(Press-News.org) People who have served time in jail or prison are less likely to have bank accounts after they are released than they were before serving time, which may hinder their long-term financial security, according to new research.
“Locked out of banking: The limits of financial inclusion for formerly incarcerated individuals” was authored by Brielle Bryan, an assistant professor of sociology at Rice University and J. Michael Collins, a professor of public affairs and human ecology and the Fetzer Family Chair in Consumer and Personal Finance at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. It is one of the first studies examining how incarceration status changes banking access.
“Financial inclusion has become a big concern globally when thinking about how to eradicate poverty and promote opportunity among the most marginalized members of society,” Bryan said. “With this study, we wanted to turn that lens toward formerly incarcerated Americans, who we know are among the most marginalized in America today.”
The researchers found that overall, bank account ownership decreased significantly after incarceration, and women and Hispanic individuals were more likely to lose access to banking following incarceration compared to other groups. The researchers also found that those who were able to maintain bank accounts while incarcerated were disproportionately white and had higher levels of education.
“Our study cannot say exactly why incarceration appears to reduce bank account access, but we have a few theories,” Bryan said. “We don’t think it has to do with lack of trust in banks among people with criminal justice system contact, because we don’t find that pretrial detention or arrests reduce bank account ownership.”
Instead, Bryan said it’s more likely to do with barriers to establishing an account that might seem minor to the general population, like providing an unexpired form of government identification or proof of residence in your own name.
“These sorts of small barriers can lead to big disadvantages for formerly incarcerated Americans,” Bryan said. “We know the alternatives to traditional banking can be exploitative and expensive – services like payday lending and check cashing. So regardless of why exactly it is happening, it’s a huge problem.”
The authors said the study’s confirmation of this lack of banking access following incarceration is important, as the absence of financial inclusion among people who have served time may have a significant impact on their long-term economic security.
“Access to banking is important for anyone, but especially for someone attempting to get back on their feet after incarceration,” the authors wrote. “Banking access allows individuals to more easily save and access funds that can be used to pay security deposits, rent, utilities, parole fees, and other outstanding legal financial obligations. Moreover, having a bank account enables individuals to deposit or cash paychecks with greater ease and less expense than alternative financial services. Accordingly, being unbanked is likely a contributing factor for several of the hardships that formerly incarcerated people face in terms of housing, credit and debt, and building wealth.”
Bryan and Collins hope the research may lead to interventions that ease the transition of incarcerated individuals as they work to reacclimate into society and access banking, citing promising models like Hawaii’s efforts to link individuals on work release to checking and savings accounts.
The study, published in Social Science Research, was based on data from the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth. The paper is online here.
END
Locked out of banking: Incarceration is associated with decreased bank account ownership
2024-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research spotlight: Generative AI “drift” and “nondeterminism” inconsistences are important considerations in healthcare applications
2024-08-12
Samuel (Sandy) Aronson, ALM, MA, executive director of IT and AI Solutions for Mass General Brigham Personalized Medicine and senior director of IT and AI Solutions for the Accelerator for Clinical Transformation, is the corresponding author of a paper published in NEJM AI that looked at whether generative AI could hold promise for improving scientific literature review of variants in clinical genetic testing. Their findings could have a wide impact beyond this use case.
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
We tested whether ...
Comprehensive atlas of normal breast cells offers new tool for understanding breast cancer origin
2024-08-12
INDIANAPOLIS — Researchers at the Indiana University Melvin and Bren Simon Comprehensive Cancer Center have completed the most extensive mapping of healthy breast cells to date. These findings offer an important tool for researchers at IU and beyond to understand how breast cancer develops and the differences in breast tissue among genetic ancestries.
Published this month in Nature Medicine, researchers developed a comprehensive atlas of breast tissue cells – including details ...
Huang studying electric distribution system protection – Modeling and testing with real-time digital simulator
2024-08-12
Liling Huang, Associate Professor, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Dominion Energy Faculty Fellow, received funding for: “Electric Distribution System Protection - Modeling and Testing with Real-Time Digital Simulator.”
Huang will address the complexities of the electric distribution system introduced by Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) through Real-Time Digital Simulator (RTDS) modeling and Hardware-in-the Loop (HIL) simulation to enhance protection system ...
