(Press-News.org) Norway introduced its Regular GP Scheme was introduced in 2001. This gave all citizens the right to choose a GP in their home municipality and facilitates personal continuity between the doctor and the patient.
These types of long-term doctor-patient relationships are associated with reduced use of emergency health services and lower mortality, both internationally and in Norway.
A widely discussed Norwegian study from 2022 showed that patients who had the same GP for more than fifteen years had a 25 per cent lower risk of dying compared to patients who had the same GP for one year or less.
However, there has been an increasing shortage of GPs in recent years. As of July 2024, just over 188,000 people in Norway do not have a regular GP, representing almost 3.5 per cent of the country’s population.
Since long-term doctor-patient relationships appear to be more beneficial than short-term ones, the assumption can be made that losing your regular GP could be detrimental. You would end up in a group of people who have only known their GP for a short period of time.
However, many factors influence the contact and length of relationship with a GP, such as age, gender and health issues, as well as the fact that people can choose to change their GP up to twice a year.
These are traits and trends that are also related to health, healthcare use and mortality. It can therefore be difficult to distinguish the effect of a long-term doctor-patient relationship from the effect of other factors related to the patient.
It is not coincidental which patients switch their GPs more frequently and thus have shorter doctor-patient relationships. This group may include people with multiple health problems who feel they have been inadequately examined, leading them to seek more hospital referrals because of these issues – rather than just the doctor-patient relationship itself being the problem.
However, some disruptions to the doctor-patient relationship are coincidental, such as when the doctor goes on holiday, has mandatory hospital service, relocates or retires.
It is reasonable to assume that these disruptions have nothing to do with factors related to the patients, and thus it becomes possible to study the effect of losing a regular GP without the interference of factors that influence both the length of doctor-patient relationships and health outcomes.
Despite the shortage of GPs in many countries, few studies have been conducted on this topic.
Since Norway has exceptionally good data on its population, healthcare use, mortality and GPs, researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) were inspired to investigate the consequences of a GP leaving their position due to unavoidable personal circumstances.
Between 2011 and 2021, 819 GPs retired and 228 relocated between counties. The researchers studied the impact on healthcare use and mortality over the course of five years by comparing the almost 1.2 million patients associated with these doctors to similar patients and GPs where there was evidence of a continuing relationship.
They found that for every 1,000 patients who lost their regular GP, there were 13 to 16 additional contacts with the out-of-hours medical service and hospital emergency departments in the first year. Over all five years, there were approximately 148 more contacts per year in general practice and 51 additional planned contacts in hospitals every year. Compared to the patients who continued with the same doctor, this represented a 3 to 5 per cent increase.
However, they found no difference in mortality rates between patients whose GP relocated or retired and those whose had not.
The researchers conclude that there may be multiple reasons why having the same GP over time is beneficial for health, and that you would not be at risk if your GP were to relocate or retire.
The increase in healthcare use appears to be small to moderate, and the risk of mortality remains unaffected.
The findings are somewhat in contrast with much of the research on continuity. This indicates that studies on the duration and disruption of doctor-patient relationships are complex, requiring different research methods to shed light on various problems.
Reference:
Kristin Hestmann Vinjerui, Andreas Asheim, Kjartan Sarheim Anthun, Fredrik Carlsen, Bente Prytz Mjølstad, Sara Marie Nilsen, Kristine Pape, Johan Håkon Bjørngaard: General practitioners retiring or relocating and its association with healthcare use and mortality: a cohort study using Norwegian national data. BMJ Quality and Safety 2024
END
What happens to patients when their GP retires or relocates?
2024-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer cells may be using lipids to hide from the immune system
2024-09-17
Cancer cells seldom start off stealthy. Quite to the contrary, they announce their presence to the immune system by planting chemical red flags right on their membranes. Once alerted, the body’s defenses can swoop in, destroying rogue cells before they can do much damage. Lying at the heart of this early warning system are lipids, fatty compounds previously seen by cancer biologists primarily as a fuel source for burgeoning tumors.
But now, a new study in Nature demonstrates that one particular lipid type is actually ...
NASA completes spacecraft to transport, support Roman Space Telescope
2024-09-17
The spacecraft bus that will deliver NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope to its orbit and enable it to function once there is now complete after years of construction, installation, and testing.
Now that the spacecraft is assembled, engineers will begin working to integrate the observatory’s other major components, including the science instruments and the telescope itself.
