(Press-News.org) An archaeogenetic study sheds new light on the isolated medieval community Las Gobas in northern Spain. Besides isolation and endogamy, the researchers have also identified the variola virus which can offer a new explanation on how smallpox entered Iberia.
Researchers from Sweden and Spain have conducted a comprehensive archaeogenetic study on a community that lived on the border between the northern Christian kingdoms and Al-Andalus during the early Medieval period. This dynamic era, especially in the Iberian Peninsula, was marked by religious competition, power struggles, and significant human mobility—factors that shaped the foundation of modern Europe.
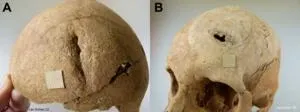
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, focused on Las Gobas, a rural site in northern Spain's Burgos province, near the village of Laño. The community existed from the mid-6th to the 11th century and is notable for its church and living areas carved into caves. The site also provides evidence of violence, likely from sword blows, found on some of the buried individuals. Forty-one burials were excavated, and 39 of them were subjected to archaeogenetic analysis.
The interdisciplinary research, led by Ricardo Rodríguez Varela from the Centre for Palaeogenetics (CPG)* in Stockholm integrated genetic, archaeological, and historical data to reveal the presence of an endogamous community in northern Iberia that remained relatively isolated despite centuries of turbulent regional history.
"Our findings indicate that this community stayed relatively isolated for at least five centuries," said Rodríguez Varela. Although Las Gobas is located just north of regions under Islamic rule, "we found relatively low levels of North African and Middle Eastern ancestry compared to other medieval individuals from the Iberian Peninsula, and we did not observe a significant increase in these ancestries after the Islamic conquest of Iberia," he concluded.
Zoé Pochon, also from CPG, highlighted the discovery of several understudied pathogens in Las Gobas human remains. "For example, Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, a bacterium that causes skin disease through contamination of open wounds, often infects humans via domestic animals, suggesting that animal-keeping was important for this community."
She also identified the variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox, in an individual from one of the more recent burials. This specific strain is similar to those found in Scandinavia, Germany, and Russia, underscoring the pan-European presence of smallpox during the Middle Ages.
Anders Götherström, the senior author of the study and also based at CPG, emphasized the exhaustive nature of their research: "It is amazing how much information we were able to gather on this group of people through our archaeogenetic investigation." He further explained, "An endogamous group, familiar with violence, appears to have established itself in Las Gobas during the 6th or 7th century. By the 10th century, smallpox seems to have affected Las Gobas, likely spreading through Europe rather than via Islamic routes, as was previously theorized for how smallpox entered Iberia."
This study provides new insights into the complex social, genetic, and health dynamics of a long-isolated community in early Medieval Spain.
Contact Information:
Ricardo Rodríguez Varela: ricardo.rodriguez.varela@arklab.su.se, +46737147174 (Please keep the phone number private—only for the journalists' use.)
Zoé Pochon: zoe.pochon@arklab.su.se, +41793329529 (Please keep the phone number private—only for the journalists' use.)
Anders Götherström: anders.gotherstrom@geoeo24.polar.se (Can be hard to reach because of field studies at Greenland.)
Publication Details: The study is published in Science Advances, DOI: 10.1126/scieadv.adp8625.
* The Centre for Palaeogenetics (CPG) is a joint venture between Stockholm University and the Swedish Museum of Natural History. The overall objective of the centre is to bring researchers from different disciplines, such as biology, archaeology and geology, together into a state-of-the-art research environment dedicated to ancient DNA analyses. https://palaeogenetics.com/
END
Study reveals isolation, endogamy and pathogens in early medieval Spanish community
2024-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chromosome copying errors pinpointed in embryo development
2024-08-28
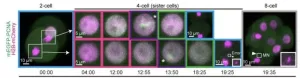
A new discovery by researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics (BDR) in Japan upends decades of assumptions regarding DNA replication. Led by Ichiro Hiratani and colleagues, the experiments published August 28 in Nature show that DNA replication in early embryos is different from what past research has taught, and includes a period of instability that is prone to chromosomal copying errors. As failed pregnancies and developmental disorders are often related to chromosomal abnormalities the findings could impact the field of reproductive medicine, perhaps leading to improved methods of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
During embryogenesis, ...
A cellular community in the brain drives Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-28
NEW YORK, NY (Aug. 28, 2024)--An analysis of more than 1.6 million brain cells from older adults has captured the cellular changes that occur in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, potentially revealing new routes for preventing the most common cause of dementia in older individuals.
The study also identified a second community of cells that drives the older brain down a different path that does not lead to Alzheimer’s disease.
