(Press-News.org) Solving the problem of error is essential for the practical application of quantum computing technologies that surpass the performance of digital computers. Information input into a qubit, the smallest unit of quantum computation, is quickly lost and error-prone. No matter how much we mitigate errors and improve the accuracy of qubit control, as the system size and computation scale increase, errors accumulate and algorithms become impossible to perform. Quantum error correction is a way to solve this problem. As the race for global supremacy in quantum technology intensifies, most major companies and research groups leading the development of quantum computing are now focusing on developing quantum error correction technology.
Dr. Seung-Woo Lee and his team at the Quantum Technology Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a world-class quantum error correction technology and designed a fault-tolerant quantum computing architecture based on it. They have demonstrated that this technology can outperform the quantum error correction technology recently developed by PsiQuantum, a global leader in the development of general-purpose quantum computers.
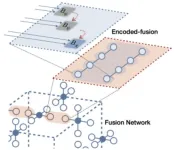
The performance of universal quantum computing with quantum error correction is evaluated by its fault-tolerance threshold. This threshold indicates how well errors in quantum computing can be corrected, and the better the error correction technology and architectural design, the higher the value. PsiQuantum, an American quantum computer developer, has proposed a quantum computing architecture that utilizes photon entanglement resources, fusion techniques, and error correction technology, and is developing universal quantum computing hardware based on it. The photon loss threshold of the PsiQuantum method is reported to be 2.7%. The new error correction technique and quantum computing architecture developed by the KIST research team outperforms this. KIST's technology can achieve a photon loss threshold of up to 14%, which is currently the highest threshold in the world. In addition, KIST's error correction technique is much more resource-efficient than its quantum counterpart, even with the same photon consumption.
The research is the first of its kind in Korea, and it is significant that Korea, a laggard in the field of quantum computing, has developed a world-class core technology. In particular, quantum error correction technology is an essential element in the development of quantum computers utilizing not only photon-based but also superconducting qubits, ion traps, and neutral atoms, which are highly competitive in R&D worldwide. This achievement shows that Korea has the potential to catch up with and even outpace the technology of leading countries in the quantum field. It is also expected to play an important role in building an independent quantum computing system by applying this achievement, which has completed domestic and international patent applications.
"Just like semiconductor chip design technology, designing fault-tolerant architecture is important for quantum computing," said Dr. Seung-Woo Lee of KIST. Even if there are 1,000 physical qubits, it would be difficult to compute a single logical quantum task unless there is a structure that performs quantum error correction." 'The practicalization of quantum computing is still a long way off, but we believe that our research has contributed to bringing that time forward,' said Dr. Lee.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Yoo Sang-im) under the KIST Major Project and Bilateral Technology Cooperation Project (2022M3K4A1094774). The research was published* on August 1 in the international journal Physical Review Letters (IF: 8.1 JCR field top 6.8%).
END
Developed proprietary quantum error correction technology beyond the world's leading quantum computing companies
Quantum error correction is a key technology in the implementation and practicalization of quantum computing
2024-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI will surpass human brains once we crack the ‘neural code’
2024-09-09
Humans will build Artificial Intelligence (AI) which surpasses our own capabilities once we crack the ‘neural code’, says an AI technology analyst.
Eitan Michael Azoff, a specialist in AI analysis, argues that humans are set to engineer superior intelligence with greater capacity and speed than our own brains.
What will unlock this leap in capability is understanding the ‘neural code’, he explains. That’s how the human brain encodes sensory information, and how it ...
RSV vaccination in older adults with health conditions is cost-effective
2024-09-09
Targeting vaccination programs for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) to older adults with underlying health conditions is a cost-effective way to reduce disease, according to a new modelling study https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240452 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
RSV infections cause major illness, especially in infants and older adults, and rates of infection increase with age. There are now vaccines available to prevent disease caused by RSV in adults, and vaccination campaigns may reduce the incidence in older adults and associated ...
Melanoma incidence and mortality trends in Sweden
2024-09-09
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study showed a significant recent downward trend in both melanoma incidence and melanoma mortality in the age group 30 to 49 years in Sweden. The reasons for these declines are unclear but may include UV protection, public health campaigns, changing population demographics, and the introduction of effective melanoma treatment. None of these possibilities were evaluated; further study is needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hildur Helgadottir, MD, PhD, email hildur.helgadottir@sll.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Breaking the trend: Skin cancer incidence in young adults declines
2024-09-09
The risk of skin cancer, malignant melanoma, now appears to be decreasing in Sweden - at least in those under 50, according to a new study.
“We can see a trend break in young adults around 2015 where the incidence curves are falling,” says first author Hildur Helgadottir, senior consultant and associate professor of oncology at the Department of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institutet.
