(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $125 million in funding for two Energy Innovation Hub teams to provide the scientific foundation needed to seed and accelerate next generation technologies beyond today’s generation of lithium (Li)-ion batteries. These multi-institution research teams, led by Argonne National Laboratory and Stanford University, will develop scientific concepts and understanding to impact decarbonization of transportation and incorporation of clean energy into the electricity grid.
Rechargeable batteries, such as Li-ion and lead-acid batteries, have had a tremendous impact on the nation’s economy. Emerging applications will require even greater energy storage capabilities, safer operation, lower costs, and diversity of materials to manufacture batteries. Meeting these challenges requires a better understanding of foundational battery and materials sciences to enable scalable battery designs with versatile and reversible energy storage capabilities beyond what is currently possible. Additional benefits may include mitigation of supply chain risks associated with the current generation of batteries.
"Providing the scientific foundation to accelerate this important research is key to our economy and making sure the U.S. plays a lead role in transforming the way we store and use electricity,” said Harriet Kung, DOE’s Acting Director for the Office of Science. “Today's awards provide our Energy Innovation Hub teams with the tools and resources to solve some of the most challenging science problems that are limiting our ability to decarbonize transportation and incorporate clean energy into the electricity grid."
The two Energy Innovation Hub teams are the Energy Storage Research Alliance (ESRA) led by Argonne National Laboratory and the Aqueous Battery Consortium (ABC) led by Stanford University. ESRA will provide the scientific underpinning to develop new compact batteries for heavy-duty transportation and energy storage solutions for the grid with a focus on achieving unprecedented molecular-level control of chemical reactivity, ion selectivity, and directional transport in complex electrochemical cells. ABC will focus on establishing the scientific foundation for large-scale development and deployment of aqueous batteries for long-duration grid storage technologies. Both of these teams will prioritize study and use of Earth-abundant materials to mitigate supply chain risks.
Both Energy Innovation Hubs teams are comprised of multiple institutions, including Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs) and other Minority Serving Institutions (MSIs). The projects provide an outstanding opportunity for workforce development in energy storage research and inclusive research involving diverse individuals from diverse institutions.
The teams were selected by competitive peer review under the DOE Funding Opportunity Announcement for the Energy Innovation Hub Program: Research to Enable Next-Generation Batteries and Energy Storage. While focused on basic science, the Funding Opportunity Announcement was developed in coordination through the DOE Joint Strategy Team for Batteries.
Total funding is $125 million for awards lasting up to five years in duration. More information can be found on the Basic Energy Sciences program homepage and Energy Innovation Hubs page.
Selection for award negotiations is not a commitment by DOE to issue an award or provide funding. Before funding is issued, DOE and the applicants will undergo a negotiation process, and DOE may cancel negotiations and rescind the selection for any reason during that time.
END
Department of Energy awards $125 Million for research to enable next-generation batteries and energy storage
Energy Innovation Hub teams will emphasize multi-disciplinary fundamental research to address long-standing and emerging challenges for rechargeable batteries
2024-09-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New provincial funding to help drive connected and autonomous vehicle research at uOttawa
2024-09-03
The University of Ottawa has been awarded a $1 million grant from the Ontario Research Fund – Research Excellence (ORF-RE) to support the “Secure, Intelligent and Trustworthy Ecosystems for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles” (SITE-CAV) project.
Led by Burak Kantarci,Full Professor, School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, uOttawa’s Faculty of Engineering, the project aims to accelerate the development and integration of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs – or vehicles equipped with sensors and decision-making software that drives and controls it without direct ...
Department of Energy selects Argonne to lead national energy storage hub
2024-09-03
Today the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the creation of two new Energy Innovation Hubs. One of the national hubs, the Energy Storage Research Alliance (ESRA), is led by DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory and co-led by DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL).
ESRA (pronounced ez-ruh) brings together nearly 50 world-class researchers from three national laboratories and 12 universities to provide the scientific ...
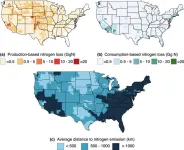
People eating beef are less likely to live near the industry’s pollution, Pitt researchers found
2024-09-03
Anyone who’s researched ways to lower their environmental impact has likely heard they should eat less meat, particularly beef. Even at scale, cows are an inefficient way to feed people — it takes nearly four tons of water to recoup one ton of beef, and many farming practices emit greenhouse gasses and pollutants.
