(Press-News.org) An ongoing survey captures how the Russian invasion of Ukraine affected attitudes in European countries not directly involved in the conflict. Margaryta Klymak and Tim Vlandas examine how the Russian invasion of Ukraine affected economic and political attitudes in eight European countries. The authors took advantage of the timing of the European Social Survey (ESS), which happened to be administered both just before and just after the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 in eight countries: Switzerland, Greece, Italy, Montenegro, Macedonia, Netherlands, Norway, and Portugal. Overall, the invasion increased support for democracy, income redistribution, and the European Union, whereas the invasion reduced authoritarian and anti-immigration attitudes. Some attitudes shifted immediately after the invasion, while others took about a month to change. The authors suggest that the sudden sense of external threat as well as the economic and migration consequences of the war drove these short and medium-term shifts. According to the authors, the study adds to the understanding of how conflicts shape attitudes by capturing attitudinal shifts in non-belligerent countries. In this case, the war led survey respondents to rally around a common European identity and democratic values.
END
The invasion of Ukraine and European attitudes
2024-08-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
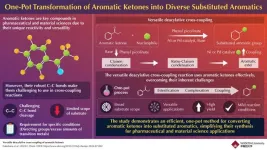
A new reaction to enhance aromatic ketone use in chemical synthesis
2024-08-20
Aromatic ketones have long been valuable intermediates in chemical synthesis, particularly in cross-coupling reactions where different chemical entities are combined to form new compounds. For instance, a process called deacylative cross-coupling removes the acyl group from the aromatic ketone, allowing it to bond with other chemicals and produce a wide variety of useful compounds. These reactions are crucial for producing a wide array of aromatic compounds used in various industries like agrochemicals.
However, the utility of aromatic ketones has been limited due to the difficulty in breaking their strong carbon-carbon bonds. These robust bonds are challenging to cleave, ...
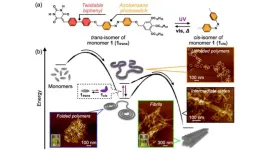
Investigating the interplay of folding and aggregation in supramolecular polymer systems
2024-08-20
In polymers, the competition between the folding and aggregation of chains, both at an individual level and between chains, can determine the mechanical, thermal, and conductive properties of such materials. Understanding the interplay of folding and aggregation presents a significant opportunity for the development and discovery of polymeric materials with tailored properties and functionalities.
This also holds true for non-covalent counterparts of conventional covalent polymers, i.e., supramolecular polymers (SPs). SPs are expected to have practical applications as novel stimuli-responsive ...
Adaptive 3D printing system to pick and place bugs and other organisms
2024-08-20
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (08/20/2024) — A first-of-its-kind adaptive 3D printing system developed by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers can identify the positions of randomly distributed organisms and safely move them to specific locations for assembly. This autonomous technology will save researchers time and money in bioimaging, cybernetics, cryopreservation, and devices that integrate living organisms.
The research is published in Advanced Science, a peer-reviewed scientific journal. The researchers ...
Fossil hotspots in Africa obscure a more complete picture of human evolution
2024-08-20
WASHINGTON (August 20, 2024) – Much of the early human fossil record originates from just a few places in Africa, where favorable geological conditions have preserved a trove of fossils used by scientists to reconstruct the story of human evolution. One of these fossil hotspots is the eastern branch of the East African Rift System, home to important fossil sites such as Oldupai Gorge in Tanzania. Yet, the eastern branch of the rift system only accounts for 1% of the surface area of Africa—a fact that makes it possible to estimate how much information scientists who rely on such small samples are missing.
In ...
Extraterrestrial chemistry with earthbound possibilities
2024-08-20
DENVER, Aug. 20, 2024 — Who are we? Why are we here? As the Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young song suggests, we are stardust, the result of chemistry occurring throughout vast clouds of interstellar gas and dust. To better understand how that chemistry could create prebiotic molecules — the seeds of life on Earth and possibly elsewhere — researchers investigated the role of low-energy electrons created as cosmic radiation traverses through ice particles. Their findings may also inform medical and environmental applications on our home planet.
Undergraduate student Kennedy Barnes will present the team’s results at the fall meeting of the American ...
Deadly sea snail toxin could be key to making better medicines
2024-08-20
Scientists are finding clues for how to treat diabetes and hormone disorders in an unexpected place: a toxin from one of the most venomous animals on the planet.
A multinational research team led by University of Utah scientists has identified a component within the venom of a deadly marine cone snail, the geography cone, that mimics a human hormone called somatostatin, which regulates the levels of blood sugar and various hormones in the body. The hormone-like toxin’s specific, long-lasting effects, which help the snail hunt its prey, could also help scientists design better ...
Planets contain more water than thought
2024-08-20
We know that the Earth has an iron core surrounded by a mantle of silicate bedrock and water (oceans) on its surface. Science has used this simple planet model until today for investigating exoplanets – planets that orbit another star outside our solar system. “It is only in recent years that we have begun to realise that planets are more complex than we had thought,” says Caroline Dorn, Professor for Exoplanets at ETH Zurich.
Most of the exoplanets known today are located close to ...
Blood platelet score detects previously unmeasured risk of heart attack and stroke
2024-08-20
Platelets are circulating cell fragments known to clump up and form blood clots that stop bleeding in injured vessels. Cardiologists have long known that platelets can become “hyperreactive” to cause abnormal clotting that blocks arteries and contributes to heart attack, stroke, and poor blood flow (peripheral artery disease) in the legs of millions of Americans.
Despite this major contribution to cardiovascular risk, routine measurement of whether each patient’s platelets clump (aggregate) too much has been infeasible to date. ...
New international Pioneer Centre for medical data research
2024-08-20
Can research on diseases as diverse as, for example, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, psychiatric disorders and endometriosis be linked? The answer is yes if the research focuses on collecting and analysing large amounts of data from both Danish and international registers and biobanks to learn more about, among other things, risk factors, relationships, patterns, treatment and consequences.
And this is exactly what a new international Pioneer Centre, The Pioneer Centre for SMARTbiomed (Statistical and Computational Methods for Advanced Research ...
NIH awards $6.9 million to advance potential Alzheimer’s disease treatment
2024-08-20
A multidisciplinary team of scientists led by Carlo Ballatore, Ph.D., at University of California San Diego and Kurt Brunden, Ph.D., at the University of Pennsylvania has been awarded a $6.9 million grant from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) to prepare a potential disease-modifying Alzheimer’s treatment for future clinical trials. In a recently published study about the new compound, called CNDR-51997, the team found it was effective in restoring brain health in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. CNDR-51997 was identified through a joint drug discovery program at Penn and UC San Diego that was supported by grants from the NIA.
The ...