“Our study highlights that Alzheimer’s is a disease of many cells and their interactions, not just a single type of dysfunctional ...
Plant signaling pathways decoded
2024-08-28
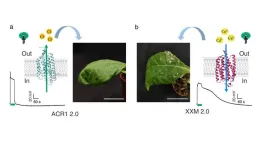
When it comes to survival, plants have a huge disadvantage compared to many other living organisms: they cannot simply change their location if predators or pathogens attack them or the environmental conditions change to their disadvantage.
For this reason, plants have developed different strategies with which they react to such attacks. Such reactions are usually triggered by certain signals from the environment. As has long been known, the intracellular calcium concentration plays an important role in the processing of these signals.
However, in addition to changes in the cytoplasmic calcium level, changes in the cell's ...
Fighting fungal foes: Walnut's genetic armor against anthracnose revealed
2024-08-28
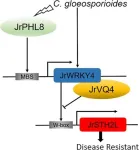
A pivotal study has pinpointed a gene module crucial for enhancing walnut trees' resistance to anthracnose, a widespread fungal disease threatening the walnut industry. The research reveals how the JrPHL8-JrWRKY4-JrSTH2L module regulates disease defense, opening up new opportunities for breeding resistant walnut varieties and promoting sustainable cultivation practices.
Anthracnose, caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, poses a significant threat to walnut production, causing severe losses ...
Rice engineers develop AI system for real-time sensing of flooded roads
2024-08-28
Roadway-related incidents are a leading cause of flood fatalities nationwide, but limited flood-reporting tools make it difficult to evaluate road conditions in real time.
Existing tools — traffic cameras, water-level sensors and even social media data — can provide observations of flooding, but they are often not primarily designed for sensing flood conditions on roads and do not work in conjunction. A network of sensors could improve situational flood level awareness; however, they are expensive to operate at scale.
Engineers at Rice University have developed a possible solution to this problem: an automated data ...
Dr. David A. Schwartz receives 39th annual Alton Ochsner Award
2024-08-28
NEW ORLEANS – Ochsner Health has announced David A. Schwartz, MD, as the 2024 winner of the Alton Ochsner Award Relating Smoking and Disease. Dr. Schwartz is a Distinguished Professor of Medicine and Immunology and director of the Program to Advance Physician Scientists and Translational Research at University of Colorado’s Anschutz School of Medicine.
Dr. Schwartz won the 39th annual Alton Ochsner Award for his research on how genetic and environmental factors, including smoking, contribute to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). He found that ...
New data: Solar at K-12 schools quadrupled nationwide during the last ten years
2024-08-28
Charlottesville, VA — Schools across the country are rapidly switching to solar power to meet their energy needs while gaining significant cost-savings, boosting climate resilience, and supporting workforce development, according to a new report from clean energy nonprofit Generation180. Since the start of 2014, the amount of solar capacity installed at K-12 schools has more than quadrupled nationwide.
According to Brighter Future: A Study of Solar on K-12 Schools, 5th edition, over 6.2 million U.S. K-12 students– or more than one in nine students – now attend a school that utilizes solar power. In 2022-2023, over 800 schools added solar arrays, which is enough ...
Thermochromic material could make indoor temperature control more energy-efficient
2024-08-28
HOUSTON – (Aug. 28, 2024) – Rice University researchers have developed a smart material that adjusts its transparency with changes in temperature, outperforming similar materials in terms of durability, transparency and responsiveness. The new polymer blend could significantly enhance energy efficiency for indoor space cooling, according to a new study published in Joule.
Cooling off can be a matter of life or death, but air conditioning ⎯ when and if available ⎯ already accounts for 7% of the world’s energy use and 3% of carbon emissions. With temperatures hitting record ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $4.8 million to exceptional early-career scientists
2024-08-28
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named 16 new Damon Runyon Fellows, exceptional postdoctoral scientists conducting basic and translational cancer research in the laboratories of leading senior investigators. This prestigious Fellowship encourages the nation's most promising young scientists to pursue careers in cancer research by providing them with independent funding ($300,000 total) to investigate cancer causes, mechanisms, therapies, and prevention.
“What is so exciting—and so challenging—about being a postdoc is that you’re called to take what you know and apply ...
Primary care providers urged to assist patients who engage in emotional eating
2024-08-28
August 28, 2024 — Primary care providers are well positioned to address emotional eating because of their long-term relationships with patients, noted Jana DeSimone Wozniak, PhD and Hsiang Huang, MD, MPH, of Harvard Medical School and Cambridge Health Alliance in Cambridge, Massachusetts. According to their article published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer, emotional eating is associated with myriad health problems, including the experience of ...