(Press-News.org) New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversity
A newly discovered species of marine crocodile from 135 million years ago described from Germany
An international team of scientists, including researchers from Germany and the UK, have described a new species of ancient marine crocodile, Enalioetes schroederi. Enalioetes lived in the shallow seas that covered much of Germany during the Cretaceous Period, approximately 135 million years ago.
This ancient crocodile was a member of the family Metriorhynchidae, a remarkable group that evolved a dolphin-like body-plan. Metriorhynchids had smooth scaleless skin, flippers, and a tailfin. They fed on a variety of prey, including fast-moving animals like squids and fish, but some metriorhynchid species had large, serrated teeth suggesting they fed on other marine reptiles. Metriorhynchids are best known from the Jurassic Period, with their fossils becoming rarer in the Cretaceous. Enalioetes schroederi is known from a three-dimensional skull, making it the best-preserved metriorhynchid known from the Cretaceous.
Sven Sachs, from the Naturkunde-Museum Bielefeld and project leader, said: “The specimen is remarkable as it is one very few metriorhynchids that is known by a three-dimensionally preserved skull. This allowed us to CT scan the specimen and so we were able to learn a lot about the internal anatomy of these marine crocodiles. The remarkable preservation allowed us to reconstruct the internal cavities and even the inner ears of the animal.”
Dr Mark Young, of the University of Edinburgh’s School of GeoSciences, explains: “Enalioetes gives us fresh insight into how metriorhynchids were evolving during the Cretaceous Period. During the Jurassic metriorhynchids evolved a body-plan radically different from other crocodiles - flippers, tailfin, loss of bony armour and smooth scaleless skin. These changes were adaptations to an increasingly marine lifestyle. Enalioetes shows us that this trend continued into the Cretaceous, as Enalioetes even larger eyes than other metriorhynchids (which were already big by crocodylian standards) and the bony inner ears were even more compact than other metriorhynchids, a sign that Enalioetes was probably a faster swimmer.”
The perfectly preserved skull along with the first neck vertebrae were discovered more than a hundred years ago by the German government architect D. Hapke in a quarry in Sachsenhagen near Hannover. The specimen has an interesting history. It was given for preparation and study to Henry Schroeder of the Prussian Geological Survey in Berlin where it was thought to have been incorporated in the collection. This led to the assumption the specimen went lost during WWII. Later the specimen was rediscovered in the Minden Museum in Western Germany. It turned out that the specimen had been returned to the finder whose family brought it to Minden where they found a new home after WW2, taking the specimen with them. The crocodile is since one of the valuable specimens in the Minden collection.
Henry Schroeder of the Berlin Geological survey provided the initial description, and after him the species is named.
By comparing the fossil with those from other museum collections, Sachs and his team determined it was a species new to science.
For further information, please contact Sven Sachs, project leader, Naturkunde-Museum Bielefeld: sachs.pal@gmail.com
END
New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversity
A newly discovered species of marine crocodile from 135 million years ago described from Germany
2024-08-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CMU researchers outline promises, challenges of understanding AI for biological discovery
2024-08-09
Machine learning is a powerful tool in computational biology, enabling the analysis of a wide range of biomedical data such as genomic sequences and biological imaging. But when researchers use machine learning in computational biology, understanding model behavior remains crucial for uncovering the underlying biological mechanisms in health and disease.
In a recent article in Nature Methods, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science propose guidelines that outline pitfalls and opportunities for using interpretable ...
Japan SciCom Forum 2024 comes to Fukuoka on October 22-23
2024-08-09
On October 22 and 23, the sixth Japan SciCom Forum Conference (JSF 2024) will be held at Kyushu University's Ito Campus. Fukuoka will become the third city, following Tokyo and Okinawa, to welcome specialists in science communication from Japan and around the world.
JSF 2024 will bring together a diverse group of science communicators, writers, researchers, and journalists, along with experts from overseas. The conference is open to anyone involved in sharing research findings internationally, as well as those interested in science communication, public outreach, and engagement.
This year's JSF will explore a wide range of topics, including ...
Organic farms certified by peers display higher product diversity
2024-08-09
In Brazil, a study compared two systems of organic product certification implemented in São Paulo state. One system involves conventional certification by auditors accredited by the Ministry of Agriculture and the National Institute of Metrology, Quality and Technology (INMETRO). The other is peer-to-peer certification.
