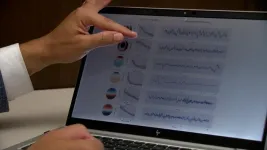
(Press-News.org) ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic scientists are using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze electroencephalogram (EEG) tests more quickly and precisely, enabling neurologists to find early signs of dementia among data that typically go unexamined.
The century-old EEG, during which a dozen or more electrodes are stuck to the scalp to monitor brain activity, is often used to detect epilepsy. Its results are interpreted by neurologists and other experts trained to spot patterns among the test's squiggly waves.
In new research published in Brain Communications, scientists at the Mayo Clinic Neurology AI Program (NAIP) demonstrate how AI can not only speed up analysis, but also alert experts reviewing the test results to abnormal patterns too subtle for humans to detect. The technology shows the potential to one day help doctors distinguish among causes of cognitive problems, such as Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementia. The research suggests that EEGs, which are more widely available, less expensive and less invasive than other tests to capture brain health, could be a more accessible tool to help doctors catch cognitive issues in patients early.
Watch: Dr. David T. Jones discusses the use of AI to analyze EEG tests
"There's a lot of medical information in these brain waves about the health of the brain in the EEG," says senior author David T. Jones, M.D., a neurologist and director of NAIP. "It's well known that you can see these waves slow down and look a bit different in people who have cognitive problems. In our study, we wanted to know if we could accurately measure and quantify that type of slowing with the aid of AI."
To develop the tool, researchers assembled data from more than 11,000 patients who received EEGs at Mayo Clinic over the course of a decade. They used machine learning and AI to simplify complex brain wave patterns into six specific features, teaching the model to automatically discard certain elements, such as data that should be ignored, in order to zero in on patterns characteristic of cognitive problems like Alzheimer's disease.
"It was remarkable the way the technology helped quickly extract EEG patterns compared to traditional measures of dementia like bedside cognitive testing, fluid biomarkers and brain imaging," says Wentao Li, M.D., a co-first author of the paper who conducted the research with NAIP while a Mayo Clinic clinical behavioral neurology fellow.
"Right now, one common way that we quantify patterns in medical data is by expert opinion. And how do we know that the patterns are present? Because that expert tells you they're present," Dr. Jones says. "But now with AI and machine learning, not only do we see things that the expert can't see, but the things they can see, we can put a precise number on."
Using EEG to spot cognitive issues would not necessarily replace other types of exams, such as MRIs or PET scans. But with the power of AI, EEG could one day provide healthcare professionals a more economical and accessible tool for early diagnosis in communities without easy access to specialty clinics or specialty equipment, such as in rural settings, according to Dr. Jones.
"It's really important to catch memory problems early, even before they're obvious," Dr. Jones says. "Having the right diagnosis early helps us give patients the right outlook and best treatment. The methods we're looking at could be a cheaper way to identify people with early memory loss or dementia compared to the current tests we have, like spinal fluid tests, brain glucose scans or memory tests."
Continuing to test and validate the tools will take several years of additional research, according to Dr. Jones. However, he says the research demonstrates that there are ways to use clinical data to incorporate new tools into clinical workflow to achieve the researchers' goal to bring new models and innovation into clinical practice, enhance the capabilities of existing assessments and scale this knowledge outside of Mayo Clinic.
"This work exemplifies multidisciplinary teamwork to advance translational technology-based healthcare research," says Yoga Varatharajah, Ph.D., co-first author of the paper who was a NAIP research collaborator when the work was completed.
Funding for the research includes support from the Edson Family Fund, the Epilepsy Foundation of America, the Benjamin A. Miller Family Fellowship in Aging and Related Diseases, the Mayo Clinic Neurology Artificial Intelligence Program and the National Science Foundation (Award No. IIS-2105233), and the National Institutes of Health, including grant UG3 NS123066.
A complete list of co-authors and financial disclosures is available in the manuscript.
###
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news.
END
AI boosts the power of EEGs, enabling neurologists to quickly, precisely pinpoint signs of dementia
2024-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI predicts male infertility risk with blood test, no semen needed
2024-07-31
According to a World Health Organization (WHO) study (2017), about half of all infertility is due to men. Semen analysis is considered essential for diagnosis of male infertility, but is not readily available at medical institutions other than those specializing in infertility treatment, and there is a high threshold for receiving it.
In this study, a group led by Associate Professor Hideyuki Kobayashi of the Department of Urology, Toho University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan developed an AI model that can predict the risk ...
