(Press-News.org) With flu season just around the corner and COVID-19 cases on the rise, a new nationwide survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center reveals hesitancy around vaccines this fall. The new data comes just as this year’s flu shot rolls out and following the FDA’s approval of an updated round of COVID-19 vaccines.
The national poll of 1,006 people found more than one-third (37%) have gotten vaccines in the past but do not plan to this year. The same percent of respondents said they don’t need any of the vaccines surveyed in the poll, including flu, COVID-19, pneumococcal and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Other survey results found:
A slight majority (56%) of adults have gotten or plan to get the flu shot this fall.
Less than half (43%) have gotten or plan to get the COVID-19 vaccine.
Adults age 65 and older are the most likely to get recommended vaccines.
“We’re at the start of respiratory virus season when you have the triple threat of flu, COVID-19 and RSV. Unfortunately, there is a lot of misinformation about vaccinations, but the reality is that they are safe and highly effective in preventing serious illness and death. Older adults, people with certain chronic medical conditions and those who are pregnant are especially at risk during respiratory virus season,” said Nora Colburn, MD, medical director of clinical epidemiology at Ohio State’s Richard M. Ross Heart Hospital.
CDC’s recommended vaccines
Flu: Annual vaccination is recommended for everyone age 6 months and older.
COVID-19: Updated vaccination is recommended for everyone age 6 months and older.
RSV: Everyone age 75 and older, adults age 60-74 who are at increased risk of severe disease and pregnant people during weeks 32-36 from September to January.
Pneumococcal: Everyone younger than 5 years and age 65 and older. Additionally, vaccination is recommended for children and adults at increased risk of severe disease.
“Vaccinations play a critical role in helping to keep individuals and communities healthy. Other things you can do is to stay home when sick, avoid those who are sick and wear a mask if you’re not feeling well and going out of your home. All of these things can help prevent you from getting sick and spreading it to others,” Colburn said.
Survey Methodology
This survey was conducted on behalf of The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center by SSRS on its Opinion Panel Omnibus platform. The SSRS Opinion Panel Omnibus is a national, twice-per-month, probability-based survey. Data collection was conducted from August 16 – August 18, 2024, among a sample of 1,006 respondents. The survey was conducted via web (n=975) and telephone (n=31) and administered in English. The margin of error for total respondents is +/-3.8 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. All SSRS Opinion Panel Omnibus data are weighted to represent the target population of U.S. adults ages 18 or older.
END
New national survey shows hesitancy about vaccines this fall
37% of poll respondents believe they don’t need to be vaccinated
2024-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Revolutionary tubular scaffolds boost stem cell-driven bone regeneration in skull defects
2024-09-12
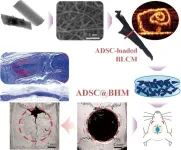
Scientists from Sun Yat-sen University's School of Biomedical Engineering have developed groundbreaking tubular scaffolds made from electrospun membranes, which significantly enhance bone regeneration in critical skull defects. These scaffolds, designed to mimic natural bone structures, create an ideal environment for adipose-derived stem cells (rADSCs) to thrive and accelerate healing. By integrating advanced materials like polycaprolactone, PLGA, and nano-hydroxyapatite, the researchers achieved remarkable results in both lab and animal studies, ...
UTokyo attosecond institute welcomes Nobel laureate
2024-09-12
Nobel laureate Pierre Agostini, winner of the 2023 prize in physics, will headline a special two-day event hosted by the University of Tokyo on Sept. 26-27. The keynote lecture by Agostini, renowned for this pioneering work in attosecond science, will be part of a larger symposium bringing together researchers from around the world to celebrate the university’s planned Attosecond Laser Facility (ALFA), and discuss the latest developments and future directions of attosecond science.
Have you taken a photo of a fast-moving animal or vehicle and noticed how blurry the subject can be? This is likely because the faster a moving subject is, the faster the camera’s shutter needs ...
Single dose of mpox vaccine effective in preventing infection, study finds
2024-09-11
Toronto, ON, September 11, 2024 — A single dose of the Modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) was 58% effective in protecting again mpox infection, according to a new study published in BMJ.
