(Press-News.org) STARKVILLE, Miss.—NASA is awarding a Mississippi State University assistant professor a $1.13 million grant to develop a new simulation tool to aid the design of hypersonic vehicles used in space exploration.
Vilas Shinde of MSU’s Department of Aerospace Engineering won the grant to develop a new flow stability and transition analysis tool, which will aid researchers and aircraft designers in understanding and predicting changes associated with the boundary layer—air flow in the vicinity of an aircraft’s surface during flight.
“Dr. Shinde has demonstrated the relevancy of his research by securing this award,” said Rani Sullivan, professor, department head, and the Bill and Carolyn Cobb chairholder. “The accurate prediction of boundary layer transition is critical for the aerodynamic design of aircraft, especially for the aerothermodynamic design of hypersonic vehicles. We are proud that Dr. Shinde and his collaborators at NASA Langley and the University of Mississippi will have the opportunity to study and develop new technologies to address important issues for aircraft systems.”
The grant, awarded through NASA’s Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research, will fund Shinde’s research over three years. The award includes $750,000 from NASA, with MSU and the University of Mississippi funding additional $285,000 and $90,000 respectively. The core theoretical and computational development will be performed at MSU in coordination with NASA, while UM will conduct an experimental investigation.
“This is a very competitive award, so the happiest moment for me was when my abstract was selected for the full proposal development,” said Shinde. “I’m fortunate to collaborate with some of the finest scientists in the field.”
Shinde’s proposed project, Development of a Lagrangian Stability Analysis Technique (LagSAT) Framework for High-Speed Boundary Layers, uses Lagrangian modal analysis to efficiently investigate fluid flow stability and transition in complex flow configurations. Shinde said this complements existing NASA simulation capabilities and the technique has several applications, aiding NASA in future-aircraft development and space exploration.
“If we think of a spaceplane re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere, it’s essential for scientists to know how and where the air flow over the vehicle transitions to turbulence,” Shinde said. “Our goal is to develop this technique to provide new insights into the boundary layer stability and transition phenomena, an effort toward making space exploration safer.”
Through the grant, he will partner with researchers at NASA, UM and colleagues within the Computational Aerosciences and Multiphysics Laboratory (CAML) at MSU.
EPSCoR was created to establish collaboration among government, higher education, and industry partners, designed to have lasting improvements in a state or region’s research infrastructure, research and development capacity and national research and development competitiveness.
The Department of Aerospace Engineering is online at www.ae.msstate.edu and on Facebook.
The Bagley College of Engineering is online at www.bagley.msstate.edu and can be found on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube at @msuengineering.
Mississippi State University is taking care of what matters. Learn more at www.msstate.edu.
END
Assistant professor's $1.1M NASA grant to develop computational tool aiding hypersonic vehicle design
2024-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Houston Methodist study shows new, more precise way to deliver medicine to the brain
2024-08-08
Houston Methodist researchers have discovered a more accurate and timely way to deliver life-saving drug therapies to the brain, laying the groundwork for more effective treatment of brain tumors and other neurological diseases.
In a study published this month in Communications Biology, an open access journal from Nature Portfolio, investigators used an electric field to infuse medicine from a reservoir outside the brain to specific targets inside the brain. This adds a new dimension to the 30-year-old process of injecting therapeutics into the brain through ...
A ‘thank you’ goes a long way in family relationships
2024-08-08
URBANA, Ill. – You’ve probably heard that cultivating gratitude can boost your happiness. But in marriage and families, it’s not just about being more grateful for your loved ones — it’s also important to feel appreciated by them. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have previously explored the positive impact of perceived gratitude from romantic partners for couples’ relationship quality. In a new study, they show the benefits of perceived gratitude ...
How a legal loophole allows unsafe ingredients in US foods
2024-08-08
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is tasked with overseeing the safety of the U.S. food supply, setting requirements for nutrition labeling, working with companies on food recalls, and responding to outbreaks of foodborne illness. But when it comes to additives already in our food and the safety of certain ingredients, FDA has taken a hand-off approach, according to a new article in the American Journal of Public Health.
