(Press-News.org) PISCATAWAY, NJ – Probably everyone has heard the conventional wisdom that a glass of wine a day is good for you--or you’ve heard some variation of it. The problem is that it’s based on flawed scientific research, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Over the years, many studies have suggested that moderate drinkers enjoy longer lives with lower risks of heart disease and other chronic ills than abstainers do. That spurred the widespread belief that alcohol, in moderation, can be a health tonic. However, not all studies have painted such a rosy picture--and the new analysis sheds light on why.
In a nutshell, studies linking moderate drinking to health benefits suffer from fundamental design flaws, said lead researcher Tim Stockwell, Ph.D., a scientist with the Canadian Institute for Substance Use Research at the University of Victoria.
The major issue: Those studies have generally focused on older adults and failed to account for people’s lifetime drinking habits. So moderate drinkers were compared with “abstainer” and “occasional drinker” groups that included some older adults who had quit or cut down on drinking because they’d developed any number of health conditions.
“That makes people who continue to drink look much healthier by comparison,” Stockwell said.
And in this case, he noted, looks are deceiving.
For the analysis, Stockwell and his colleagues identified 107 published studies that followed people over time and looked at the relationship between drinking habits and longevity. When the researchers combined all the data, it looked like light to moderate drinkers (that is, those who drank between one drink per week and two per day) had a 14% lower risk of dying during the study period compared with abstainers.
Things changed, however, when the investigators did a deeper dive. There were a handful of “higher quality” studies that included people who were relatively young at the outset (younger than 55, on average) and that made sure former and occasional drinkers were not considered “abstainers.” In those studies, moderate drinking was not linked to a longer life.
Instead, it was the “lower quality” studies (older participants, no distinction between former drinkers and lifelong abstainers) that did link moderate drinking to greater longevity.
“If you look at the weakest studies,” Stockwell said, “that’s where you see health benefits.”
The notion that moderate drinking leads to a longer, healthier life goes back decades. As an example, Stockwell pointed to the “French paradox”--the idea, popularized in the 1990s, that red wine helps explain why the French enjoy relatively low rates of heart disease, despite a rich, fatty diet. That view of alcohol as an elixir still seems to be “ingrained” in the public imagination, Stockwell noted.
In reality, he said, moderate drinking likely does not extend people’s lives--and, in fact, carries some potential health hazards, including increased risks of certain cancers. That’s why no major health organization has ever established a risk-free level of alcohol consumption.
“There is simply no completely ‘safe’ level of drinking,” Stockwell said.
-----
Stockwell, T., Zhao, J., Clay, J., Levesque, C., Sanger, N., Sherk, A., & Naimi, T. (2024). Why do only some cohort studies find health benefits from low volume alcohol use? A systematic review and meta-analysis of study characteristics that may bias mortality risk estimates. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 85(4), 441–452. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.23-00283
END
The research was wrong: study shows moderate drinking won’t lengthen your life
2024-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
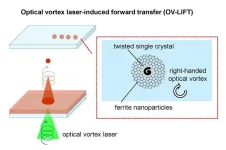
Save your data on printable magnetic devices? New laser technique’s twist might make this reality
2024-07-25
The proliferation of all things digital doesn’t mean that printing technology is no longer relevant. In fact, printing technology is required to make the semiconductors necessary for the digital world. And as an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has shown using a new printing technique, printable magnetic devices for high-density data storage might soon be realized.
Dr. Ken-ichi Yuyama, a lecturer at the Graduate School of Science, and his colleagues report in APL Materials on the development of a new type of laser-induced forward transfer ...
Early onset dementia more common than previously reported – the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease seems to be on the rise
2024-07-25
A new major study by the University of Eastern Finland, the University of Oulu and Neurocenter Finland explored early-onset dementia in the working-age population in Finland. The study cohort was one of the largest in the world to date, and the findings were published on 24th of July 2024 in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Current epidemiological data on early-onset dementia is scarce and based on small study cohorts, with no recent data from Finland available. For the present ...
Pesticides potentially as bad as smoking for increased risk in certain cancers
2024-07-25
In modern day agriculture, pesticides are essential to ensure high enough crop yields and food security. These chemicals, however, can adversely affect plant and animal life as well as the people exposed to them.