“They call it a spacecraft bus for a reason — it gets the telescope to where it needs to be ...
University of Health Sciences earns $5.3 million from NIH to boost cancer research, support emerging scientists
2024-09-17
A $5.3 million National Institutes of Health grant awarded to the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences will support advanced cancer research in Oklahoma. The Centers of Biomedical Research Excellence (COBRE) grant is designed to build research capacity and help early-career researchers establish independently funded laboratories.
This is the third and final phase of the COBRE grant, which was first awarded in 2012, followed by phase two in 2017. The grant has supported and paralleled the growth of OU Health Stephenson Cancer Center, Oklahoma’s ...
Central America could play troubling new role in cocaine trade
2024-09-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – For many decades, the coca plant – the main ingredient in cocaine – has been grown almost exclusively in South America. But a new study shows that nearly half of northern Central America appears to be highly suitable for cultivating this lucrative cash crop.
Findings showed that 47% of Honduras, Guatemala and Belize have the right climate and soil for commercial coca growing. Most of southern Central America was not suitable.
It’s not a hypothetical concern. Researchers began ...
SwRI and UTSA will create synthetic process for antibiotic drug discovery
2024-09-17
SAN ANTONIO — September 17, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) is collaborating with The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) to explore and develop a novel platform or chemical process for synthesizing antibiotic compounds with a $125,000 grant. The project, one of two winning proposals this cycle, is supported by the Connecting through Research Partnerships (Connect) program designed to foster collaboration between SwRI and UTSA.
“SwRI and UTSA will work together to combat the growing threat antimicrobial resistance poses to global health by developing a proof-of-concept platform to potentially create a whole ...
Norwegian Afghanistan veterans more prone to anger
2024-09-17
From 2001 to 2021, roughly 9200 Norwegian soldiers served in Afghanistan. The vast majority of them have managed well in the years that have followed. According to a new survey conducted by the Norwegian Armed Forces Joint Medical Services, however, a significant number of the veterans struggle with mental health issues.
“All Norwegian veterans who served in Afghanistan were invited to participate in a large health survey in 2020,” says Associate Professor Andreas Espetvedt Nordstrand at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology ...
Black hole pairs may unveil new particles
2024-09-17
In a paper published in Physical Review Letters this week, physicists from Amsterdam and Copenhagen argue that close observations of merging black hole pairs may unveil information about potential new particles. The research combines several new discoveries made by UvA scientists over the past six years.
Gravitational waves that are emitted by the merger of two black holes carry detailed information about the shape and evolution of the orbits of the components. A new study by physicists Giovanni Maria Tomaselli and Gianfranco Bertone from ...
Amsterdam UMC led research sets a step forward in the battle against MRSA
2024-09-17
Staphylococcus aureus, mostly known from its antibiotic-resistant variant Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), is among the leading causes of both community- and hospital-acquired infections. According to the most recent data, MRSA killed around 120,000 people in 2022 globally and far more are killed by antibiotic-susceptible strains of S. aureus. So far however, all attempts at developing a protective vaccine for S. aureus have been unsuccessful. Research from Amsterdam UMC, in collaboration with UMC Utrecht, Leiden University, and the University of California, San Diego, have discovered an important immune component that offers protection against infection, ...
Childhood trauma linked to major biological and health risks
2024-09-17
A new study led by UCLA Health found that a person’s sex and their unique experiences of childhood trauma can have specific consequences for their biological health and risk of developing 20 major diseases later in life.
Although a large body of research has shown that childhood adversity can have long-lasting impacts on a person’s biology and health, there has been little research looking into how different types of stressors affect specific biological functions and health risks.
The new findings, published in the journal ...
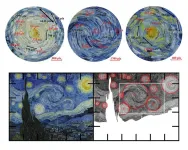
Beneath the brushstrokes, van Gogh’s sky is alive with real-world physics
2024-09-17
WASHINGTON, Sept. 17, 2024 – Vincent van Gogh’s painting “The Starry Night” depicts a swirling blue sky with yellow moon and stars. The sky is an explosion of colors and shapes, each star encapsulated in ripples of yellow, gleaming with light like reflections on water.
Van Gogh’s brushstrokes create an illusion of sky movement so convincing it led atmospheric scientists to wonder how closely it aligns with the physics of real skies. While the atmospheric motion in the painting cannot be measured, the brushstrokes can.
In an article published this week in Physics ...