Protein mutant stability can be inferred from AI-predicted structures
AlphaFold2 predicts structural effects of mutations that are correlated with changes in stability
2024-08-29
(Press-News.org)
Researchers at the Center for Algorithmic and Robotized Synthesis within the Institute for Basic Science have taken a significant step forward in understanding the stability of proteins by leveraging the power of AI. The research team used AlphaFold2 to explore how mutations affect protein stability—a crucial factor in ensuring proteins function correctly and do not cause diseases like Alzheimer's.
DeepMind’s AlphaFold algorithm, which can accurately predict a protein’s structure from its gene, has been a game-changer across the field of biology, making structural biology accessible to everyone. Despite this immense success, two fundamental questions remain unanswered: Will the predicted structures fold correctly and stay folded? And a general question about AI algorithms: how does AlphaFold actually work?
A critical limitation of AlphaFold is that it was trained on a set of stable proteins that stay folded at physiological temperatures. As a result, it predicts the most likely folded structure without knowing if it will certainly fold or will be unstable. Knowing and predicting protein stability is crucial because unstable proteins can misfold, leading to dysfunction and potentially serious diseases, so the cells must spend much energy to get rid of them. Furthermore, most proteins are only marginally stable, making them highly susceptible to mutations that can cause them to unfold. Thus, protein engineering is much about careful navigation in a minefield of dysfunctional protein sequences that do not fold. All this implies that the next step in using AlphaFold should be to try to predict those changes in stability due to mutations.
A fundamental question tested in this study was whether AlphaFold has learned the underlying physics of protein folding or is simply a high-dimensional regression machine that merely recognizes statistical patterns. This question is about the capacity to generalize: if AlphaFold has somehow learned the physical forces in action, it ought to work on protein sequences it has not seen before.
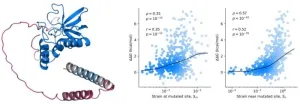
That’s exactly what the two IBS researchers, John MCBRIDE and Tsvi TLUSTY, wanted to test in their study. Their way to tackle this question was to examine if AlphaFold can correctly predict the effects of mutations on stability. There are infinitely more mutations than data points used in the training of AlphaFold, meaning that even very sophisticated regression will not suffice to account for the full range of mutation effects. This task is highly challenging since critical changes in stability often involve small structural changes that are hard to predict. Still, it turns out that there are some useful clues within the structural changes predicted by AlphaFold that provide valuable information on possible stability changes.
IBS researchers showed this by comparing structural changes inflicted by mutations to differences in experimentally measured stability between the wild-type and mutated protein [1]. A critical ingredient was using a probe that is very sensitive to small changes. The researchers devised an innovative metric, known as the effective strain, [2] to detect small but important changes in protein structure that are linked to stability.
Looking at thousands of mutations, they found that the effective strain measure correlates with the magnitude of the change in stability. That is to say, large structural changes (predicted by AlphaFold) also predict large changes in stability.
Lead author John MCBRIDE stated, “This is a strong indication that the structures predicted by AlphaFold encode significant physical information, particularly about stability. It is necessary to develop new physical models to decode this information further.”
These insights open up new possibilities for protein engineering, a field that involves designing proteins with specific functions. By better understanding how mutations affect stability, scientists can navigate the complex landscape of protein design more effectively, potentially leading to advances in drug development and treatments for diseases caused by protein misfolding.
This research marks an important milestone in the ongoing exploration of how AI can be used to unravel the complexities of biology and underscores the need for further studies to fully unlock the potential of AI in scientific discovery.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-29
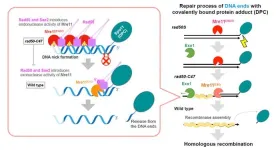
DNA damage is a cellular phenomenon that introduces structural abnormalities in double-stranded DNA. External factors, such as radiation or chemical agents, as well as internal factors, such as blocked DNA replication, can generate double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. To counteract DNA damage, cells engage in DNA repair to preserve genetic integrity and ensure cell survival as failure to repair DSBs has serious health complications like increased risk of cancer.
DSBs are repaired by two mechanisms called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR). NHEJ is the predominant DNA repair mechanism in human somatic cells and is ...
2024-08-29
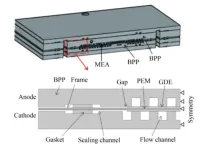
Fuel cells offer a promising solution for clean energy with advantages over traditional electric power systems, including extended driving range and higher energy density. Despite these benefits, the high costs and durability concerns associated with fuel cell stacks have limited their commercialization. The durability of membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs), a key component of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), is particularly affected by the frame sealing structure, which is often overlooked in research.
