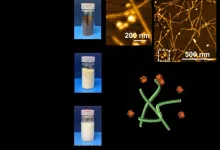
(Press-News.org) Along with all the coffee we drink every day, over 6 million tons of spent coffee grounds are produced annually worldwide. Some of these grounds are reused as biofuel but the rest are disposed of in landfills. Over the last decade, research has focused on how to reuse these grounds. The primary focus has been on the polysaccharides from the cellulose and hemicellulose in the ground up coffee bean’s cell walls. Polysaccharides are used in composites, biopolymers, food packaging, construction materials and cellulose nanofibers (CNFs). CNFs specifically, which are cellulose reduced to nanoparticle size, 3 to 5 nm, have many uses in the food, cosmetic, and coating industries.
Japanese researchers from Yokohama National University pioneered a method that used spent coffee grounds as a new waste material to isolate CNFs using TEMPO-mediated oxidation in 2020. However, that left up to ~40% of the coffee grounds’ hemicellulose unused. So, they turned their attention to holocellulose, the combination of hemicellulose and cellulose, to extract holocellulose nanofibers (HCNFs).
“Chemically unmodified and uniform quality HCNFs from agricultural/food waste are highly desirable for food additives such as emulsifiers. We hypothesized that the high hemicellulose contents in the holocellulose from spent coffee grounds and their unique structure could achieve completed nanofibrillation down to 3–5 nm wide and 1–3 μm long by mechanical disintegration,” said Izuru Kawamura, a professor at the Faculty of Engineering at Yokohama National University. In fact, they not only formed HCNF, but they also discovered a method of preservative-free long-term storage of the HCNF with added benefits for transport and handling, thereby significantly increasing its utility for the food and cosmetic industries.
Their research was published in Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications on June 25.
To form HCNF out of the spent coffee grounds, the researchers removed lignin and lipids and then reduced the rest of the holocellulose fibrils to the nanoscale via nanofibrillation, the process of disintegrating fibril bundles into nanofibrils. The researchers used a jet mill with ultrahigh water pressure to mechanically nanofibrillate the holocellulose to form the HCNF.
The least degraded hemicellulose left in the spent coffee grounds after roasting is mannan. In the grounds, mannan has been shown to form a network between cellulose fibrils. This association is strong enough that even undergoing chemical treatments may not break it and, in some circumstances, mannan may recrystallize. The presence of mannan was essential in the ease of reconstituting the HCNFs after they had been freeze-dried. Generally during dehydration, the physical properties of nanocellulose change and they lose the ability to redisperse in water. However, when freeze-dried HCNFs were placed in room temperature water, a simple shake caused them to redisperse back into the nanoscale.
“The spent coffee grounds-derived HCNFs were completely nanofibrillated to 2–3 nm wide and 0.7–1 μm long, which was finer in width and shorter in length than general CNFs or HCNFs obtained by mechanical nanofibrillation, and desirable morphologies for food additives,” said Noriko Kanai, assistant professor, Faculty of Environment and Information Sciences, Yokohama National University. Not only did they form finer and shorter HCNFs, but the discovery of the distinctive behavior of the HCNF in its freeze-dried state has many benefits. “The advantages of the once-freeze-dried HCNFs from spent coffee grounds are 1) preservative-free for long-term storage, 2) volume reduction during transportation, and 3) easy handling with only handshaking without solvent change or additional refinement process,” said Kanai.
The research teams next project will move forward with the work they have done with HCNFs. “Dried HCNFs have some advantages for commercial use, such as long-term storage without preservatives and volume reduction for transportation. As a next step, we are exploring the possibility of upcycling spent coffee grounds-derived HCNFs as cosmetic and food additives,” Kawamura said.
Other contributors include Kohei Yamada, Chika Sumida, Miyu Tanzawa, Yuto Ito, Toshiki Saito, Risa Kimura, and Toshiyuki Oyama from the Graduate School of Engineering Science, Yokohama National University; Miwako Saito-Yamazaki from GRACE Co., Ltd, Yokohama; Akira Isogai from the Department of Biomaterial Sciences, Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo.
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI and JST COI-NEXT program.
##
Yokohama National University (YNU or Yokokoku) is a Japanese national university founded in 1949. YNU provides students with a practical education utilizing the wide expertise of its faculty and facilitates engagement with the global community. YNU’s strength in the academic research of practical application sciences leads to high-impact publications and contributes to international scientific research and the global society. For more information, please see: https://www.ynu.ac.jp/english/
END
Upcycling spent coffee grounds by isolating Mannan-rich Holocellulose nanofibers
2024-08-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long-term coral reef monitoring continues to deliver crucial insights
2024-08-09
As the effects of a changing climate and other ecological insults compound, many coral reefs face severe perturbations and a generally poor prognosis for recovery. In an article published in BioScience's new "Perspective and Insight" category, Dr. Peter J. Edmunds of California State University, Northridge, argues for the continued monitoring of coral reefs, even when the seascapes they inhabit are in a significantly degraded state.
Drawing from his ongoing 37-year study in the US Virgin Islands, Edmunds argues that "only consistent, rigorous, and detail-oriented ...