University of Pittsburgh researchers are the first to trace one of those pollutants, nitrogen, along the U.S. beef supply chain at the county level. They found high spatial disconnect between where ...
Can technology turn exercise pain into pleasure?
2024-09-03
Virtual reality (VR) video games that combine screen time with exercise are a great way to get fit, but game designers face a major challenge – like with regular exercise, adherence to ‘exergames’ is low, with most users dropping out once they start to feel uncomfortable or bored.
Computer scientists at the University of Bath believe they’ve found a solution: create exergames that use sensors to continuously measure a person’s emotional state while they exercise, then tweak the game – for instance, making ...
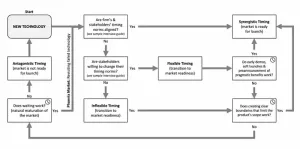
When is the right time to launch new technologies?
2024-09-03
New research from Bayes Business School (formerly Cass) finds that being on the cutting edge of technology is not enough to ensure success in the market, and managers must strategically time launches to create a source of opportunity and credibility for the firm.
The study, led by Dr Thomas Robinson, Senior Lecturer in Marketing at Bayes, with Dr Ela Veresiu, Associate Professor of Marketing at Schulich School of Business, York University, Toronto, develops a framework for guiding organisations on the best situations for a product launch.
The research identifies four timing situations that can confront marketing managers. Knowing ...
Mayo researchers develop tool that measures health of a person’s gut microbiome
2024-09-03
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A team of Mayo Clinic researchers has developed an innovative computational tool that analyzes the gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms within the digestive system, to provide insights into overall well-being.
In a new study published in Nature Communications, the tool demonstrated at least 80% accuracy in differentiating healthy individuals from those with any disease. The tool was developed by analyzing ...
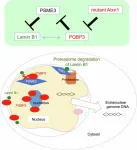
Unveiling the molecular mechanisms linking aging with neurodegenerative diseases
2024-09-03
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers elucidate the role of PQBP3 in stabilizing the nuclear membrane and its relationship to senescence and neurodegeneration
Tokyo, Japan – Aging is the prime cause of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. But what exactly increases the prevalence of these brain disorders as one grows older? The molecular forces linking aging, cellular senescence, and the onset of these neurodegenerative conditions ...
Keep devices out of bed for better sleep – Otago study
2024-09-03
Despite what we’ve been led to believe, the timing of evening screen use, rather than the activity itself, negatively impacts youth sleep, a University of Otago study has found.
Current sleep guidelines recommend no screen use in the hour or two before bed. However, the researchers found screen time in the two hours before bed had little impact on youth sleep, it was screen time once in bed that caused problems.
Lead author Dr Bradley Brosnan, of the Edgar Diabetes and Obesity Research Centre, says screen time is a mainstay in adolescents’ bedtime routines, and sleep guidelines need to be revaluated to better reflect modern life.
Published in JAMA Pediatrics, ...
Dr. Torabi to study vulnerabilities in electric vehicle charging management systems
2024-09-03
Dr. Sadegh Torabi, Assistant Professor, Information Sciences and Technology, College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), and Research Fellow at the Center for Secure Information Systems (CSIS), is set to receive funding for the project: “Collaborative Research: CISE MSI: RPEP: OAC: Macroscopic and Microscopic Inference and Analysis of Vulnerabilities within EV Charging-Management Systems.”
Via this project, Dr. Torabi and his partners will establish a collaborative ecosystem among academia, industry, and the public sector to bolster the resilience of the EV Charging Infrastructure (CI). The critical nature of EV CI has made them targets for malicious attacks, often state-sponsored, ...
Think simpler, flow faster
2024-09-03
Analyzing and simulating fluid flow is a challenging mathematical problem that impacts various scenarios, including video game engines, ocean current modeling and hurricane forecasting. The core of this challenge lies in solving the Navier–Stokes equations, a set of classical equations that describe fluid dynamics. Recently, deep learning has emerged as a powerful tool to accelerate equation solving. Using this technique, a team designed a novel approach that can provide accurate solutions 1,000 times faster than traditional equation solvers. The team’s study was published June 26 in Intelligent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
[Press-News.org] Department of Energy awards $125 Million for research to enable next-generation batteries and energy storageEnergy Innovation Hub teams will emphasize multi-disciplinary fundamental research to address long-standing and emerging challenges for rechargeable batteries