(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – The invention of a tool capable of unlocking previously impossible organic chemical reactions has opened new pathways in the pharmaceutical industry to create effective drugs more quickly.
Traditionally, most drugs are assembled using molecular fragments called alkyl building blocks, organic compounds that have a wide variety of applications. However, because of how difficult it can be to combine different types of these compounds into something new, this method of creation is limited, especially for complex medicines.
To help solve this issue, a team of chemists report the discovery of a particular type of stable nickel complex, a chemical compound that contains a nickel atom.
Since this compound can be made directly from classic chemical building blocks and is easily isolated, scientists can blend them with other building blocks in a manner that promises access to a new chemical space, said Christo Sevov, the principal investigator of the study and an associate professor in chemistry and biochemistry at The Ohio State University.
“There are really no reactions that can very reliably and selectively construct the bonds that we are now constructing with these alkyl fragments,” Sevov said. “By attaching the nickel complexes to them as temporary caps, we found that we can then stitch on all sorts of other alkyl fragments to now make new alkyl-alkyl bonds.”
The study was published in Nature.
On average, it can take a decade of research and development before a drug can successfully be brought to market. During this time, scientists also create thousands of failed drug candidates, further complicating an already extremely expensive and time-intensive process.
Despite how elusive nickel alkyl complexes have been for chemists, by relying on a unique merger of organic synthesis, inorganic chemistry and battery science, Sevov’s team found a way to unlock their astonishing capabilities. “Using our tool, you can get much more selective molecules for targets that might have fewer side effects for the end user,” said Sevov.
According to the study, while typical methods to construct a new molecule from a single chemical reaction can take much time and effort, their tool could easily allow researchers to make upwards of 96 new drug derivatives in the time it would normally take to make just one.
Essentially, this ability will reduce the time to market for life-saving medicines, increase drug efficacy while lowering the risk of side effects, and reduce research costs so chemists can work to target severe diseases that impact smaller groups, the researchers say. Such advances also pave the way for scientists to study the bonds that make up the fundamentals of basic chemistry and discover more about why these challenging bonds work, said Sevov.
The team is also already collaborating with scientists at numerous pharmaceutical companies who hope to use their tool to see how it impacts their workflow. “They’re interested in making thousands of derivatives to fine-tune a molecule’s structure and performance, so we teamed up with the pharmaceutical companies to really explore the power of it,” Sevov said.
Ultimately, the team hopes to keep building on their tool by eventually turning their chemical reaction into a catalytic process, a method that would allow scientists to speed up other chemical reactions by providing an energy-saving way to do so.
“We’re working on making it so much more efficient,” Sevov said.
Other co-authors include Samir Al Zubaydi, Shivam Waske, Hunter Starbuck, Mayukh Majumder and Curtis E. Moore from Ohio State, as well as Volkan Akyildiz from Ataturk University and Dipannita Kalyani from Merck & Co., Inc. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Camille and Henry Dreyfus Teacher Scholar Award.
#
Contact: Christo Sevov, Sevov.1@osu.edu
Written by: Tatyana Woodall, Woodall.52@osu.ed
END
Novel chemical tool aims to streamline drug-making process
Results seen as possible breakthrough in organic chemistry
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New discoveries about how mosquitoes mate may help the fight against malaria
2024-08-30
Link to Google Drive folder containing images with caption and credit information:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1UM9rl47Xd_Bs-ov0HpVwC-rtUDonM3oJ?usp=sharing
Post-embargo link to release:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2024/08/30/mosquito-swarm/
Embargoed by Current Biology
For public release at 11 a.m. U.S. Eastern Time (8 a.m. U.S. Pacific Time) on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024
A high-pitched buzzing sound in your ear is an unmistakable sign that a female mosquito is out on the hunt — for they, not males, drink blood. Hearing ...
It’s worth challenging that troubling medical bill, study finds
2024-08-30
Many people who receive a problematic medical bill don’t challenge it – but new USC Schaeffer Center research shows they are likely missing out on a chance for financial relief.
About 1 in 5 people said they recently received a medical bill they disagreed with or couldn’t afford, including 61.5% who said they contacted a billing office to address their concern, according to survey results published Aug. 30 in JAMA Health Forum. Most who reached out said they received some form of payment help or had their bill corrected.
It’s ...
