(Press-News.org) About The Study: Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) was safe but did not offer clinically meaningful improvements. Further studies—for example, through modified FMT approaches or bowel cleansing—are warranted regarding the specific impact of donor microbiota composition and dysbiosis conversion on motor and nonmotor outcomes as well as medication needs in Parkinson disease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Filip Scheperjans, M.D., Ph.D., email filip.scheperjans@hus.fi.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2305)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2305?guestAccessKey=45baac08-7cff-4f48-b05f-47aaa3ebe263&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=072924
END
Fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of Parkinson disease
JAMA Neurology
2024-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advancing health disparities science through social epigenomics research
2024-07-29
About The Article: The studies highlighted in this special issue of JAMA Network Open demonstrate important scientific progress in the complex integration of social determinants of health and health disparities with biological pathways and health outcomes to improve understanding of the mechanisms underlying health disparities among various underserved populations. Continued progress remains important in integrating different disciplines to transform the field of health disparities research.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Arielle S. Gillman, Ph.D., M.P.H., email arielle.gillman@nih.gov.
To ...
Advanced ‘Parkinson's in a dish’ model accelerates brain disease research
2024-07-29
Researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, have developed a model that rapidly converts stem cells to brain cells with protein structures characteristic of Parkinson’s disease (PD), enabling the study of the condition’s unique and highly variable disease pathology in a petri dish. The study details how the model can one day be used to develop personalized diagnostic and treatment methods for Parkinson’s disease. Results are published in Neuron.
“We sought to assess how quickly we could ...
What will the new cardiovascular risk calculator mean for patients?
2024-07-29
A recently unveiled cardiovascular disease risk calculator that measures a patient’s risk for heart attack and stroke is better calibrated and more precise than its previous version, but if current treatment guidelines for cholesterol and blood pressure therapy remain unchanged, the new calculator may have unintended consequences, according to research from Harvard Medical School.
The analysis, published July 29 in JAMA, estimates that the new risk calculator would render nearly 16 million people newly ineligible under current treatment thresholds that guide clinical decisions about who should get cholesterol ...
Patients in hospitals that provide inpatient addiction services were more likely to start and continue lifesaving medication for opioid use disorder treatment after discharge
2024-07-29
Previous research has found that over 80 percent of people with opioid use disorder (OUD) do not receive evidence-based lifesaving medications. While access to these medications is better in New York City than elsewhere in the United States, numerous structural and social barriers impede access to treatment, and more than 100,000 people in the U.S. continue to die from drug overdoses each year.
To help close this alarming treatment gap, researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine partnered with the New York ...
Healthy diet with less sugar is linked to younger biological age
2024-07-29
Researchers at UC San Francisco have found a link between following a diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals, especially one without much added sugar, and having a younger biological age at the cellular level.
They looked at how three different measures of healthy eating affected an “epigenetic clock” – a biochemical test that can approximate both health and lifespan – and found that the better people ate, the younger their cells looked. Even when people ate healthy diets, ...
From tree holes to trash
2024-07-29
A team of biologists from the University of Delhi and Zoological Survey of India, Harvard University, and the University of Minnesota has discovered a unique breeding behavior in a species of frog endemic to the Andaman Islands of India. In a new study published in the Harvard Museum of Comparative Zoology’s journal Breviora, scientists describe a combination of traits that makes reproduction in this frog unique.
The Andamanese Charles Darwin’s frog, Minervarya charlesdarwini, belongs to the family Dicroglossidae, a large radiation of Asian frogs that comprises over ...
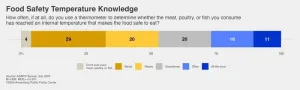
Despite risk, many unsure of temperature to heat food to prevent illness
2024-07-29
PHILADELPHIA – With bird flu virus detected in cow’s milk, U.S. health authorities have warned the public against potential sources of exposure, including drinking raw or unpasteurized milk, and have reiterated a general warning that consuming uncooked or undercooked poultry or beef products can make you sick.
Relatively few people say they drink raw milk. Only 3% of U.S. adults report having consumed raw milk in the past 12 months, while 4% were not sure whether they had, according to a new nationally representative Annenberg Public Policy Center health survey of nearly 1,500 empaneled U.S. adults conducted in July.*
But many more people say they do ...
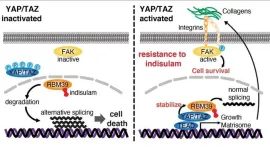
YAP/TAZ interactions can confer resistance to anti-tumor drug indisulam
2024-07-29
In a healthy human body, tissue growth and development are coordinated by many different mechanisms. Within our bodies, these mechanisms regulate the healthy growth of cells, limit their size and number, and control the timing of cell death through apoptosis. However, when these regulatory pathways are altered, or break down, cell growth and proliferation may increase beyond what is safe and this can lead to cancer. One critical cell growth regulatory mechanism is the Hippo signaling pathway. This pathway regulates the expression of several genes that control cell proliferation ...
Asbestos-related cancer: exaggerated risk perception
2024-07-29
Asbestos, a group of naturally occurring fibrous minerals, has been historically used for its durability and resistance to heat. Despite its advantageous properties, asbestos is a well-documented carcinogen, linked to diseases such as lung cancer (LC) and malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). The controversy surrounding the degree of carcinogenicity of different asbestos types, especially chrysotile versus amphibole asbestos, continues to influence scientific and regulatory discussions. This review delves into the various aspects of asbestos-related research, focusing on historical context, risk assessment, environmental ...
Gropp, former NCSA leaders selected for HPCwire’s inaugural ‘35 Legends’ list
2024-07-29
NCSA Director Bill Gropp and two former Center directors were chosen for the first-ever HPCwire “35 Legends” list in celebration of the publication’s 35th anniversary.
Thirty-five honorees will be announced each year, selected by HPCwire editors and advisors based on their contributions to the high-performance computing community over the past 35 years and celebrated for the different ways they’ve helped move HPC forward.
Gropp, NCSA’s Founding Director Larry Smarr and Former Director Daniel Reed were among the first 17 honorees announced in July. The remaining HPCwire 35 Legends will be ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of Parkinson diseaseJAMA Neurology