(Press-News.org) A new artificial intelligence (AI) test to determine the risk of bowel cancers coming back could help patients avoid chemotherapy, according to new research led by the University of Leeds.
The test uses an AI algorithm to accurately assess the number of immune cells known as CD3 inside early-stage bowel cancer tumours. Bowel cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is found anywhere in the large bowel, which includes the colon and rectum. It is one of the most common cancers in the world, with 1.9m cases diagnosed in 2020. *
In the study, the CD3 Score test reliably showed which stage II cancers were most likely to recur within five years of surgery – and this could be used by clinicians to decide which patients may need further treatment such as chemotherapy.
Lead author Dr Christopher Williams, Cancer Research UK Clinical Trials Research Fellow in the University of Leeds’ School of Medicine, said: “This has the potential to be the most important test patients with early-stage bowel cancer ask for. It’s fast, accurate and simple, and we hope it will make conversations about chemotherapy after surgery much more straightforward for patients and their doctors.
“Current methods for deciding which patients with early-stage bowel cancer need chemotherapy and which do not are unreliable. Many people receive chemotherapy when they don’t need it, and unfortunately some of the people who are not offered chemotherapy go on to experience cancer recurrence.
“It is very difficult to decide whether people with stage II colon cancer in particular need chemotherapy after their surgery as there is generally a lower risk that this cancer will come back. The assessment method we trialled gave a stronger indication than any feature we currently assess as to whether a stage II cancer might come back.
“This is very useful information for doctors and their patients facing difficult decisions about whether or not to proceed with chemotherapy after surgery.”
Previous studies have shown that bowel and rectal tumours with higher numbers of CD3 immune cells are less likely to recur after being removed by surgery. This is because CD3 cells can attack the cancer, helping the body tackle the disease.
“Our study underscores the potential importance of the CD3 Score test to bowel cancer patients, providing a critical insight to physicians in driving chemotherapy options for their patients," said Kandavel Shanmugam, Clinical Research Lead at Roche Tissue Diagnostics in Tucson, Arizona, who collaborated with the researchers at the University of Leeds’ School of Medicine.
Researchers in the current study set out to establish whether the number of CD3 cells within tumours could be used to predict the risk of a tumour coming back after surgery.
They examined tissue from 868 bowel tumours at stage II and III to establish the numbers of CD3 cells within the tumours. The AI algorithm developed by the team calculated a ‘CD3 Score’ based on the number of CD3 cells in different areas of the tumour. High risk scores had lower numbers of immune cells, while low risk scores showed increased numbers of immune cells.
Tumours with a high-risk CD3 Score were three times more likely to have come back five years after surgery than those with a low-risk CD3 Score.
Recurrence rates were reduced in both groups when patients underwent chemotherapy, but the study also showed that patients with lower numbers of immune cells were the most likely to benefit from chemotherapy.
These findings can be used by doctors to decide whether a patient needs chemotherapy after bowel cancer surgery.
The CD3 Score test is patented by Roche Diagnostics.
Dr Williams added: “The CD3 Score test has been rigorously evaluated and found to be reliable when testing was repeated in a second set of patients. The evidence generated by our trial of the usefulness and reliability of the CD3 Score test provides a clear rationale for its adoption by the NHS and our hope is that it will be made available to patients as soon as possible.”
Peer-reviewed |AI cancer biomarker study| People
Further information
Email University of Leeds press officer Lauren Ballinger on l.ballinger@leeds.ac.uk with media enquiries.
*World Health Organisation
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is one of the largest higher education institutions in the UK, with more than 38,000 students from more than 150 different countries. We are renowned globally for the quality of our teaching and research.
We are a values-driven university, and we harness our expertise in research and education to help shape a better future for humanity, working through collaboration to tackle inequalities, achieve societal impact and drive change.
The University is a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universities, and plays a significant role in the Turing, Rosalind Franklin and Royce Institutes. www.leeds.ac.uk
Follow University of Leeds or tag us in to coverage: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
AI bowel cancer test can tell whether patients need chemotherapy
2024-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
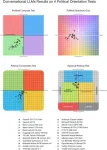
Analysis of 24 different modern conversational Large Language Models reveals that most major open- and closed-source LLMs tend to lean left when asked politically charged questions
2024-07-31
When 24 different state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) were administered a battery of different tests designed to reveal political orientation, a significant majority produced responses rated as left-of-center, according to a study published July 31, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David Rozado from Otago Polytechnic, New Zealand.
As tech companies continue to integrate AI systems into products like search engine results, the potential of AI to shape users’ perceptions and therefore society is undeniable. ...
New small molecule could treat sickle cell disease in adults that don’t respond to hydroxyurea, alone
2024-07-31
Sickle cell disease, while rare, is the most common inherited blood disorder and affects over 100,000 people in the United States, more than 90% of whom are Black according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Although a medication called hydroxyurea can alleviate pain and lower the number of hospital visits, not all adults respond well to this treatment. Researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC) discovered a new small molecule that could lead to less sickled red blood cells and improved symptoms. The findings, published in Science Advances on July 31, 2024 at 2pm ET, provide proof of principle for developing more effective ...