She and her research colleagues have analyzed data from the Swedish Melanoma Registry and followed melanoma incidence and mortality for different age segments over time. This means that they have compared individuals in a certain age range at one ...
ChatGPT outperformed trainee doctors in assessing complex respiratory illness in children
2024-09-09
The chatbot ChatGPT performed better than trainee doctors in assessing complex cases of respiratory disease in areas such as cystic fibrosis, asthma and chest infections in a study presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress in Vienna, Austria [1].
The study also showed that Google’s chatbot Bard performed better than trainees in some aspects and Microsoft’s Bing chatbot performed as well as trainees.
The research suggests that these large language models (LLMs) could be used to support trainee doctors, nurses and general practitioners to triage patients more quickly and ease pressure on health services.
The ...
Night owls are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes – and it’s not just because of an unhealthy lifestyle, Dutch study finds
2024-09-09
Night owls have a higher BMI, larger waists, more hidden body fat and are almost 50% more likely to develop type 2 diabetes (T2D) than those who go to bed earlier, new research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September), has found.
Lead researcher Dr Jeroen van der Velde, of Leiden University Medical Centre, Leiden, Netherlands, says: “Previous studies have indicated that a late chronotype – preferring to go to bed late and wake up later – is associated with an unhealthy lifestyle. Late chronotypes are ...
Air travel may affect insulin pump delivery in people with type 1 diabetes
2024-09-09
Altitude changes during commercial flights may affect the blood glucose levels of people with type 1 diabetes who are treated with insulin pump therapy, according to new research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), Madrid (9-13 Sept).
“We investigated the effect atmospheric pressure changes during flight can have on insulin pumps following concerns that glucose levels may drop below the normal ranges during or immediately after flights,” explained lead author Dr Ka Siu Fan from the Royal Surry County Hospital and University ...
Fruit and oats raise risk of type 1 diabetes but berries provide protection, research suggests
2024-09-09
New research being presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September), shows that eating fruit, oats and rye in childhood is associated with a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes (T1D). Eating berries, however, is linked to lower odds of developing the condition.
T1D is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing islet cells in the pancreas. This prevents the body from producing enough of the hormone insulin to properly regulate blood sugar levels.
What triggers the immune system’s attack is unknown but is thought to involve a combination ...
Patients receiving steroids are more than twice as likely to develop diabetes, UK study has found
2024-09-09
Patients who are being treated with systemic glucocorticoids are more than twice as likely to develop diabetes as those not receiving the treatment, the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September) will hear.
Glucocorticoids (sometimes known as steroids) fight inflammation and are used to treat a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, including asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, cancers and other medical problems.
While they can be very effective in decreasing inflammation, glucocorticoids have many adverse effects including ...
Perioperative nivolumab may provide meaningful improvement in event-free survival compared to only neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy for resectable NSCLC
2024-09-08
(San Diego, Calif--September 8, 2024, 10:05 a.m. PCT) – New data from landmark analysis presented today report a decreased risk of disease recurrence or death in patients with resectable NSCLC who received adjuvant nivolumab following neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy and surgery compared to those who received only neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy.
The data was reported at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
This is the first analysis of individual patient-level data from two phase 3 trials, CheckMate 77T and CheckMate 816, to examine which patients may derive benefit from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research finds heart health benefits in combining mango and avocado daily
New research finds peanut butter consumption builds muscle power in older adults
Study identifies aging-associated mitochondrial circular RNAs
The brain’s primitive ‘fear center’ is actually a sophisticated mediator
Brain Healthy Campus Collaborative announces winner of first-ever Brain Health Prize
Tokyo Bay’s night lights reveal hidden boundaries between species
As worms and jellyfish wriggle, new AI tools track their neurons
ATG14 identified as a central guardian against liver injury and fibrosis
Research identifies blind spots in AI medical triage
$9M for exploring the fundamental limits of entangled quantum sensor networks
Study shows marine plastic pollution alters octopus predator-prey encounters
Night lights can structure ecosystems
A parasitic origin for the ribosome?
A gold-standard survey of the American mood
Tool for identifying children at risk of speech disorders
How Japanese medical trainees view artificial intelligence in medicine
MambaAlign fusion framework for detecting defects missed by inspection systems
Children born with upper limb difference show the incredible adaptability of the young brain
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
Fast-paced lives demand faster vision: ecology shapes how “quickly” animals see time
Global warming and heat stress risk close in on the Tour de France
New technology reveals hidden DNA scaffolding built before life ‘switches on’
New study reveals early healthy eating shapes lifelong brain health
Trashing cancer’s ‘undruggable’ proteins
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
[Press-News.org] Developed proprietary quantum error correction technology beyond the world's leading quantum computing companiesQuantum error correction is a key technology in the implementation and practicalization of quantum computing