(Press-News.org) Flexibility exercises are often included in the exercise regimens of athletes and exercisers. New research in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports suggests that levels of flexibility may affect survival in middle-aged individuals.
After analyzing data on 3,139 people (66% men) aged 46–65 years, investigators obtained a body flexibility score, termed Flexindex. This score was derived from a combination of the passive range of motion in 20 movements (each scored 0–4) involving 7 different joints, resulting in a score range of 0–80.
Flexindex was 35% higher in women compared with men. During an average follow-up of 12.9 years, 302 individuals (9.6%) comprising 224 men and 78 women died. Flexindex exhibited an inverse relationship with mortality risk and was nearly 10% higher for survivors compared with non-survivors in both men and women.
After taking age, body mass index, and health status into account, men and women with a low Flexindex had a 1.87- and 4.78-times higher risk of dying, respectively, than those with a high Flexindex.
“Being aerobically fit and strong and having good balance have been previously associated with low mortality. We were able to show that reduced body flexibility is also related to poor survival in middle-aged men and women,” said corresponding author Claudio Gil S. Araújo, MD, PhD, of the Exercise Medicine Clinic – CLINIMEX, in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
He added that as flexibility tends to decrease with aging, it may be worth paying more attention to flexibility exercises and routinely including assessments of body flexibility as part of all health-related physical fitness evaluations.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/sms.14708
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports is a multidisciplinary journal published 12 times per year. It aims to publish high quality and impactful articles in the fields of orthopaedics, rehabilitation and sports medicine, exercise physiology and biochemistry, biomechanics and motor control, health and disease relating to sport, exercise and physical activity, as well as on the social and behavioural aspects of sport and exercise.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Can flexibility help people live longer?
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does cognitive behavioral therapy benefit cancer survivors?
2024-08-21
A recent analysis of all relevant published studies reveals clear benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for improving mental health and quality of life in cancer survivors. The findings, which are published in Cancer Medicine, extend CBT’s effects beyond what has long been known in the general population.
For the analysis, investigators uncovered 132 clinical trials comparing CBT with controls, including standard therapy, waitlist control, or active/alternative therapy.
Across the trials, CBT moderately ...
What’s the best method for extracting edible protein from insects?
2024-08-21
Edible insects are emerging as an alternative protein source that has various benefits compared with conventional animal sources. New research published in the Journal of Food Science compared four different methods for extracting protein from mealworms, which were designated by the European Union as the first insect to be used as a novel food source in 2015.
For the research, investigators compared alkali, salt, enzyme, and screw press methods for extracting mealworm protein. Alkali extraction enhanced protein content, enzyme treatment improved nutritional value and antioxidant capacity, and salt-assisted extraction exhibited anti-inflammatory effects. Enzyme and salt treatments ...
Study confirms the utility of screening to identify autism in toddlers born preterm
2024-08-21
New research published in Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology reveals that children born preterm are more likely to screen positive for autism than full-term children.
For the study, 9,725 toddlers were screened at 15-, 18-, or 24-month well child visits using a test called the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised.
Screening results that were positive for autism were most common among children born extremely preterm (51.35%) and least common among those born full-term (6.95%). Subsequent ...
Obese children are more likely to develop skin conditions related to the immune system
2024-08-21
Philadelphia, August 21, 2024 – Childhood obesity can contribute to the development of common immune-mediated skin diseases (IMSDs), such as alopecia areata, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis, new research finds. Maintaining a healthy weight could potentially help lower the chances of developing these skin conditions. A novel study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier, details the findings of an analysis of 2,161,900 Korean children from 2009 to 2020 to investigate the relationship between obesity or dynamic changes in body weight and the development of IMSDs.
IMSDs have detrimental effects on quality of life, including emotional, physical, social, ...
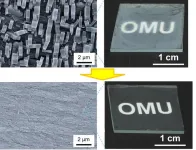
Quality control: neatly arranging crystal growth to make fine thin films
2024-08-21
Table salt and refined sugar look white to our eyes, but that is only because their individual colorless crystals scatter visible light. This feature of crystals is not always desirable when it comes to materials for optical and electrical devices, however.
Metal-organic frameworks are one such material. Crystalline with micropores, thin films of these nanomaterials have been attracting attention as a next-generation material that could also have an impact on environmental issues such as hydrogen storage and carbon dioxide capture. An Osaka Metropolitan University, Graduate School of Engineering team has found a way to control ...
How does organic farming benefit honeybees?
2024-08-21
Organic farming and flower strips promote the health of honey bees. In their vicinity, colonies grow stronger and are generally healthier. This is most likely because the insects have a diverse and continuous food supply there and are less exposed to pesticides. These are the findings of a new study by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Göttingen, published in the Journal of Applied Ecology. The team analysed data from 32 bee colonies at 16 locations in Germany with different proportions of organic fields, flower strips and semi-natural habitats.
According ...
Survey: Most Americans comfortable with AI in healthcare
2024-08-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Artificial intelligence (AI) is all around us – from smart home devices to entertainment and social media algorithms. But is AI okay in healthcare? A new national survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center finds most Americans believe it is, with a few reservations.
The national poll of 1,006 people found:
75% believe using AI to minimize human errors is important.
71% would like AI to reduce wait times.
70% are comfortable with AI taking notes during an appointment.
66% believe ...
Students' toxin research shows public health benefits of citizen science
2024-08-21
Long-term exposure to arsenic, a hidden danger in many New England drinking water supplies, poses serious health risks, including cancer and cognitive challenges. A groundbreaking citizen science initiative called "All About Arsenic" has emerged in response, empowering students and communities to tackle such health threats head-on.
The benefits are detailed in a peer-reviewed article published today in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives. An accompanying commentary by researchers at Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public ...
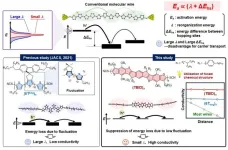
Molecular wires with a twist
2024-08-21
Osaka, Japan – From the high-voltage wires that carry electricity over long distances, to the tungsten filaments in our incandescent lights, we may have become accustomed to thinking that electrical conductors are always made of metal. But for decades, scientists have been working on advanced materials based on carbon-based oligomer chains that can also conduct electricity. These include the organic light-emitting devices found in some modern smartphones and computers.
In quantum mechanics, electrons are not just point particles with definite ...
The power of play: Strengthening senior wellbeing through generational bonds
2024-08-21
Watching your children frolic through a playground is one of the many joys of being a parent or grandparent, but new research has found that engaging in play with kids could help improve mental health.
Researchers from the University of South Australia (UniSA) and the University of Canberra (UC) have explored the benefits of intergenerational play through specially designed playgrounds for kids and adults.
Intergenerational play brings young children and older people together to engage in enjoyable and creative activities such as storytelling, using playground equipment, and games.
The world is facing an ...