(Press-News.org) Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify Mst1–FoxO1–C/EBP-ß signaling pathway that promotes heart cell survival
Tokyo, Japan – Understanding the mechanisms behind cell death and survival is crucial when it comes to conditions like heart failure, which affects millions of people worldwide. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a mechanism which protects cardiac myocytes against ischemia, or a lack of blood supply.
In this study published online on 25 July 2024 in Nature Communications, researchers from the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) in Japan identify a cellular signaling pathway which stimulates protective mechanisms in cardiac myocytes, potentially opening up avenues for the development of new therapies.
The Forkhead box O (FoxO) family of proteins is involved in many cellular functions, and their cellular activity is tightly controlled. Elaborating further, Dr. Maejima Yasuhiro, the author of the study, says, “The most puzzling aspects of FoxO cellular function is that it regulates both cell death-promoting and -inhibiting mechanisms, even in the same cells.”
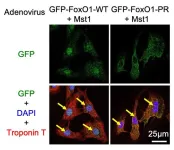
Hence, the TMDU researchers focused on the role of FoxOs as well as Mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1 (Mst1), which is known to interact with FoxOs to regulate processes like cell survival. They found that Mst1 binds to and phosphorylates FoxO1. Additionally, when both Mst1 and FoxO1 were expressed together in cardiac myocytes, it increased the activity of genes that produce protective antioxidants, while suppressing genes involved in cell death.
But how does this protective mechanism work? To answer this question, the researchers took a closer look at the genes targeted by FoxO1. They found that the antioxidant genes had binding sites for both FoxO1, and another protein called C/EBP-β, while genes involved in cell death had binding sites only for FoxO1.
Subsequently, further experiments showed that in the presence of FoxO1, Mst1 phosphorylated C/EBP-β. This increased FoxO1-C/EBP-β binding, which then stimulated antioxidant production and other pro-survival mechanisms.
What effect does this mechanism have on heart cells? In mice that were genetically engineered to lack FoxO1 or C/EBP-β in the heart, exposure to ischemia for four hours actually lead to an increased amount of dead cardiac tissue. On the other hand, when mice that lacked FoxO1 were engineered to express a form of phosphorylated C/EBP-β, the amount of dead tissue in the heart decreased. Taken together, these results showed that this Mst1-FoxO1-C/EBP-β interaction protected the heart against ischemia.
In the long term, these findings could pave the way for the development of new treatments for heart failure. “If the level of C/EBP-β phosphorylation can be increased without activation of Mst1, promoting cell survival without activating the detrimental functions of Mst1 may be possible,” explains Prof. Junichi Sadoshima. In other words, drugs that can selectively promote the protective functions of Mst1 would help protect cardiac myocytes in the case of life-threatening conditions such as heart failure.
Thus, this study not only provides a huge breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms that govern cell death and survival, but also brings new hope for patients suffering from heart failure.
###
The article, “Mst1-mediated phosphorylation of FoxO1 and C/EBP-β stimulates cell-protective mechanisms in cardiomyocytes” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50393-y
END
New avenues for treating heart failure: uncovering a protective mechanism in the cardiac myocytes
2024-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Shedding light on how oral bacteria can aggravate rheumatoid arthritis
2024-09-05
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers investigate the molecular mechanisms that link periodontal disease to rheumatoid arthritis
Tokyo, Japan – Periodontal disease, which affects the gums and tissues that surround the teeth, is one of the most prevalent dental conditions worldwide. Most often caused by the formation and accumulation of bacterial biofilm around the teeth, periodontal disease can ultimately lead to tooth loss if left unattended. Interestingly, the inflammatory effects of periodontal bacteria can go well beyond the mouth, leading to systemic effects. Over the past few decades, clinical studies have revealed that the periodontal ...
Regenstrief to host semiannual LOINC® conference in Washington, D.C., Sept. 17-20
2024-09-05
Regenstrief Institute will host its semiannual LOINC® conference September 17-20, 2024, in Washington, D.C.
LOINC, a global healthcare terminology standard, will be the subject of the three-day conference during which experts worldwide will collaborate during presentations across three points of emphasis: implementation and policy, innovation and mapping.
Keynote presenters will be:
Wednesday, September 18 – Jesse Ehrenfeld, M.D., MPH, the president of the American Medical Association.