New study finds Medicare Advantage (MA) enrollees experience similar declines in frailty over one year compared with Traditional Medicare (TM) enrollees
2024-08-30
Enrollment in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans is not associated with altered frailty trajectories compared with enrollment in Traditional Medicare (TM), according to research published today in JAMA Network Open.
In the article Frailty in Medicare Advantage Beneficiaries and Traditional Medicare Beneficiaries, lead author Sandra M. Shi, MD, MPH and colleagues suggest that more work is needed to better understand the health services needs of older adults with frailty.
“A growing proportion of the population is enrolling in Medicare Advantage (MA), which typically ...
Autoimmune sequelae after Delta or Omicron variant SARS-CoV-2 infection in a highly vaccinated cohort
2024-08-30
About The Study: This cohort study observed no significantly elevated long-term risk of autoimmune sequelae after SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron BA.1 or BA.2 variant infection, except for a modestly increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease and bullous skin disorders in the hospitalized subgroup during the predominance of the Omicron variant. Booster vaccination appeared to mitigate the risk of long-term autoimmune sequelae.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Liang ...
Racial disparities in cancer stage at diagnosis and survival for adolescents and young adults
2024-08-30
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that racial disparities in cancer stage at diagnosis and survival exist among adolescent and young adult patients when disaggregated according to federal guidelines, which has health policy and funding implications. These results support the need for tailored interventions and informed public policy to achieve cancer care equity for all races.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kekoa Taparra, MD, PhD, email ktaparra@stanford.edu.
To ...
Structural equality and support index in early childhood education
2024-08-30
About The Study: This cohort study found that early childhood programming is associated with social determinants of health in adulthood. These findings reinforce the importance of early childhood education in addressing health disparities and contributing to healthier, more equitable communities and suggest that educational attainment is a key mechanism for health promotion.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Arthur J. Reynolds, PhD, email ajr@umn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.32050)
Editor’s ...
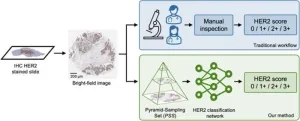
Automated HER2 scoring in breast cancer images using deep learning and pyramid sampling
2024-08-30
HER2 is a critical protein that plays a pivotal role in breast cancer cell growth and aggressiveness. Its expression level is a key indicator for treatment decisions, including the use of HER2-targeted therapies. Currently, HER2 status assessment relies heavily on immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of tissue slides followed by manual inspection by pathologists. This process, though widely adopted, suffers from several limitations, including poor reproducibility among pathologists and extended turnaround times. These challenges are further exacerbated in resource-constrained ...
Functional information offers individualized adaptive cancer therapies
2024-08-30
BUFFALO, NY- August 30, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Volume 11 of Oncoscience on July 19, 2024, entitled, “Functional information offers individualized adaptive cancer therapies.”
As introduced in this editorial, the Oxford Computer Science Dictionary offers both general and technical definitions of information. Generally, information is anything that can cause a change in a human mind's opinion about the current state of the real world. Technically, information is anything that reduces the uncertainty of a system's state. Claude Shannon provided an objective measure of information, known as entropy (H), by mathematically defining ...
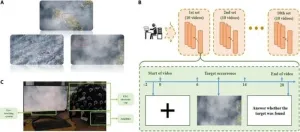
Low-quality video target detection based on EEG signal using eye movement alignment
2024-08-30
In a research paper, scientists from the Beijing Institute of Technology proposed an event related potential (ERP) extraction method to solve the asynchronous problem of low-quality video target detection, designed the time-frequency features based on continuous wavelet transform, and established an EEG decoding model based on neural characterization. The average decoding accuracy of 84.56% is achieved in pseudo-online test.
The new research paper, published July 4 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, introduces a low-quality ...
Data science coalition invites teachers and parents to have a say in the future of data science learning
2024-08-30
CHICAGO — Data science and data literacy are rapidly becoming essential skills for success across industry sectors and career fields. Now, Data Science 4 Everyone (DS4E) is inviting everyone — teachers, higher education faculty, parents, and students — to help shape what learning in this crucial area will look like.
It’s an area essential to success in today’s world and tomorrow’s. Nurses use data science skills when they read a patient’s chart; engineers analyze data to design hardware and products; and business owners use data to guide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Novel chemical tool aims to streamline drug-making processResults seen as possible breakthrough in organic chemistry