The study, reported in an article published in the journal Organic Agriculture, suggests that peer-to-peer certification adds the virtue of agrobiodiversity to organic farming in light of the significantly larger number of products offered by farms with this type of certification. “This ...
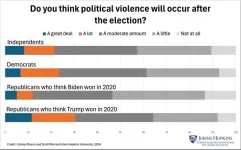
Republicans who believe Trump won in 2020 expect significant chaos in November
2024-08-09
Republicans who believe Donald Trump won the 2020 election are anticipating a much more chaotic election cycle this year than other GOP, Democratic, and independent voters, according to new polling data from the SNF Agora Institute at Johns Hopkins University.
Among Republican respondents who believe President Joe Biden did not lawfully win the 2020 election, about 31% think that either “a lot” or “a great deal” of political violence will occur after the 2024 election—compared to 24% of Democratic voters, 21% of independents and just 12% of GOP voters who acknowledge Biden’s victory four years ago, the poll found.
In ...
Memory problems in old age linked to a key enzyme, study in mice finds
2024-08-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Everyone has moments of forgetfulness from time to time, especially as we get older. But older adults don’t just have difficulty remembering new information. They also have a harder time modifying those memories when new details emerge. Yet, little is known about the mechanisms behind memory updating and how those mechanisms go awry with age.
A team of researchers from Penn State has identified an enzyme that contributes to age-related impairments in memory updating. When blocked, older mice were better able to incorporate new information and performed similarly ...
National study shows how internal medicine chief residency has changed over 20 years
2024-08-09
New research shows how the chief resident position in academic internal medicine residency programs has evolved over the past 20 years, revealing how the position has changed, the types of careers these individuals pursue, and improvement in gender representation.
These findings, published this summer by the American Journal of Medicine, stem from a 20-year multicenter study that involved the University of Colorado Internal Medicine Residency Program. CU Department of Medicine faculty member William Turbyfill, MD, was among the study’s site investigators.
Turbyfill, who practices in the Veterans Affairs ...
VA’s Disrupted Care National Project discovers vascular surgery rates still decreasing since COVID-19 pandemic
2024-08-09
White River Junction, VT – Recently published findings from the VA Disrupted Care National Project (DCNP) revealed the number of vascular surgeries performed across the United States continued to decline even after large drops during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A multi-institutional team of researchers, led by the White River Junction VA Medical Center, analyzed 21,031 vascular surgeries of three common procedures from 2019 to 2023 using Medicare claim data. There was a dramatic drop of 47% at the beginning of the pandemic, but while rates of care recovered partially another ...
Looking to boost your heart health? Try a baked potato
2024-08-09
The potato is small enough to fit inside a person’s hand yet contains enough nutrients to whittle waistlines and lower blood sugar in adults with Type 2 diabetes. Yet, despite the fact that potatoes – particularly the skins – are packed with health-boosting nutrients, they routinely get a bad rap among dieters.
That may soon change, thanks to new research by Neda Akhavan, assistant professor in the Department of Kinesiology and Nutrition Sciences within UNLV’s School of Integrated Health ...
Experts provide further proof of role testosterone plays in preventing severe Covid
2024-08-09
A new study has revealed important information about how a patient’s testosterone level can help protect them from severe Covid-19.
Previous research involving Swansea University investigated how sex hormones are likely to be important determinants of Covid-19 severity.
Now digit ratio expert Professor John Manning, of the Applied Sports, Technology, Exercise and Medicine (A-STEM) research team, has been working with colleagues in Poland and Sweden to look more closely at the subject.
He says their findings, which have just been published ...
Vegan diet better than Mediterranean diet for weight loss and reducing harmful inflammatory dietary compounds, finds new research
2024-08-09
WASHINGTON, D.C.—Eating a low-fat vegan diet reduces harmful inflammatory dietary compounds called advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) by 73%, compared to no reduction on a Mediterranean diet, according to new research by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine published in Frontiers in Nutrition. The decrease in AGEs on the vegan diet was associated with an average weight loss of 13 pounds, compared with no change on the Mediterranean diet.
The reduction of dietary AGEs on the low-fat vegan diet came mainly from excluding the consumption ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
[Press-News.org] New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversityA newly discovered species of marine crocodile from 135 million years ago described from Germany