The current FDA process allows the food industry to regulate itself when it comes to thousands of added ...
USC researchers develop AI model that predicts the accuracy of protein–DNA binding
2024-08-08
A new artificial intelligence model developed by USC researchers and published in Nature Methods can predict how different proteins may bind to DNA with accuracy across different types of protein, a technological advance that promises to reduce the time required to develop new drugs and other medical treatments.
The tool, called Deep Predictor of Binding Specificity (DeepPBS), is a geometric deep learning model designed to predict protein–DNA binding specificity from protein–DNA complex structures. DeepPBS ...
Increasing solid-state electrolyte conductivity and stability using helical structure
2024-08-08
Solid-state electrolytes have been explored for decades for use in energy storage systems and in the pursuit of solid-state batteries. These materials are safer alternatives to the traditional liquid electrolyte—a solution that allows ions to move within the cell—used in batteries today. However, new concepts are needed to push the performance of current solid polymer electrolytes to be viable for next generation materials.
Materials science and engineering researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have explored the role of helical secondary structure on the conductivity of solid-state peptide polymer ...
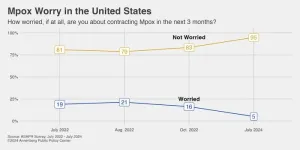
The threat of mpox has returned, but public knowledge about it has declined
2024-08-08
PHILADELPHIA – It has been two years since the World Health Organization declared a global health emergency over an outbreak of mpox, a disease endemic to Africa that had spread to scores of countries. Now, in the summer of 2024, a deadlier version of the infectious disease has spread from the Democratic Republic of Congo to other African nations, the strain that originally hit the United States has shown signs of a resurgence, and this week the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a new alert on mpox to health care providers.
But while the American public quickly learned about the disease during the summer of 2022, as ...
How does traumatic brain injury progress to Alzheimer’s disease?
2024-08-08
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A traumatic brain injury, or TBI, is caused by a contusion to the head that may result in injury to the brain. This type of injury combined with the inherited genetic risk factors can result in the accelerated development of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia, or ADRD. TBIs range from mild to severe, with the majority being mild. They are especially common in adolescents engaging in contact sports and in the elderly who tend to fall with greater frequency as they age. Regardless of the source, TBI and how it progresses to ADRD is an understudied area of research.
A $3.5 million grant to the University of California, ...
Researchers find unexpectedly large methane source in overlooked landscape
2024-08-08
When Katey Walter Anthony heard rumors of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, ballooning under the lawns of fellow Fairbanks residents, she nearly didn’t believe it.
“I ignored it for years because I thought ‘I am a limnologist, methane is in lakes,’” she said.
But when a local reporter contacted Walter Anthony, who is a research professor at the Institute of Northern Engineering at University of Alaska Fairbanks, to inspect the waterbed-like ground at a nearby golf course, she started to pay attention. Like others in Fairbanks, they lit “turf bubbles” on fire and confirmed the presence of methane ...
Royal Commission for AlUla collaborates with SETI Institute to support development of Alula Manara Observatory
2024-08-08
Royal Commission for AlUla Collaborates with SETI Institute to Support Development of AlUla Manara Observatory
Experts from SETI Institute will support the advancement of telescope technology and data analysis at AlUla Manara Observatory.
The collaboration will enhance the future observatory's capabilities as it welcomes global scientists, researchers, and tourists interested in astronomy and space science.
Ambitions to foster curiosity, knowledge sharing, and upskilling local capabilities in astronomical and space sciences field
Mountain View, CA , 8 August 2024 -- The Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU) and SETI Institute ...
Cutting a few calories won’t hurt your workout
2024-08-08
A new UC Riverside study demonstrates that calorie restriction doesn’t deter mice from exercising, challenging the belief that dieting drains workout energy.
The study, published in the journal Physiology & Behavior, shows that cutting calories by 20% did not significantly reduce the distance that mice voluntarily chose to run each day.
The researchers set out to understand what happens to mice when the amount of food available to them is reduced. The findings, they hoped, would be relevant ...