(Press-News.org) BALTIMORE, September 16, 2024— A new study from Kennedy Krieger Institute shows that the majority of children diagnosed with long COVID are likely to experience orthostatic intolerance (OI), a condition that causes the body to struggle with regulating blood pressure and heart rate when standing up. As a result, children often feel dizzy, lightheaded, fatigued and may experience “brain fog” or cognitive difficulties.
Orthostatic intolerance includes disorders such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and orthostatic hypotension. Among the patients studied, dizziness (67%), fatigue (25%), and body pain (23%) are found to be common symptoms, which worsen when standing and improve when lying down. These symptoms can make it difficult to perform everyday activities like exercising, attending school, and socializing, severely impacting their quality of life.
This new research, conducted at Kennedy Krieger’s Pediatric Post-COVID-19 Rehabilitation Clinic, reveals that OI is prevalent among children dealing with the long-term effects of the COVID-19 virus. Researchers found 71% of the patients studied at the Institute experienced at least one orthostatic condition.
Dr. Laura Malone, Director of the Pediatric Post-COVID-19 Rehabilitation Clinic at Kennedy Krieger, is the senior author of this study. She explains these findings show the importance of screening pediatric long COVID patients for OI, as many have symptoms that could be missed without proper testing.
“Research proves this condition is common. Sixty-five out of the 92 children we studied were battling side effects like dizziness and fatigue from OI” Dr. Malone said. “Early diagnosis and treatment will give them the chance to recover and return to their normal routines.”
The study findings call for a multi-faceted approach to treatment. Research emphasizes the importance of increased salt and fluid intake, exercise training, and physical therapy. Medications to manage heart rate and blood pressure are also being explored. However, Dr. Malone says more research is needed to fully understand OI.
“Our goal is to provide more targeted and tailored treatments that will help these children,” Dr. Malone said. “This study is just the beginning, and we hope it will spark further research to support for children with long COVID.”
Click here to discover more about Kennedy Krieger’s research on long COVID and its nationally recognized clinic in Baltimore.
About Kennedy Krieger Institute
Kennedy Krieger Institute, an internationally known, non-profit organization located in the greater Baltimore/Washington, D.C. region, transforms the lives of more than 27,000 individuals a year through inpatient and outpatient medical, behavioral health and wellness therapies, home and community services, school-based programs, training and education for professionals and advocacy. Kennedy Krieger provides a wide range of services for children, adolescents and adults with diseases, disorders or injuries that impact the nervous system, ranging from mild to severe. The Institute is home to a team of investigators who contribute to the understanding of how disorders develop, while at the same time pioneer new interventions and methods of early diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Visit www.kennedykrieger.org/ for more information about Kennedy Krieger.
###
END
New research highlights the precarious status of one of Madagascar's most threatened amphibians, the harlequin mantella (Mantella cowanii), revealing small population sizes and the possible extirpation of the species from several of its historic habitats. The findings underscore the urgent need for targeted conservation action to prevent the species from slipping further towards extinction.
Research Findings: A Dire Situation
Amphibians around the world are facing unprecedented population declines, and Mantella cowanii is no exception. The study, which focused on confirming the frog’s presence at historic localities and estimating its population size ...
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation has joined forces with the Restless Legs Syndrome Foundation to fund research leading to new treatments and a cure for RLS.
Earlier this year, the AASM Foundation began an agreement with the RLS Foundation to co-fund basic and clinical RLS research. The partnership for 2024 includes the following research priorities:
Neurobiological interaction: Elucidate the points of interaction between RLS-relevant neurotransmitters, neuronal pathways, and iron deficiency.
Pharmacologic treatments: Elucidate effects of novel pharmacological approaches on RLS.
Clinical practice: Research based on innovations in patient ...
Discovery expands understanding of how language is produced by the brain
Current method of mapping brain language function for surgery using electrical stimulation hasn’t changed in 50 years
Finding could make it easier on patients and doctors to identify critical language sites in the brain to preserve function after surgery
CHICAGO --- When surgeons perform brain surgery on people with brain tumors or epilepsy, they need to remove the tumor or abnormal tissue while preserving parts of the brain that control language and movement.
A new Northwestern Medicine study may better inform doctors’ ...
Astronomers have used the NASA/ESA James Webb Space Telescope to confirm that supermassive black holes can starve their host galaxies of the fuel they need to form new stars.
The international team, co-led by the University of Cambridge, used Webb to observe a galaxy roughly the size of the Milky Way in the early universe, about two billion years after the Big Bang. Like most large galaxies, it has a supermassive black hole at its centre. However, this galaxy is essentially ‘dead’: it has mostly stopped forming new stars.
“Based ...
Imagine you’re looking at millions upon millions of mysterious genetic mutations. With CRISPR gene-editing technology, a select few of these mutations might have therapeutic potential. However, proving it would mean many thousands of hours of lab work. Just figuring out which ones are worth exploring further would take a lot of time and money. But what if you could do it in the virtual realm with artificial intelligence?
CREME is a new AI-powered virtual laboratory invented by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Peter Koo and his team. It allows geneticists to run thousands of virtual experiments ...
Statement Highlights:
There are a variety of interrelated social and structural factors that contribute to differences in cardiovascular health among Asian Americans, and these factors are likely different within individual Asian ethnic subgroups.
Asian Americans and Asian immigrants are quite diverse and comprise many ethnic groups.
Social determinants, such as immigration-related factors, discrimination, socioeconomic status, English proficiency and cultural beliefs, may influence health behaviors, access to health care and the ability ...
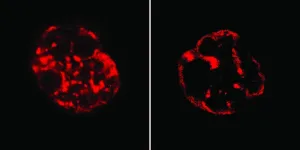
Researchers from the Kind Group have gained new insights into the mechanism behind the spatial organization of DNA within the cells of early embryos. When an embryo is first formed after fertilization, each cell has the potential to become any cell type of the body. The researchers have studied the spatial organization of DNA that is so particular to these early developmental stages. The paper was published in Nature Genetics on September 16th, 2024.
Every cell in our body contains the same DNA. ...
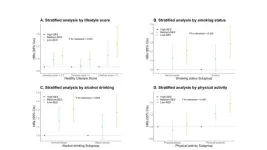
A recent study conducted by researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine and Fudan University has revealed a significant association between socioeconomic status (SES) inequality and the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Published in Health Data Science, the study highlights how a healthy lifestyle can mitigate some of the risks associated with low SES.
Socioeconomic disparities have long been a concern in various health outcomes. This study, led ...
Researchers at Uppsala University have developed a gel inspired by cow slime for patients suffering from disc herniation. By adding the mucin gel immediately after surgery, it is possible to create a protective barrier around the discs to prevent the immune system from attacking their nucleus pulposus. This keeps the discs intact and reduces the risk of further damage.
“This new approach offers hope for those suffering from back pain caused by disc herniation and may prevent further damage after removing ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Developing friendships is often seen as a natural part of childhood but it may be easier for some kids than others.
And many parents worry about their children’s friendships, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health, with one in five saying their child ages six to 12 has no friends or not enough friends.
Ninety percent of parents believe their child would like to make new friends.
“Friendships can play a significant role in children’s overall health and development, emotional well-being, ...