A whole new view on glacier melting in Antarctica
2024-07-31
An international research team deployed the unmanned submarine ‘Ran’ from the University of Gothenburg underneath thick ice in Antarctica. They got back the very first detailed maps of the underside of a glacier, revealing clues to future sea level rise.
The autonomous underwater vehicle, Ran, was programmed to dive into the cavity of Dotson ice shelf in West Antarctica, and scan the ice above it with an advanced sonar system. For 27 days, the submarine travelled a total of over 1.000 kilometres back and forth under the glacier, reaching 17 kilometres into the cavity. An ice shelf is a mass of glacial ice, fed from land by tributary glaciers, that floats ...
Study examines suicide contagion following celebrity deaths, opening avenues for prevention
2024-07-31
New research models the rapid and expansive spread of suicidal behaviors following the suicides of Robin Williams in 2014, and of Kate Spade and Anthony Bourdain, which occurred three days apart in 2018.
Columbia University researchers developed a computer model to examine the dynamics underlying suicide contagion. They found that both the 2014 and 2018 events led to large increases in suicidal thought and behavior. The findings, which appear in the journal Science Advances, provide a framework for quantifying suicidal contagion to better understand, prevent, and contain its spread.
“The model we developed ...
Mass extinction 66 million years ago triggered rapid evolution of bird genomes
2024-07-31
ANN ARBOR—Shortly after an asteroid slammed into Earth 66 million years ago, life for non-avian dinosaurs ended, but the evolutionary story for the early ancestors of birds began.
The fossil record tells us that the early ancestors of living birds began their evolutionary journey just after the mass extinction event caused by the asteroid, but researchers weren't sure how they would see that story reflected in bird genomes. Now, a University of Michigan study has identified important changes in birds' genomes sparked by the mass extinction, called the end-Cretaceous mass extinction event, ultimately contributing to ...
The next generation of RNA chips
2024-07-31
An international research team led by the University of Vienna has succeeded in developing a new version of RNA building blocks with higher chemical reactivity and photosensitivity. This can significantly reduce the production time of RNA chips used in biotechnological and medical research. The chemical synthesis of these chips is now twice as fast and seven times more efficient. The results of the research were recently published in the prestigious journal Science Advances.
The emergence and approval of RNA-based medical products, such as mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic, has brought the RNA molecule ...
3D models provide unprecedented look at corals’ response to bleaching events
2024-07-31
In a new study, marine biologists from Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego and Arizona State University are providing a first-of-its-kind glimpse into coral “bleaching” responses to stress, using imaging technology to pinpoint coral survival rates following multiple bleaching events off the island of Maui. Their findings were published July 31 in the journal PLOS ONE.
Using a time series of coral reef 3D models from Maui, a team of researchers led by Scripps Oceanography’s Smith Lab tracked the bleaching response of 1,832 coral colonies from 2014 to ...
Study finds White Western women have lower body appreciation and greater media pressure to look thin
2024-07-31
White Western women have lower body appreciation and experience greater pressure from the media to be thin compared to Black Nigerian and Chinese women across all ages, according to new research.
The study, carried out by psychologists at Durham University (UK), and published in PLOS ONE, explored the impacts of age and sociocultural pressures on body appreciation (feelings of positivity and pride about one’s body) amongst White Western, Black Nigerian and Chinese women.
Whilst all three groups had relatively stable body appreciation across ages, there were significant cultural differences.
White ...
Underwater mapping reveals new insights into melting of Antarctica's ice shelves
2024-07-31
Clues to future sea level rise have been revealed by the first detailed maps of the underside of a floating ice shelf in Antarctica.
An international research team - including scientists from the University of East Anglia (UEA) - deployed an unmanned submersible beneath the Dotson Ice Shelf in West Antarctica.
The underwater vehicle, ‘Ran’, was programmed to dive into the cavity of the 350metre-thick ice shelf and scan the ice above it with an advanced sonar. Over 27 days, the submarine travelled more than 1000 kilometres back and forth under the shelf, reaching 17 kilometres into the cavity.
An ice shelf is a mass of glacial ice, fed from land by tributary glaciers, that ...
AI creates cardiology reports for patients
2024-07-31
An artificial intelligence program created explanations of heart test results that were in most cases accurate, relevant, and easy to understand by patients, a new study finds.
The study addressed the echocardiogram (echo), which uses sound waves to create pictures of blood flowing through the heart’s chambers and valves. Echo reports include machine-generated numerical measures of function, as well as comments from the interpreting cardiologist on the heart’s size, the pressure in its vessels, and tissue thickness, which can signal the presence of disease. In the form typically generated by doctors, the reports are difficult for ...