Researchers from ICES, Public Health Ontario, and the MAP Centre for Urban Health Solutions at St. Michael’s Hospital of Unity Health Toronto have conducted a target trial emulation to estimate the effectiveness of the mpox vaccine.
During the mpox outbreak in 2022, Ontario, Canada introduced the vaccine ...
One dose of smallpox vaccine moderately effective in preventing mpox infection
2024-09-11
One dose of modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) smallpox vaccine is moderately effective in preventing mpox infection and should be made available to communities at risk, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
With mpox infections rising again across the globe, the researchers say these findings “strengthen the evidence that MVA-BN is effective at preventing mpox infection and should be made available and accessible to communities at risk.”
No randomised clinical trials of vaccination against mpox have been conducted. Estimates of the effectiveness of a single dose of vaccination from observational studies range from ...
More than half of UK government nutrition advisors are paid by food companies
2024-09-11
More than half of the experts on the UK government’s nutrition advisory panel have links to the food industry, reveals an investigation by The BMJ today.
At least 11 of the 17 members of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) have conflicts of interest with the likes of Nestle, sugar manufacturer Tate and Lyle, and the world’s largest ice cream producer, Unilever, reports freelance journalist Sophie Borland.
And at least six out of the 11 members of SACN’s Subgroup on Maternal and Child Nutrition have ties to food firms, including baby food manufacturers and formula milk brands.
SACN ...
Shorter-course radiation better option for breast cancer patients than conventional schedule
2024-09-11
Giving higher doses per fraction of radiation therapy over a shorter time after breast cancer surgery significantly reduces the risk of side effects and improves quality of life compared with a conventional schedule, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
Although survival and recurrence rates were similar, this approach, known as hypofractionation, is safer, more convenient for patients, and reduces costs for healthcare systems, and should be the preferred treatment option, say the researchers.
Conventional fractionation radiation therapy has been the standard of care for most patients with breast ...
Obesity treatments being restricted by cash poor local services
2024-09-11
Obesity treatments are being restricted by cash poor local services across England with many patients being denied specialist drugs, surgery and support, an investigation by The BMJ has found.
Patients in nearly half the country can’t get appointments with specialist teams for weight loss support and care, including treatment with drugs such as semaglutide. And in nearly one in five local health areas, patients don’t have access to a bariatric surgery service, reports Elisabeth Mahase.
The government estimates that obesity costs the NHS in England around £6.5bn a year and is the second biggest preventable cause ...
Laughter may be as effective as drops for dry eyes
2024-09-11
Laughter may be as effective as eye drops in improving symptoms of dry eye disease, finds a clinical trial from China published by The BMJ today
The researchers suggest that laughter exercise could be an initial treatment for relieving symptoms of dry eye disease.
Dry eye disease (DED) is a chronic condition estimated to affect around 360 million individuals worldwide. Common symptoms include uncomfortable, red, scratchy or irritated eyes.
Evidence suggests that laughter therapy alleviates depression, anxiety, stress, and chronic pain, while strengthening immune ...
Path to prosperity for planet and people if Earth’s critical resources are better shared: report
2024-09-11
Earth will only remain able to provide even a basic standard of living for everyone in the future if economic systems and technologies are dramatically transformed and critical resources are more fairly used, managed and shared, according to an international research team including scientists from The Australian National University (ANU).
The report, published in The Lancet Planetary Health, outlines how cities and businesses have the power to play a crucial role and become the “stewards” of critical Earth ...
Long-course radiotherapy is better than short-course for organ preservation in rectal cancer
2024-09-11
The COVID-19 pandemic has enabled researchers to show that a long course of radiotherapy given before surgery may be a better treatment for avoiding surgery, preserving the rectum and anus, and preventing regrowth of the primary tumour than a short course of radiotherapy for patients with rectal cancer – a type of bowel cancer. However, the overall survival and survival free of recurrence of the disease remained the same for both treatments.
These findings are from a new study published in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] New national survey shows hesitancy about vaccines this fall37% of poll respondents believe they don’t need to be vaccinated