AACR CEO Dr. Margaret Foti selected as the 2024 Beacon Award Winner for her significant impact in the fight against cancer
2024-08-09
Rockville, MD (8/9/2024) – The AIM-HI Accelerator Fund today announces Margaret Foti, PhD, MD (hc), Chief Executive Officer of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), is selected unanimously by the 2024 Blue Ribbon Selection Committee as the recipient of the 2024 Beacon Award for Women Leaders in Oncology, from a pool of outstanding global nominees.
The Beacon Award for Women Leaders in Oncology was established in 2022 by the AIM-HI Accelerator Fund and sponsored by the National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR). The Beacon Award recognizes outstanding women leaders in health and life sciences who have significantly impacted cancer ...
Abbruscato, Kang receive first Stocco Research Chair endowment appointments
2024-08-09
In a July 9 ceremony, Thomas Abbruscato, Ph.D., and Min Kang, Pharm.D., became the first recipients of the Douglas Stocco Research Chair, an endowment formerly known as the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center’s (TTUHSC) Research Endowment. The Texas Tech University System Board of Regents officially renamed the endowed chair in late November 2023 and made two appointments available.
Abbruscato, professor and chair in the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the TTUHSC Jerry H. Hodge School of Pharmacy, said it is an honor to receive the endowment.
“Personally, I am humbled to have ...
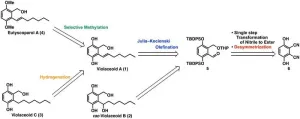
From fungi to pharmaceuticals: a milestone for the production of eutyscoparol A and violaceoid C
2024-08-09
The natural world is rich in chemical compounds with remarkable medicinal properties. A notable example is penicillin, discovered by chance from the Penicillium mold. This discovery revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections and highlighted the potential of natural compounds in medicine. Since then, the identification, isolation, and synthesis of novel bioactive compounds from plants, fungi, and bacteria have become fundamental to drug development.
Recently, two groups of naturally occurring bioactive compounds have garnered significant attention: violaceoids A–F ...
Glossy black-cockatoos prefer the fruits of ancient rocks
2024-08-09
New research from the University of Adelaide has shown that glossy black-cockatoos prefer to feed from trees growing in acidic soils.
Glossy black-cockatoos are seed-eating birds that feed almost exclusively on the cones of drooping sheoak trees. However, counterintuitively, they select trees that grow on the poorest soils found on ancient sedimentary rocks.
“Sheoak trees are three times more likely to be used as feeding trees if they are growing on non-limestone sedimentary rocks,” says Dr Gay Crowley, from the University of Adelaide’s School of Social Sciences.
Dr Crowley compared 6,543 feeding records with 23,484 ...
ADHD symptoms in autistic children linked to neighborhood conditions
2024-08-09
Autistic youth who were born in underserved neighborhoods are more likely to have greater attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms than those born in communities with more resources. This is one finding of a new study led by researchers at the UC Davis MIND Institute.
This is the first time researchers have investigated how neighborhood factors are associated with ADHD in autistic and non-autistic children. The study provides new insights into mental health conditions and has the potential to inform public policy changes to improve health equity.
It was published in the journal JCPP Advances.
“We found that some neighborhood ...
Many survey respondents rated seeking out sexually explicit ‘deepfakes’ as more acceptable than creating or sharing them
2024-08-09
Content warning: This post contains details of sharing intimate imagery without consent that may be disturbing to some readers.
While much attention on sexually explicit “deepfakes” has focused on celebrities, these non-consensual sexual images and videos generated with artificial intelligence harm people both in and out of the limelight. As text-to-image AI models grow more sophisticated and easier to use, the volume of such content is only increasing. The escalating problem led Google to announce last week that it will work to filter out these deepfakes in search results, and the Senate recently passed ...
Strike Force: Utah State leads collaborative $2.3M NSF grant to study earthquake critical zones
2024-08-09
LOGAN, UTAH, USA -- Utah State University geoscientist Alexis Ault recalls the devastating aftermath of back-to-back 7.8 and 7.6-magnitude earthquakes on Feb. 6, 2023, near the Turkey-Syria border that killed more than 50,000 people and displaced millions.
“We witnessed the destruction firsthand, as well as the resilience of the country and population trying to get their footing and rebuild,” says Ault, associate professor in USU’s Department of Geosciences, who traveled to the disaster site about six months after ...
Achieving quantum memory in the hard X-ray range
2024-08-09
Light is an excellent carrier of information used not only for classical communication technologies but also increasingly for quantum applications such as quantum networking and computing. However, processing light signals is far more complex, compared to working with common electronic signals.
An international team of researchers including Dr. Olga Kocharovskaya, a distinguished professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Texas A&M University, has demonstrated a novel way of storing and releasing X-ray pulses at the single photon level — a concept first ...
Study shows donor kidneys with toxoplasma do not increase risks for transplant patients
2024-08-09
A new study from UC Davis Health could help to increase the supply of donor kidneys.
Researchers have found that transplant patients who receive kidneys infected with the parasite toxoplasma have virtually the same outcomes as those who receive toxoplasma-negative organs.
Despite longstanding concerns, those who received kidneys from toxoplasma antibody positive donors (TPDs) had almost identical mortality and rejection rates. The research was published in Transplant International.
“Organs from donors who were positive for toxoplasma did ...