Now, in a population-based, nation-wide study, researchers in the US have put increased cancer risk through agricultural pesticide use into context with smoking, a better understood cancer risk factor. The results were published in Frontiers in Cancer Control and Society.
“In our study we found that for some cancers, the effect of agricultural pesticide usage is comparable in magnitude to the effect of smoking,” said the study’s ...
NUS researchers develop new battery-free technology to power electronic devices using ambient radiofrequency signals
2024-07-25
Ubiquitous wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G rely on radio frequency (RF) signals to send and receive data. A new prototype of an energy harvesting module – developed by a team led by scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) – can now convert ambient or ‘waste’ RF signals into direct current (DC) voltage. This can be used to power small electronic devices without the use of batteries.
RF energy harvesting technologies, such as this, is essential as they reduce battery dependency, extend device lifetimes, minimise environmental impact, and enhance the feasibility of wireless sensor networks and IoT devices in remote ...
New protein discovery may influence future cancer treatment
2024-07-25
Researchers from the University of Otago, Christchurch, have spearheaded the discovery of a protein function which has the potential to guide the development of novel cancer treatment options and improve the diagnosis of various cancers.
The exciting research finding, carried out alongside Dr Vanessa Morris from the University of Canterbury’s School of Biological Sciences as well as researchers in Australia and Denmark, centres on the activity of a tumour- suppressing protein called p16.
The discovery, published in the British scientific journal Nature Communications and first authored by ...
Timing matters: Scripps Research study shows ways to improve health alerts
2024-07-25
LA JOLLA, CA—When seemingly healthy people receive an alert from a wearable sensor telling them they might have a respiratory virus—based on small changes in their unique heartrate, sleep and activity patterns—what do they do? According to a new study by Scripps Research scientists carried out at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, only a quarter of people follow up such an alert with an at-home viral test.
That is just one conclusion of the new study, published in The Lancet Digital Health on July 24, 2024, which tested the feasibility ...
New gene therapy approach shows promise for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
2024-07-25
INDIANAPOLIS - Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have made a significant breakthrough in developing a new gene therapy approach that restores full-length dystrophin protein, which could lead to new treatments for people with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
The study, recently published in Nature Communications, demonstrates the effectiveness of their novel gene therapy technology in improving muscle tissue and overall strength in mice models with Duchenne ...
Chemical analyses find hidden elements from renaissance astronomer Tycho Brahe’s alchemy laboratory
2024-07-25
In the Middle Ages, alchemists were notoriously secretive and didn’t share their knowledge with others. Danish Tycho Brahe was no exception. Consequently, we don’t know precisely what he did in the alchemical laboratory located beneath his combined residence and observatory, Uraniborg, on the now Swedish island of Ven.
Only a few of his alchemical recipes have survived, and today, there are very few remnants of his laboratory. Uraniborg was demolished after his death in 1601, and the building materials were scattered for reuse.
However, during an excavation ...
Pacific Northwest launches clean hydrogen energy hub
2024-07-25
RICHLAND, Wash.—The Pacific Northwest is set to begin work building out a clean hydrogen economy with today’s announcement of a Phase 1 funding award from the Department of Energy. The $27.5 million award to the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Association (PNWH2), a multi-state nonprofit organization, will be matched by industry partners up to $125 million in Phase 1 of the project.
DOE’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory will serve as an advisor to the PNWH2 by conducting life-cycle analysis to predict and understand the planned hydrogen energy infrastructure impact on decreasing emissions and aiding in community engagement.
Public ...
Tiny deletion in heart muscle protein briefly affects embryonic ventricles but has long-term effects on adult atrial fibrillation
2024-07-25
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Millions of adults have atrial fibrillation — an irregular beating of the upper chambers of the heart that yields increased risk of heart failure, stroke and death. Many genetic mutations in the developing fetus can lead to adult atrial fibrillation, including mutations that shorten the massive protein titin in cardiac muscle cells.
Now, in a study in zebrafish and human heart muscle cells, researchers show that a tiny deletion in the A-band of titin — the loss of just nine amino acids out of more than 27,000 to 35,000 amino acids of an intact titin protein — causes a developmental ...