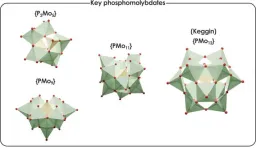
New computational methodology to predict the complex formation of interesting nanostructures
POMSimulator: new enhancements elevate this open-source tool's data utilization
2024-08-20
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from the group of Prof. Carles Bo, at the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ-CERCA), have described a computational methodology that simulates complex processes involving different chemical species and diverse conditions. These processes lead to the formation of nanostructures called polyoxometalates (POMs), with important applications in catalysis, energy storage, biology and medicine.
"Our group has recently developed unique methods to study the chemistry of polyoxometalates in solution, their speciation and formation mechanisms. This research has the potential to discover the experimental conditions needed to make new materials." as explains Prof. Carles Bo.
The versatile POMs
POMs are a distinguished family of nanostructures composed of transition metal atoms linked by oxygens, forming a wide range of well-defined structures of different sizes and shapes. These nanostructures are formed via self-assembly processes of simple metal oxides, depending on different factors such as pH, temperature, pressure, total metal concentration, ionic force, and the presence of reducing agents and counter-ions. The sum of all these conditions complicates the control of their synthesis.
Researchers can now predict the effect of these factors and the suitable conditions to produce one specific species of POM, employing statistical methods that facilitate the efficient and scalable processing of numerous speciation models and their corresponding systems of non-linear equations. This is important as the first key application of these nanostructures is related to catalysis, where POMs are known to accelerate several important reactions. For example, using these simulations it is possible to describe the suitable conditions that lead the production of a species of POM responsible to catalyse CO2 fixation.
POMSimulator
The group of Prof. Bo has presented an open–source software package named POMSimulator that helps in understanding the formation mechanisms of POMs. By releasing a public version of the code, the researchers aim to provide a tool for complementing the discovery of novel POMs. Moreover, having an accessible version of the code means that other researchers can modify the source code based on their needs.
The methodology now presented is a more robust version of this POMSimulator that provides new and valuable insights into the distribution of species under different chemical conditions, thereby enriching the knowledge of complex systems speciation.
"In the times of Big Data, Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, it is crucial to use every bit of information in our hands. Our work has taken POMSimulator to the next level of data usage." said by Jordi Buils, first author of this work and PhD student at Prof. Carles Bo group.
This new approach has been published in Chemical Science, the Royal Society of Chemistry’s peer-reviewed flagship journal, and it has been selected as a Chem Sci Pick of the Week, a way to highlighting the cutting-edge work published in the journal.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-20
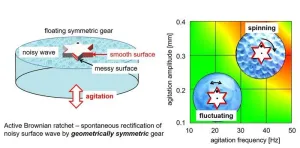
The ratchet mechanism is a fascinating energy-conversion system that converts disorderly or random motion into orderly, directed movement through a process known as spontaneous rectification. It is a critical component of mechanical systems, typically consisting of a gear and a pawl, which restricts the movement of the gear in one direction. In biological systems, the concept of a Brownian ratchet has been proposed to help understand the mechanism of molecular motors, where chemical reactions rectify the random thermal motion of molecules.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, uniform thermal ...
2024-08-20
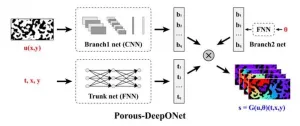
Porous media play a critical role in various industrial fields due to their complex pore networks and considerable specific surface areas. The transport and reaction phenomena within porous media are key factors influencing fundamental parameters such as energy storage efficiency, catalytic performance, and adsorption rates. To accurately describe these complex transport and reaction processes, solving parameterized partial differential equations (PDEs) is necessary. However, due to the complex structure of porous media, traditional methods, such as the finite element method ...
2024-08-20
ROCKVILLE, Md. – August 19, 2024 – The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global molecular diagnostic professional society, and world-renowned pathologist Michael Laposata, MD, PhD, today announced the filing of a lawsuit challenging the recent U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Rule that regulates laboratory developed test (LDT) procedures as medical devices under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The lawsuit was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas against the FDA; Robert M. Califf, MD, in his official capacity as Commissioner of Food and Drugs; the U.S. Department of Health ...
2024-08-20
Nylon, Teflon, Kevlar. These are just a few familiar polymers — large-molecule chemical compounds — that have changed the world. From Teflon-coated frying pans to 3D printing, polymers are vital to creating the systems that make the world function better.
Finding the next groundbreaking polymer is always a challenge, but now Georgia Tech researchers are using artificial intelligence (AI) to shape and transform the future of the field. Rampi Ramprasad’s group develops and adapts ...
2024-08-20
LA JOLLA (August 14, 2024)—Professor Rusty Gage has been awarded the 2024 J. Allyn Taylor International Prize in Medicine by the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry and the Robarts Research Institute at Western University. One of the most prestigious medical research awards in Canada, the Taylor Prize recognizes scientists for transformative, career-defining work in basic sciences, translational research, and medical innovations.
This year’s prize specifically honors a research leader in aging-related medical science and research—a long-term focus of Gage and his lab. Gage will receive $50,000 and be celebrated at a Robarts Research ...
2024-08-20
We know that quality sleep is as essential to survival as food and water. Yet, despite spending a third of our lives in slumber, it largely remains a scientific mystery.
Not that experts haven’t tried.
Sleep analysis, also known as polysomnography, is used to diagnose sleep disorders by recording multiple types of data, including brain (electroencephalogram or EEG) and heart (electrocardiogram or ECG). Typically, patients are hooked up to dozens of sensors and wires in a clinic, tracking brain, ...
2024-08-20
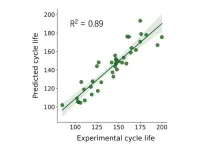
1. NIMS and SoftBank Corp. have jointly developed a model capable of predicting the cycle lives of high-energy-density lithium-metal batteries by applying machine learning methods to battery performance data. The model proved able to accurately estimate batteries’ longevity by analyzing their charge, discharge and voltage relaxation process data without relying on any assumption about specific battery degradation mechanisms. The technique is expected to be useful in improving the safety and reliability of devices powered by lithium-metal batteries.
2. Lithium-metal ...
2024-08-19
Natasha Sheybani, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Virginia School of Engineering, will collaborate with researchers at Children’s National Hospital to study the combination of two therapies for pediatric brain cancer.
High-risk brain tumors in children often don’t respond well to existing chemotherapy and radiation treatments, but Sheybani and her collaborators hope their fusion of therapies will offer a better option.
Over the two-year project, researchers ...
2024-08-19
URBANA, Ill. – As the world faces the challenges of mitigating climate change and providing resources for a growing population, there is increasing focus on developing circular economies for sustainable production. But to evaluate strategies and impacts, it is necessary to have reliable metrics. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a Circularity Index that provides a comprehensive method to quantify circularity in bioeconomic systems. In a new paper, they outline the method and apply it to two case studies – a corn/soybean farming operation and the entire U.S. food and agriculture system.
“The ...
2024-08-19
Not all forest fires have devastating effects. Low- and moderate-severity forest wildfires can reduce the intensity of future conflagrations for as long as 20 years in certain climates, according to new research by the University of California, Davis.
The extent of reduced severity of these second fires, or reburns, and the duration of the moderating effect, varies by climate, forest type and other factors. But initial fires continue to mitigate future severity even during extreme weather, such as wind, high temperatures and drought, research published in the journal Ecological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New computational methodology to predict the complex formation of interesting nanostructures
POMSimulator: new enhancements elevate this open-source tool's data utilization