Single 5-nm quantum dot detection via microtoroid resonator photothermal microscopy
2024-08-23
(Press-News.org)
The detection of individual particles and molecules has opened new horizons in analytical chemistry, cellular imaging, nanomaterials, and biomedical diagnostics. Traditional single-molecule detection methods rely heavily on fluorescence techniques, which require labeling of the target molecules. In contrast, photothermal microscopy has emerged as a promising label-free, non-invasive imaging technique. This method measures localized variations in the refractive index of a sample's surroundings, resulting from light absorption by sample components, which induces temperature changes in the surrounding region. Whispering gallery mode (WGM) resonators are ultra-sensitive temperature sensors due to their ultra-high quality (Q) factors.
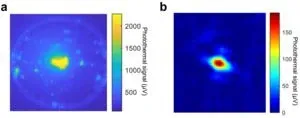
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a research group led by Prof. Judith Su from the Wyant College of Optical Sciences and the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Arizona demonstrated label-free ultra-sensitive photothermal microscopy using microtoroid WGM optical resonators. This technique enables the detection of single nanoparticles as small as 5 nm quantum dots with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) exceeding 10,000. This method significantly enhances photothermal sensitivity, achieving a detection limit of 0.75 pW in heat dissipation. This advancement allows for the accurate detection of single molecules, showcasing the capabilities of photothermal microscopy.
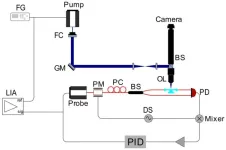
Su’s group previously developed a system called Frequency Locked Optical Whispering Evanescent Resonator (FLOWER), which uses frequency locking to track the resonance shift of optical microcavities. This photothermal microscopy system employs FLOWER to measure the photothermal signal. The resonance shift, excited by a free-space pump laser, is measured by the system. The pump laser, with a 203.7 Hz amplitude modulation (AM), illuminates the microtoroid through a galvo mirror scan system. The resulting 203.7 Hz oscillation of the resonance shift is detected by FLOWER. A lock-in amplifier is used to measure the amplitude of the resonance shift oscillation. A 2D spatial scan of the pump laser generates a photothermal image of the microtoroid, with high photothermal spots used to detect single nanoparticles.
The researchers envision the potential of photothermal microscopy:
“Moreover, future advancements may involve spectroscopy measurements by varying the pump laser's wavelength or exciting with different wavelengths to enable multicolor imaging. In future work, although not necessary for many applications, we can also combine this system with specific capture agents such as aptamers or sorbent polymers to provide enhanced specificity. The integration of photothermal microscopy with FLOWER opens possibilities for real-time observation of dynamic changes and interactions of target molecules. We believe that overall, FLOWER based photothermal microscopy represents a versatile platform for label-free imaging and single-molecule detection. The demonstrated high sensitivity and discrimination capabilities pave the way for advancements in nanoscale imaging and characterization techniques.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-23
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that is similar to both Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease but studies on long-term treatments are lacking. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, highlights the potential cognitive benefits of cholinesterase inhibitor treatment.
Lewy body disease, which includes dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, following Alzheimer’s disease. DLB accounts for approximately ...
2024-08-23
NEW YORK, August 23, 2024 — In a groundbreaking advancement, researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have experimentally demonstrated that metasurfaces (two-dimensional materials structured at the nanoscale) can precisely control the optical properties of thermal radiation generated within the metasurface itself. This pioneering work, published in Nature Nanotechnology, paves the way for creating custom light sources with unprecedented capabilities, ...
2024-08-23
University of Leeds News
Embargoed until 23 August 10:00 BST
A selection of AQ Stripes graphic images are available here
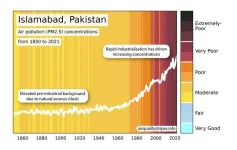
The global concentrations of one of the main air pollutants known to affect human health have been graphically illustrated for the first time by a team of scientists.
The Air Quality Stripes which were created by the University of Leeds, the University of Edinburgh, North Carolina State University, and the UK Met Office, starkly contrast the significant improvements in air quality across much of Europe with the alarming deterioration in parts ...
2024-08-23
Still unknown what causes neurological complications of COVID-19 including ‘long COVID,’ ‘brain fog’ and loss of taste and smell
Viruses with a deletion in the spike protein are better able to infect the brains of mice
‘These findings suggest there might be treatments that could work better to clear the virus from the brain’
CHICAGO --- Scientists have discovered a mutation in SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, that plays a key role in its ability to infect the central nervous system. The findings may help scientists understand its neurological symptoms and the mystery of “long COVID,” and ...
2024-08-23
A variety of vegetarian diets appear to protect against risk of mortality and contributing conditions, with a pesco-vegetarian diet — which includes fish — providing the most protection against risk in very elderly people, according to a new study.
Researchers at Loma Linda University Health found that vegetarian diets are associated with lower risk for all-cause mortality and many cause-specific mortalities, especially among males and in middle-aged subjects. However, slightly higher risks were observed among very elderly vegetarians for neurological conditions such as stroke, dementia, and Parkinson’s Disease. Despite this, ...
2024-08-23
Cervical cancer, the fourth most common cancer type in women, causes approximately 350,000 deaths each year, mainly in middle- and low-income countries. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is known to cause 95% of these cases. Public health authorities in 37 countries currently vaccinate girls between nine and 14 years of age, before they typically start sexual activity.
HPV is also known to increase the risk of genital warts and cancers of the penis, anus, mouth, and throat in infected men, which is one of the reasons why the WHO and the US Center for Disease Control (CDC) ...
2024-08-23
Human wellbeing is connected to nature for food, climate regulation and culture, making the protection of nature a human rights matter.
Added to that, recent developments in international human rights law highlight that governments need to consider human-nature connections when making decisions that may affect the environment.
In a commentary published in npj Ocean Sustainability, an interdisciplinary group of researchers – including experts in ecosystem services, environmental governance, deep-sea ecology, and law – underscore that these developments should prompt a rethink of how any environmental decisions that hold the potential to impact biodiversity ...
2024-08-23
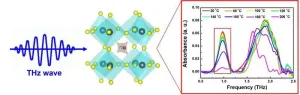
Hybrid perovskites have great potential for use in advanced electronic devices like solar cells and LEDs. However, one major issue holding them back is that they don't last as long as needed for widespread commercial use. As these materials age, their performance drops, which is a big problem for both researchers and companies. To tackle this issue, it's important not only to improve the stability of these perovskites but also to develop methods for detecting how they age in real-time. By understanding how these materials degrade over time, we can make them more durable and efficient.
In a recent study, researchers led by Prof. Yiwen Sun at Shenzhen University used the terahertz ...
2024-08-23
Primate ornamentation plays a crucial role in communication not only within social groups but also between them, according to a new study. The research reveals that the males of species with overlapping home ranges often display vibrant colors or elaborate features, traits that may help reduce intergroup aggression by enabling quick assessments of potential rivals.
Ornaments are sexually selected traits that serve as powerful signals, often indicating an individual’s genetic quality, health or physical strength. These differences ...
2024-08-23
AUGUST 2024 TIP SHEET: A mouthwash-like rinse to predict head and neck cancer recurrence, new research identifies biomarkers to predict which colon cancer patients benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy, the Dolphins Cancer Challenge and StacheStrong team up to boost brain cancer research, the CDC issues anal cancer screening guidelines for HIV patients based partly on research at Sylvester, and three Sylvester physicians who become the latest early-career faculty scholars are highlighted in this month’s tip sheet from Sylvester Comprehensive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Single 5-nm quantum dot detection via microtoroid resonator photothermal microscopy