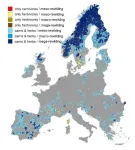
(Press-News.org) Europe's abandoned farmlands could find new life through rewilding, a movement to restore ravaged landscapes to their wilderness before human intervention. A quarter of the European continent, 117 million hectares, is primed with rewilding opportunities, researchers report August 15 in the Cell Press journal Current Biology. They provide a roadmap for countries to meet the 2030 European Biodiversity Strategy's goals to protect 30% of land, with 10% of those areas strictly under conservation.
The team found that 70% of the rewilding opportunities in Europe lie in colder climates. Northern Europe—particularly Scandinavia, Scotland, and the Baltic states—and several highland regions in the Iberian Peninsula show the greatest potential.
"There are many areas in Europe that have a low enough human footprint, as well as the presence of key animal species, to potentially be rewilded," says first author and biogeographer Miguel B. Araújo (@Araujo_lab) of the National Museum of Natural Sciences, CSIC, Spain, and the University of Évora, Portugal. "We also highlight the need for different strategies depending on the conditions of each region."
The researchers established criteria to determine areas with rewilding potentials: extensive tracts of land, covering more than 10,000 hectares, with little human disturbance that feature vital species. Based on the size of the land and the types of animals that inhabit the area, they further identified two strategies for rewilding—passive and active.
Passive rewilding relies on natural recolonization, where animals gradually move back into abandoned areas on their own. The approach works best in regions with a healthy population of key herbivores, such as deer, ibex, moose, and rabbits, as well as carnivores, such as wolves, bears, and lynxes. Regions without key herbivore or carnivore species would require active rewilding by reintroducing the missing species to kickstart the ecosystem's recovery. Both strategies aim to create a self-sustaining, biodiverse landscape.
"I often refer to herbivores as the ecosystem engineers as they graze and shape the vegetation, while predators would be the architects creating 'fear landscapes' that herbivores avoid," says Araújo. "The interaction between herbivores and carnivores creates mosaic patterns in the landscapes, essential for biodiversity."
Some countries, including the United Kingdom, France, Spain, and Scandinavian nations, are positioned to reach their conservation goals if they adopt the study's suggested rewilding zones and strategies. However, given that Europe is densely populated with humans, other countries wouldn't meet their conservation aims if they relied solely on the study's recommendations, highlighting the need for alternative conservation approaches. These countries include Ireland, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Denmark.
"Conservation strategies involving ecological restoration of densely populated areas could help some countries reach conservation goals," says Araújo. "Countries could reclaim land to turn it into conservation areas or establish networks of small, protected habitats. Traditional multi-use landscapes, like the oak parklands in the Iberian Peninsula and various extensive agricultural and forestry systems across Europe, could also help if managed sustainably."
As governments and organizations continue to invest in land conservation, the researchers hope their findings and framework will help these efforts to acquire or manage areas with the greatest potential for successful rewilding. However, despite the prospects, the researchers caution that time is of the essence.
"We're racing against time," says Araújo. "The areas that look most promising for rewilding today may not be the same in 50 years due to the impacts of climate change."
###
This work was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, and the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Programme.
Current Biology, Araújo and Alagador: “Expanding European protected areas through rewilding.” https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)00948-5
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
A study of over 15,000 youth with self-inflicted injury treated in Emergency Departments (EDs) found that around 25 percent were seen in the ED within 90 days before or 90 days after injury, pointing to an opportunity for ED-based interventions, such as suicide risk screening, safety planning, and linkage to services. Nearly half of ED visits after the self-inflicted injury encounter were for mental health issues.
“Self-inflicted injury is an important predictor of suicide risk,” said Samaa Kemal, MD, MPH, emergency medicine physician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie ...
About The Study: Uterus transplant was technically feasible and was associated with a high live birth rate following successful graft survival. Adverse events were common, with medical and surgical risks affecting recipients as well as donors. Congenital abnormalities and developmental delays have not occurred to date in the live-born children.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Liza Johannesson, MD, PhD, email Liza.Johannesson@bswhealth.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.11679)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: Consistent with prior research on adverse childhood experience (ACE; defined as abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction before age 18) exposure and presence of a firearm in the household during childhood, this study found that cumulative ACE exposure was associated with higher odds of household firearm ownership in adulthood. The relationship may be due to a heightened sense of vulnerability to physical violence and greater perceived threats to personal safety associated with a traumatic childhood, which lead individuals to seek self-protection.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alexander Testa, PhD, email alexander.testa@uth.tmc.edu.
To ...
American women have the highest rate of maternal deaths among high-income countries, with outcomes worse for minoritized groups. In an effort to understand the maternal health of pregnant people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, including autism and intellectual disability, researchers from Drexel University’s Policy and Analytics Center in the A.J. Drexel Autism Institute examined Medicaid data to identify perinatal and postpartum outcomes among people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. The study was recently published in JAMA Network Open.
“While ...
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL AUG. 15, 2024 @ 11 A.M. EDT) – For years, mouthwash has been marketed as an essential hygiene item to prevent bad breath, even though it offers minimal if any health benefits.
But what if a mouthwash-based test to detect biomarkers can help physicians predict disease recurrence in head and neck cancer patients?
That futuristic scenario seems closer to reality after a new study by researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, UC San Diego Health and collaborating cancer centers.
Their findings, ...
The Department of Health Behavior & Health Education at the University of Michigan School of Public Health will become the Department of Health Behavior & Health Equity, effective August 15, 2024. The new name reflects the department’s increasing focus on issues of health equity in research, teaching and service.
“Health equity is at the core of our mission and actions in public health,” said F. DuBois Bowman, dean of Michigan Public Health. “I am grateful to the many members of the Health Behavior & Health Equity community ...
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new two-photon fluorescence microscope that captures high-speed images of neural activity at cellular resolution. By imaging much faster and with less harm to brain tissue than traditional two-photon microscopy, the new approach could provide a clearer view of how neurons communicate in real time, leading to new insights into brain function and neurological diseases.
“Our new microscope is ideally suited for studying the dynamics of neural networks in real time, which is crucial for understanding fundamental brain functions such as learning, memory and decision-making,” said research team leader ...
(WASHINGTON, August 15, 2024) – Over half of people with iron deficiency were found to still have low iron levels three years after diagnosis, and among patients whose condition was effectively treated within that timeframe, they faced longer-than-expected delays, pointing to substantial gaps in appropriate recognition and efficient treatment of the condition, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
Iron deficiency, or when the body’s iron stores are too low, is common, and may affect up to 40% of adolescents and young women. Iron is important in maintaining many body functions, including the production of ...
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has launched a program that will support Native American communities to lead public health research to address overdose, substance use, and pain, including related factors such as mental health and wellness. Despite the inherent strengths in Tribal communities, and driven in part by social determinants of health, Native American communities face unique health disparities related to the opioid crisis. For instance, in recent years, overdose death rates have been highest among American Indian and Alaska Native people. Research prioritized by Native communities is essential ...
Weill Cornell Medicine has received a five-year, $12.4 million grant from the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, for an extensive program of basic and translational research on the biology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common form of lymphoma.
The investigator-initiated Program Project grant, led by Dr. Leandro Cerchietti, the Richard A. Stratton Associate Professor in Hematology and Oncology at Weill Cornell Medicine, and Dr. Christopher Flowers, professor and chair of the Department of Lymphoma and Myeloma at The University ...