(Press-News.org) Affective sensitivity to air pollution (ASAP) describes the extent to which affect, or mood, fluctuates in accordance with daily changes in air pollution, which can vary between individuals, according to a study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Michelle Ng from Stanford University, USA, and colleagues.
Individuals’ sensitivity to climate hazards is a central component of their vulnerability to climate change. Building on known associations between air pollution exposure and adverse mental health outcomes, Michelle Ng and colleagues introduce the ASAP construct and illustrate its measurement using intensive longitudinal data. Specifically, the authors applied statistical models to intensive repeated measures data obtained from 150 US individuals for more than a year. The researchers used the models to examine whether and how individuals’ daily affective states fluctuate with the daily concentrations of outdoor air pollution in their county. They looked at two components of individuals’ affective state: arousal, the level of physiological activation, and valence, the positivity or negativity of their mood.
The work demonstrated the viability of using air pollution data obtained from local air quality monitors alongside psychological data to assess individuals’ ASAP. The researchers found that individuals’ affect arousal was lower than usual on days with higher than usual air pollution. Most importantly, there were substantial differences in ASAP between individuals.
The finding that individuals’ day-to-day affect may be disrupted by air pollution has important implications. For example, ASAP could help partially explain one of the mechanisms by which exposure to air pollution increases longer-term risk for adverse mental health outcomes, such as symptoms of anxiety and depression. In addition, if air pollution blunts an individual’s affect, the blunting might be associated with a lack of climate action.
The authors state that ASAP can be leveraged to better integrate affect and mental health in climate adaptation planning, for example to inform climate vulnerability assessments and design personalized interventions to support affect in the context of air pollution exposure.
The authors add: “According to the World Health Organization, 90% of the world’s population breathes air that does not meet its standards for livable air quality. We propose a person-specific construct called “affective sensitivity to air pollution” based on our finding that individuals differ significantly in how their affective states fluctuate in accordance with their daily exposures to air pollution.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0307430
Citation: Ng M, Gerstorf D, Conroy DE, Pincus AL, Ram N (2024) Affective Sensitivity to Air Pollution (ASAP): Person-specific associations between daily air pollution and affective states. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0307430. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0307430
Author Countries: USA, Germany
Funding: This work was generously supported by the US National Institute on Aging (RC1-AG035645) and the US National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program (DGE-1656518).
END
Individuals vary in how air pollution impacts their mood
Statistical models show how daily air pollution is linked to a person’s affective states
2024-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
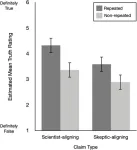
Repetition boosts belief in climate-skeptical claims, even among climate science endorsers
2024-08-07
Climate science supporters rated climate-skeptical statements as “truer” after just a single repetition, according to a study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE led by Mary Jiang from The Australian National University, Australia, and coauthored by Norbert Schwarz from the University of Southern California, USA, and colleagues. The results held true even for the strongest climate science supporters surveyed.
Amidst the influx of content that a person consumes each day, the principle of motivated ...
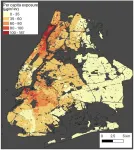
Study quantifies air pollution for NYC subway commuters
2024-08-07
New York City subway commuters who are economically disadvantaged or belong to racial minority groups have the highest exposure to fine particulate matter during their commutes, according to a new study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Shams Azad of New York University, USA.
Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is a type of air pollution that, due to its small size, when inhaled by a person can enter the bloodstream. PM2.5 is known to cause short- and long-term health complications. For the last few decades, cities have promoted public transportation to reduce traffic congestion and improve ambient outdoor air quality. Subway systems reduce pollution by decreasing ...
TikTok videos glamorizing disordered eating behavior and extremely thin body image ideals make women feel worse about their bodies
2024-08-07
Women who spend a lot of time on TikTok — especially those seeing a lot of pro-anorexia content — feel worse about their appearance, a new study shows. The results suggest that high TikTok exposure could harm mental health, reducing body image satisfaction and increasing the risk for disordered eating behavior. Madison Blackburn and Rachel Hogg from Charles Sturt University in Australia present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 7, 2024.