Thursday, September ...
Cause, potential treatments ID'd for persistent COVID-19 lung problems
2024-09-05
Arthritis drugs already available for prescription have the potential to halt lingering lung problems that can last months or years after COVID-19 infections, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine and Cedars-Sinai suggests.
By examining damaged human lungs and developing an innovative new lab model, the scientists identified faulty immune processes responsible for the ongoing lung issues that plague an increasing number of people after they’ve otherwise recovered from COVID-19. These lasting harms of COVID infection, ...
Pregnant women exposed to PFAS may be at risk for obesity, heart disease later in life
2024-09-05
WASHINGTON—Women with higher levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) during pregnancy may experience long-term weight gain and heart problems later in life, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
PFAS are manmade chemicals found in food packaging, cookware, clothes, drinking water, personal care products and many other consumer goods. These endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can interfere with hormones and cause health issues such as obesity, infertility and cancer.
“Our study supports the idea that pregnancy may be ...
Skin fungus colonization accelerates breast cancer tumor growth
2024-09-05
Washington, D.C. — A common skin fungus, Malassezia globosa may invade deep tissues through the skin or by other means, then cause tumor growth, according to a new study. The study results were reported in mBio, an open access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“It is important to take care of skin not only for beauty, but also for health,” said corresponding study author Qi-Ming Wang, Ph.D., a professor in the School of Life Sciences, Institute of Life Sciences and Green Development, Hebei University, Hebei, China. “As ...
New study in JNCCN supports chemotherapy option that reduces side effects for people with gastrointestinal cancers
2024-09-05
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 5, 2024] — New research just-published online by JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network finds that for many commonly used treatment regimens targeting metastatic gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, such as FOLFOX, FOLFIRI, or FOLFIRINOX, it is possible to administer 5-FU solely through continuous infusion, minus the bolus (quick-delivery via intravenous push) component, without negatively affecting patient outcomes.
The study reviewed results from 11,765 patients across 280 cancer clinics who were diagnosed with ...
Study shows long term-effects of immigration on Chinese Americans’ cardiovascular health
2024-09-05
A new UCLA-led study found that cardiovascular disease risk among Chinese American immigrants increases with length of residence and varies by location in the U.S. The study, which leveraged data from the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) cohort, sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), observed the heart health of 746 Chinese Americans in both Los Angeles and Chicago over a period of roughly 18 years. The study found that participants who resided in Chicago showed lower mortality levels from heart disease compared to those who lived in Los Angeles.
“This is the first long-term prospective study in nearly two decades to investigate the effects of ...
High blood pressure a concern for adolescents and young adults in U.S.
2024-09-05
Research Highlights:
In the first study, nearly 23% of young adults (ages 18-39 years) included in the NHANES 2017-2020 datasets had high blood pressure (130/80 mm Hg or greater). In addition, they were more likely to self-report being uninsured, food insecure and low-income compared to older adults.
The second study, which also used the 2017-2020 NHANES datasets, found that among 2,600 youths ages 8-19, 8.7% had elevated blood pressure and 5.4% had high blood pressure, as defined by age-sex-height percentiles in accordance with guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
These two studies point to the need for policies and programs to support youth and young adults ...
Remote monitoring and pharmacist helped improve hard-to-control blood pressure
2024-09-05
Research Highlights:
A new study finds that up to 74% of participants with resistant or difficult-to-control high blood pressure, including those with chronic kidney disease, were able to improve control of their blood pressure within 12 months after using a Bluetooth-enabled remote monitoring system coupled with pharmacist interactions.
Two-thirds of patients had interacted with pharmacists who co-managed their blood pressure via telehealth, often making medication adjustments and addressing medication adherence, which was associated with ...
Popular home blood pressure monitoring cuff devices may not fit some US adults
2024-09-05
Research Highlights:
An analysis of at-home blood-pressure monitors estimates that the arm cuffs for 10 of the most popular potentially do not fit up to 18 million adults in the U.S. and nearly 12% of Black adults.
To ensure accurate blood pressure monitoring, the researchers suggest that manufacturers and retailers be aware of the disparities and improve access and selection of diverse blood pressure cuff sizes for consumers.
Note: The studies featured in this news release are research abstracts. Abstracts ...