Singh receives funding for AI innovation for economic competitiveness
2024-08-12
JP Singh, Distinguished University Professor, Schar School of Policy and Government, received funding for: “George Mason University Center for AI Innovation for Economic Competitiveness.” He is collaborating on the project with Co-Principal Investigator Amarda Shehu, Associate Vice President of Research, Institute for Digital Innovation, Professor, Computer Science, College of Engineering and Computing (CEC); Jesse Kirkpatrick, Research Associate Professor, Philosophy, College of Humanities and Social Sciences; Acting Director, Institute for Philosophy and Public Policy, Philosophy and Religious Studies; Terry Clower, Northern Virginia Chair in Local ...
Bacteria in lakes fight climate change
2024-08-12
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas frequently produced in the sea and in fresh water. Lakes in particular release large quantities of this climate-killer. Fortunately, however, there are microorganisms that counteract this: They are able to utilize methane to grow and generate energy, thus preventing it from being released into the atmosphere. These microorganisms, known as methanotrophs, are therefore regarded as an important "biological methane filter".
Methanotrophs comprise various groups of microorganisms, and many questions about their way of life have yet to be answered. A study by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for ...
How cell nuclei organize eyes and brain
2024-08-12
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — In work conducted both at UC Santa Barbara and the Physics of Life Excellence Cluster of TU Dresden, biophysicist Otger Campàs and his research group have found that cell nuclei control the architecture and mechanics of eye and brain tissues during embryonic development. These results add a new role for the cell’s nucleus in tissue organization, well beyond its established role in genetic regulation.
“We were measuring tissue stiffness in the zebrafish retina, and realized that it depended on the packing of nuclei. This was totally unexpected because tissue mechanics is believed to depend on cell surface interactions, but not ...
$1.5 million grant will build global network to prevent exploitation of Indigenous data
2024-08-12
TUCSON, Arizona — Researchers at the University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health and the U of A Native Nations Institute are establishing a framework that protects the way Indigenous data is collected and used around the world, thanks to a $1.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation.
For as long as researchers, health care providers and government agencies have studied Indigenous communities, there has been mistrust about the data collected. Indigenous peoples have raised concerns about who owns and profits from the data, as well as how it is used. Using the grant, the researchers, in ...
Engineers bring efficient optical neural networks into focus
2024-08-12
EPFL researchers have published a programmable framework that overcomes a key computational bottleneck of optics-based artificial intelligence systems. In a series of image classification experiments, they used scattered light from a low-power laser to perform accurate, scalable computations using a fraction of the energy of electronics.
As digital artificial intelligence systems grow in size and impact, so does the energy required to train and deploy them – not to mention the associated carbon emissions. Recent research suggests that if current AI server production continues at its current pace, their annual energy consumption could outstrip that of ...
"All of us urgently need to band together to pass a robust and just earth to future generations," says eminent environmental lawyer Edith Brown Weiss
2024-08-12
Amsterdam, August 12, 2024 – An article in a special issue on The Planetary Future published in Environmental Policy and Law (EPL) by IOS Press (now part of Sage), considers the Planetary Trust as an essential framework underlying today’s kaleidoscopic world, reviews important developments in implementing the Trust, and focuses on important steps to take now to ensure a just, robust Earth system for present and future generations.
Bharat H. Desai, PhD, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Centre for International Legal Studies, and Editor-in-Chief ...
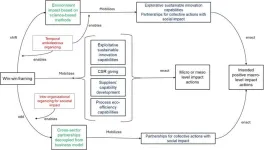
Framing sustainability strategies for the enactment of corporate actions with positive macro-level impact: Evidence from a developing country
2024-08-12
Transforming Sustainability Strategies: Ecuadorian Corporations Leading the Way
The Bigger Picture: Shifting from Micro to Macro Impacts
The research redefines sustainability by examining how strategic framing can elevate corporate actions to achieve significant macro-level impacts. Moving beyond individual and community-focused efforts, the study highlights broad-scale changes that enhance societal and environmental well-being, including nationwide poverty reduction, environmental improvements, and public health advancements.
Corporations ...