Since its launch, the short-form video app TikTok has had more than 2 billion downloads. The app’s algorithm curates content on a “For ...
Work-from-home success might depend on home office setup
2024-08-07
In a new survey study, Dutch employees who worked from home tended to report higher levels of productivity and less burnout if they were more satisfied with their home office setup. The study also linked more air ventilation in the home office to higher self-reported productivity. Martijn Stroom and colleagues at Maastricht University in the Netherlands report these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 7, 2024.
In recent years, thanks in large part to the COVID-19 pandemic and technological advancements, ...
Trained dogs can sniff out CWD, a disease of major concern, in the droppings of farmed and wild deer, offering potential for non-invasive surveillance
2024-08-07
Trained dogs can sniff out CWD, a disease of major concern, in the droppings of farmed and wild deer, offering potential for non-invasive surveillance
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0303225
Article Title: Biodetection of an odor signature in white-tailed deer associated with infection by chronic wasting disease prions
Author Countries: USA
Funding: TWRA AP-14839 Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service and WILDLIFE RESOURCES AGENCY, TENNESSEE https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/ourfocus/business-services/financial-management-division/financial_services_branch/agreements_service_center/terms-conditions-for-aphis-awards ...
Ice cream made from mare's milk blended with cow's cream not only tastes good, but may have beneficial probiotic qualities
2024-08-07
Ice cream made from mare's milk blended with cow's cream not only tastes good, but may have beneficial probiotic qualities
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304692
Article Title: The use of mare’s milk for yogurt ice cream and synbiotic ice cream production
Author Countries: Poland
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
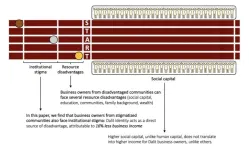
Indian business owners from the stigmatized Dalit group experience a business income gap of around 16% compared to others
2024-08-07
Indian business owners from the stigmatized Dalit group experience a business income gap of around 16% compared to others
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0307660
Article Title: It’s not who you know, but who you are: Explaining income gaps of stigmatized-caste business owners in India
Author Countries: India, UK, Australia
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
International Space Station crew carries out first-ever archeological survey in space
2024-08-07
An archaeological strategy adapted for space used daily photos to reveal how astronauts actually use areas aboard the International Space Station – and how this differs from intended uses. Justin Walsh of Chapman University, California, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 7, 2024.
More than 270 people from 23 countries have visited the International Space Station (ISS) over more than two decades. Crew member interviews can reveal how people adapt to a novel environment—one featuring isolation, confinement, and microgravity—that is far removed ...
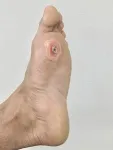
Electric bandage holds promise for treating chronic wounds
2024-08-07
Researchers have developed an inexpensive bandage that uses an electric field to promote healing in chronic wounds. In animal testing, wounds that were treated with these electric bandages healed 30% faster than wounds treated with conventional bandages.
Chronic wounds are open wounds that heal slowly, if they heal at all. For example, sores that occur in some patients with diabetes are chronic wounds. These wounds are particularly problematic because they often recur after treatment and significantly increase the risk of amputation and death.
One of the challenges associated ...
Researchers unlock life history secrets of Jurassic mammals using X-ray imaging
2024-08-07
A new study published in Science Advances reveals how early mammals grew and developed during their pivotal Jurassic radiation. Using a technique called synchrotron X-ray tomography to image growth rings in fossilised tooth roots, the researchers were able to estimate lifespans, growth rates, and even the timing of sexual maturity in these ancient creatures.
“This is the first time we've been able to reconstruct the growth patterns of these early mammals in such detail,” said Dr Elis Newham, a Postdoctoral Research Associate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Individuals vary in how air pollution impacts their moodStatistical models show how daily air pollution is linked to a person’s affective states