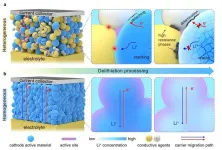
Researchers pioneer new approach to enhance all-solid-state lithium batteries
2024-07-31
Researchers at the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators from leading international institutions, have introduced an innovative cathode homogenization strategy for all-solid-state lithium batteries (ASLBs).
This new approach, detailed in their recent publication in Nature Energy on July 31, significantly improves the cycle life and energy density of ASLBs, representing an important advancement in energy storage technology.
Current ASLBs face challenges due to heterogeneous composite cathodes, which require ...
Surprising finding in glioblastomas:
2024-07-31
Glioblastomas are highly aggressive, usually incurable brain tumors. If all therapeutic options are exhausted, patients have an average life expectancy of less than two years. Now researchers from the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK) at the West German Tumor Center Essen have made a surprising discovery: in the vicinity of glioblastomas, they found islands of highly potent immune cells in the neighboring bone marrow of the skull, which play a central role in defending against cancer. The new data may open up prospects ...
Blood proteins may help to track the pathological progression of Lewy’s body disease
2024-07-31
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease-related changes in Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies could be made possible by monitoring the amyloid-β (Aβ) and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) proteins. Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan also discovered the blood levels of neurofilament light chain (NfL) protein is elevated at an early stage of Parkinson's disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). This discovery may provide a method to identify potential patients and to make early interventions. The findings were published in npj Parkinson’s Disease.
The two forms of Lewy body disease are PD and DLB. ...
Pandemic exacerbated depression in older adults with diabetes
2024-07-31
TORONTO, ON – A recent study of more than 2,700 older Canadians reported older adults with diabetes faced a heightened risk of depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this cohort, almost 50% of those who had a pre-pandemic history of depression experienced depression during the pandemic.
Those who experienced loneliness were among the most impacted.
“During the pandemic, loneliness almost tripled the risk of depression in older adults with diabetes,” says clinical pharmacist and first author ZhiDi Deng. “This not only highlights ...
AI opens door to safe, effective new antibiotics to combat resistant bacteria
2024-07-31
In a hopeful sign for demand for more safe, effective antibiotics for humans, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have leveraged artificial intelligence to develop a new drug that already is showing promise in animal trials.
Publishing their results in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the scientists describe using a large language model—an AI tool like the one that powers ChatGPT—to engineer a version of a bacteria-killing drug that was previously toxic in humans, so that it would be safe to use.
The prognosis for patients ...
Study finds many cocoa products contaminated by heavy metals
2024-07-31
For Embargoed Release: July 31, 2024 at 3:00 am ET USA
Media Contact: Katelyn Deckelbaum, katelyn.deckelbaum@gwu.edu and Kathy Fackelmann, kfackelmann@gwu.edu
Study Finds Many Cocoa Products Contaminated by Heavy Metals
Dark chocolate lovers may want to limit their consumption to an ounce a day to stay on the safe side, according to the authors
WASHINGTON (July 24, 2024) - A new study from George Washington University found a disquieting percentage of cocoa products in the U.S. contain heavy metals that exceed guidelines, including higher concentrations in organic products.
GW researchers analyzed ...
Monarch butterflies need help, and a little bit of milkweed goes a long way
2024-07-31
Monarch butterflies, with their striking orange and black wings, are some of the most recognizable butterflies in North America. But they're in trouble. Monarch caterpillars can only eat the leaves of milkweed, a native wildflower. As milkweed has disappeared, so have the monarchs, to the point that they're at risk of extinction. Research shows that planting milkweed in home gardens can add significant monarch habitat to the landscape. In a new study in the journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, ...
Newly discovered sheets of nanoscale “cubes” make excellent catalysts
2024-07-31
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created sheets of transition metal chalcogenide “cubes” connected by chlorine atoms. While sheets of atoms have been widely studied e.g. graphene, the team’s work breaks new ground by using clusters instead. The team succeeded in forming nanoribbons inside carbon nanotubes for structural characterization, while also forming microscale sheets of cubes which could be exfoliated and probed. These were shown to be an excellent catalyst for generating hydrogen.
Two-dimensional materials are a breakthrough in nanotechnology, realizing ...
Keck Hospital of USC earns five stars on CMS 2024 quality star rating report for second year in a row
2024-07-31
LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC earned five stars, the highest rating possible, on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) 2024 quality star rating report. This is the second year in a row the hospital has received five stars.
Only approximately 16% of hospitals across the country, 483 out of 3,076, received five stars out of a one-to-five-star rating system.
“Receiving this prestigious recognition for the second time in a row validates the hospital’s continuous commitment to patient safety and best patient outcomes and is a testament to the dedication and hard ...