assistant professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in ...
Health equity scholar Darrell Hudson named Health Behavior and Health Education chair at the University of Michigan School of Public Health
2024-07-19
Leading health equity researcher Darrell Hudson, MPH ‘05, PhD ‘09, has been named chair of the Department of Health Behavior and Health Education at the University of Michigan School of Public Health. His appointment for a five-year term, effective August 26, 2024, was approved by the University of Michigan Board of Regents this week.
“Dr. Hudson has solidified his national reputation as a leading health equity scholar, making impactful research contributions through rigorous, interdisciplinary, and innovative scholarship,” said F. DuBois Bowman, dean of Michigan Public Health. “His research is timely ...