The study, conducted by Tiankuo Chu ...
2024-08-29
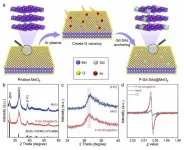
An international group of researchers has developed a novel approach that enhances the efficiency of the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), a key process in renewable energy technologies. By introducing rare earth single atoms into manganese oxide (MnO2), the group successfully modulated oxygen electronic states, leading to unprecedented improvements in OER performance.
Their findings were published in the journal Nano Energy on June 10, 2024.
Transition-metal-based oxides have been widely explored for their potential as active OER catalysts. However, the capacity of these catalysts is hindered by the adsorbate evolution mechanism, which ...
2024-08-29
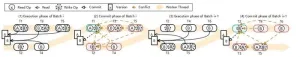
The concurrency control in deterministic databases, i.e., deterministic concurrency control, ensures that each transaction batch produces a unique result. In this way, replicas can process transactions in batches without communicating with each other to ensure consistency, which is simpler and more efficient than non-deterministic databases in achieving high availability through replication.
Early deterministic concurrency control protocols, e.g. Calvin, Bohm, PWV, rely on the prior knowledge of the read-write set, which is impractical in most scenarios. The state-of-the-art Ari breaks this limitation. However, Aria has three issues. First, ...
2024-08-29
The National Science Foundation has announced a $22 million grant to establish a “BioFoundry” laboratory for the study of extreme microorganisms with collaborating facilities at UC Riverside, UC Santa Barbara, and Cal Poly Pomona.
The BioFoundry for Extreme and Exceptional Fungi, Archaea, and Bacteria, or ExFAB, will focus on developing techniques to learn from nature’s more unusual microorganisms. These microbes are considered “extreme” because they have unusual nutritional requirements, grow at extremely high or low temperatures, or grow without ...
2024-08-29
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — This week, the National Science Foundation announced the award of a six-year, $22M grant to UC Santa Barbara under its biofoundries program for the establishment of the BioFoundry for Extreme and Exceptional Fungi, Archaea and Bacteria (ExFAB), a collaboration led by UC Santa Barbara (UCSB), together with UC Riverside (UCR), and Cal Poly Pomona (CPP). ExFAB establishes the nation’s first biofoundry that focuses on largely untapped and unexplored extreme microbes. UCSB's award is one of only five grants made under NSF's BioFoundry program during this funding cycle, which awarded ...
2024-08-29
Misconceptions about dyslexia are held by professionals who assess children for the learning difficulty, according to a new study which calls for evidence-based standardised assessment procedures.
The research, led by Durham University, found that almost half of dyslexia professionals in the study believed at least one unproven indicator for dyslexia, which could lead to children being misdiagnosed.
In a survey of 275 dyslexia professionals, the most common myth – which is not backed up by solid evidence – was that people with dyslexia read letters in reverse order, believed by 61 per cent of specialists.
Just over 30 per cent of professionals also ...
2024-08-29
A recently developed block copolymer could help push the limits of integration and miniaturization in semiconductor manufacturing, report scientists in Tokyo Tech and TOK. Chemically tailored for reliable directed self-assembly, the proposed compound can arrange itself into perpendicular lamellar structures whose half-pitch width is less than 10 nanometers, outperforming conventional and widely used block copolymers.
Miniaturization is one of the fundamental qualities of modern electronics and is largely responsible for the incredible increments in performance witnessed ...
2024-08-29
Researchers at Macquarie University have developed a new way to produce ultraviolet (UV) light sensors, which could lead to more efficient and flexible wearable devices.
The study, published in the journal Small in July, shows how acetic acid vapour – essentially vinegar fumes – can rapidly improve the performance of zinc oxide nanoparticle-based sensors without using high-temperatures for processing.
Co-author Professor Shujuan Huang, from the School of Engineering at Macquarie University, says: “We found by briefly exposing the sensor to vinegar vapour, adjoining ...
2024-08-29
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors used to treat type 2 diabetes might prevent dementia, providing greater benefits with longer treatment, suggests a large study from Korea published by The BMJ today.
As this study was observational, the researchers note that the effect size could have been overestimated and say randomised controlled trials are now needed to confirm these findings.
According to the World Health Organization, the number of people with dementia globally is expected to reach 78 million ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Protein mutant stability can be inferred from AI-predicted structures
AlphaFold2 predicts structural effects of mutations that are correlated with changes in stability