(Press-News.org)
Connecticut, U.S.A -- Some chemicals create environmental problems; others, fortunately, can help clean them up.
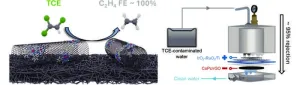
Chemists from Yale University and their colleagues have developed an electrochemical catalyst and membrane that offers an efficient and sustainable way to treat water contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE), a common and persistent environmental pollutant. Their findings highlight the potential for advanced electrochemical treatments in environmental remediation and open the door for further innovations in the field.
Their results were published in Carbon Future on September 5.
TCE is a common industrial solvent or cleaning agent used in refrigerants, dry cleaning, and metal and electronic degreasing. However, TCE’s toxic properties can cause harm to multiple organs and induce cancer. Water contamination by TCE is not uncommon.
While bioremediation was one of the first methods used to tackle TCE pollution, it is often slow and generates byproducts that are even more toxic. Chemical remediation is faster and more efficient but often requires strong chemicals and does not completely decompose TCE. Consequently, electrochemical treatment, which uses electrical currents to decompose contaminants, is emerging as a more effective and sustainable solution for TCE remediation.
“Electrochemical methods have shown promise for treating water contaminated by chlorinated volatile organic compounds, but efficiently removing and repurposing TCE has been a challenge due to the lack of effective catalysts,” said Hailiang Wang, a professor at Yale University’s Department of Chemistry and Energy Sciences Institute and the lead corresponding author of this study.
Responding to this need, the research team developed a catalyst composed of cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPc) molecules mounted on multiwalled carbon nanotubes (CNTs). This catalyst breaks down TCE at record rates, turning it into ethylene and chloride ions with nearly 100% Faradaic efficiency. This means that almost all the electrical current is used to convert TCE into harmless products without generating harmful byproducts, making it promising for practical applications.
“The key to our success is the first electron transfer step, which doesn’t involve protons, and the single site nature of our catalyst” said Yuanzuo Gao, a graduate student in Wang’s group and the first author of this study. “These helped us avoid the hydrogen evolution reaction and thereby promote TCE dechlorination.”
The hydrogen evolution reaction is a side reaction that consumes electrons that could otherwise be used to break down pollutants, diminishing the current efficiency of the process.
To enhance the practical application of this catalyst, the team incorporated CoPc molecules into an electrified membrane made from reduced graphene oxide (rGO), a modified form of graphene known for its strength, lightweight nature and high conductivity. This membrane filtration device achieved 95% removal of TCE from simulated water samples that mimic actual water treatment conditions, marking a significant advancement in the technology’s practical use.
This study underscores the potential of advanced electrochemical methods to address complex environmental challenges and drive progress in water treatment and industrial pollution control.
“By combining CoPc molecules with CNT and rGO supports, we have created highly selective and active electrocatalysts for the treatment of TCE in water,” Gao said.
About Carbon Future
Carbon Future is an open access, peer-reviewed and international interdisciplinary journal, published by Tsinghua University Press and exclusively available via SciOpen. Carbon Future reports carbon-related materials and processes, including catalysis, energy conversion and storage, as well as low carbon emission process and engineering. Carbon Future will publish Research Articles, Reviews, Minireviews, Highlights, Perspectives, and News and Views from all aspects concerned with carbon. Carbon Future will publish articles that focus on, but not limited to, the following areas: carbon-related or -derived materials, carbon-related catalysis and fundamentals, low carbon-related energy conversion and storage, low carbon emission chemical processes.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
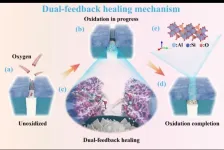
Fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) have been the primary choice for radome materials in hypersonic vehicles due to their high toughness, strength, and other advantageous properties. However, oxidation by oxygen in the atmospheric environment at elevated temperatures remains a significant obstacle to their further development. Thermal protection coatings offer a crucial avenue to mitigate this issue. Nonetheless, inherent material differences or fiber orientations within CMCs can lead to disparate thermal expansion rates between the matrix and fibers during temperature variations, inevitably ...
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 12, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—and the NCCN Foundation® proudly announce plans to make every book in the library of NCCN Guidelines for Patients® available in Spanish; with select editions available in additional languages as well.
NCCN publishes the NCCN Guidelines for Patients library through funding from the NCCN Foundation. It now features more than 70 books with easy-to-understand information about prevention, ...
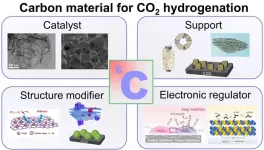
One of the primary drivers of climate change, CO2 emissions, have reached over 35 million tons worldwide. With global annual temperatures still rising, reducing CO2 emissions has become a necessity. To turn this necessity into an opportunity, researchers have been working to find ways to capture the CO2, thereby reducing emissions and then converting that CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels.
One of the difficulties in working with CO2 is that it is very thermodynamically stable. To overcome this, additional ...
Gastric cancer remains a formidable adversary, ranking as the fifth most common cancer and the third-leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with over 1,000,000 new cases and close to 770,000 deaths each year. In Singapore, gastric cancer ranks among the top 10 causes of cancer-related deaths and claims about 300 lives each year.
The peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity, is frequently involved in advanced-stage cancers, including gastric, colon, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers. For gastric cancer, the peritoneum ...
National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers and collaborators have found that being a carrier for sickle cell disease, known as having sickle cell trait, increases the risk of blood clots, a risk that is the same among diverse human populations that may not traditionally be associated with sickle cell disease. The study provides estimated clinical risks for people with sickle cell trait, which can inform clinical practice guidelines. Researchers examined the largest and most diverse set of people ...
(WASHINGTON – September 12, 2024) The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), or blood clots, in individuals with sickle cell trait (SCT) is higher than in individuals without the trait. However, the risk is lower than for those with heterozygous factor V Leiden (FVL), according to a study published today in Blood Advances that analyzed genetic data from 23andMe research participants.
More than 100 million people worldwide and approximately 7% of Black individuals in the United States have SCT. Unlike sickle cell disease, ...
A research paper by scientists at Purdue University presented a deep learning method that enables the customization of complex strain fields according to specific requirements.
The new research paper, published on Aug. 14 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, used a deep learning method based on image regression and achieved to predict and customize complex strain fields.
Traditional bioreactors, powered by pneumatic actuators or motors, struggle to generate complex strain fields due to limited control over individual actuators. However, fields like cardiovascular biomechanics and tissue engineering require more advanced customization. “In the field of biomechanics, customizing ...
Highlights:
Diastatic yeasts can spoil craft beer through hyperattenuation, which boosts the alcohol content and causes bottles to explode.
Killer toxins, which are produced by other yeast strains, hint at a remedy.
In a proof-of-concept study, researchers found that killer toxins inhibited up to 95% of diastatic yeasts.
More work is needed to fine tune the recipe, but killer yeasts may help brewers remedy potentially contaminated beers.
Washington, D.C. — Sept. 12, 2024 — When diastatic strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ...
DALLAS, September 12, 2024 — The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service in 2024, is recognizing 21 students, educators and elementary, middle and high schools from across the country who are making a bold impact in the battle against cardiovascular disease – the nation’s leading cause of death. These exceptional individuals and institutions were honored for their unwavering commitment to the Association’s in-school programs, Kids Heart Challenge™ ...
A new study has revealed for the first time how different synthesis methods can profoundly impact the structural and functional properties of high entropy oxides, a class of materials with applications in everyday electronic devices. The study was published this week in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“The specific material that we’ve studied here is a high entropy oxide with a spinel crystal structure, which is a mixture of five different transition metal oxides. A lot of the excitement that we ...