(Press-News.org) A pioneering study presented today at ECTRIMS 2024 has identified critical biomarkers that can predict disability worsening in multiple sclerosis (MS). The breakthrough research has the potential to transform treatment strategies for millions of MS patients worldwide, paving the way for more personalised and effective treatment plans.1
In this multicentre observational study, conducted across 13 hospitals in Spain and Italy, Dr. Enric Monreal and his team found that elevated serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels—a protein indicating nerve cell damage—at the onset of MS can predict both relapse-associated worsening (RAW) and progression independent of relapse activity (PIRA).* Additionally, serum glial fibrillary acidic protein (sGFAP) levels—a protein derived from astrocytes that enters the bloodstream when the central nervous system (CNS) is injured or inflamed—correlate with PIRA in patients with low levels of sNfL.
The study analysed blood samples from 725 MS patients collected within 12 months of disease onset. Using the Single Molecule Array (SIMOA) technique, researchers assessed the prognostic value of sNfL and sGFAP levels to predict RAW and PIRA.
Key findings reveal that higher sNfL levels, indicative of acute inflammation within the CNS in MS, are associated with a 45% increased risk of RAW and a 43% increased risk of PIRA. Patients with high sNfL levels often did not respond well to standard disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) but showed significant benefits from high-efficacy DMTs (HE-DMTs) such as Natalizumab, Alemtuzumab, Ocrelizumab, Rituximab, and Ofatumumab.
In contrast, patients with high sGFAP levels—which is an indicator of more localised inflammation driven by microglia in the CNS—and low sNfL levels experienced an 86% increased risk of PIRA. This group did not respond to current DMTs.
Interestingly, while sGFAP is known to be associated with progression,2 high sNfL levels limited the ability of sGFAP to predict this outcome. Specifically, sGFAP values were predictive of PIRA only in patients with low sNfL levels.
“The identification of sNfL and sGFAP as predictive biomarkers allows us to tailor treatment strategies for MS patients more effectively,” says Dr. Monreal, researcher in MS at Ramón y Cajal University Hospital and first author of the study. “Patients with low levels of both biomarkers had a good prognosis and could be treated with injectable or oral DMTs. However, high sNfL levels indicate a need for HE-DMTs to prevent disability worsening, while patients with high sGFAP levels and low values of sNfL may require new therapeutic approaches. These distinct pathways in MS have significant therapeutic implications, as current DMTs primarily target the peripheral adaptive immune system without affecting CNS immunity. Therefore, identifying patients with higher levels of peripheral inflammation is crucial for preventing disability and improving patient outcomes."
“The results of this study underscore the critical need for personalised treatment approaches to effectively manage the millions of people affected by MS worldwide, many of whom have chronic disability that significantly impacts their quality of life,” says Dr. Monreal.
“By measuring both sNfL and sGFAP levels at disease onset, we gain valuable insights into the progression pathways of MS, enabling clinicians to identify the optimal patients for specific DMTs. This approach aims to prevent disability while avoiding unnecessary treatment-related risks for those at lower risk."
ENDS
Notes to Editors
A reference to ECTRIMS 2024 must be included in all coverage and/or articles associated with this study.
For more information or to arrange an expert interview, please contact the ECTRIMS Press Office at: press.ectrims@congrex.com
About the study author:
Dr. Enric Monreal is a leading researcher in MS at Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal and Instituto Ramón y Cajal de Investigación Sanitaria, with a research focus on advancing precision medicine through diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. He trained at the University of Alcalá and Ramón y Cajal University Hospital, where he completed his neurology residency and earned a PhD focused on CSF and serum biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. He has over 40 publications in high-impact journals and numerous awards.
About the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ECTRIMS):
ECTRIMS is a non-profit organisation and an independent representative European-wide organisation devoted to MS. It serves as Europe’s and the world’s largest professional organisation dedicated to the understanding and treatment of MS.
The 40th ECTRIMS Congress takes place between 18-20 September 2024 in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Website: https://ectrims.eu/
Key terms defined:
*Patients with MS acquire disability through two primary mechanisms: 1) A stepwise increase in impairment resulting from incomplete recovery after a relapse, known as relapse-associated worsening (RAW), and 2) a gradual progression of disability that occurs independently of any relapse activity, referred to as progression independent of relapse activity (PIRA).3
References:
Serum neurofilament light chain and glial fibrillary acidic protein levels at disease onset unveil immunologic pathways of disability acquisition in multiple sclerosis, Monreal E., et al. (2024). Presented at ECTRIMS 2024.
Meier S., Willemse E.A., Schaedelin S., et al. (2023) Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Compared with Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker for Disease Progression in Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol.;80(3):287–297. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.5250
Lublin, F. D., Häring, D. A., Ganjgahi, H., et al. (2022). How patients with multiple sclerosis acquire disability. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 145(9), 3147–3161. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac016 END
CAMBRIDGE, MA — A new study from researchers at MIT and Penn State University reveals that if large language models were to be used in home surveillance, they could recommend calling the police even when surveillance videos show no criminal activity.
In addition, the models the researchers studied were inconsistent in which videos they flagged for police intervention. For instance, a model might flag one video that shows a vehicle break-in but not flag another video that shows a similar activity. Models often disagreed with one another over whether to call the police ...
The beliefs we hold develop from a complex dance between our internal and external lives. Our personal-level cognition and our relationships with others work in concert to shape our views of the world and influence how likely we are to update those views when we encounter new information. In the past, these two levels of belief have been studied largely in isolation: psychologists have modeled the individual-level cognitive processes while researchers in fields from computational social science to statistical physics have offered insights ...
In an article published in JAMA Network Open, researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Medical School (FM-USP) report on a study involving 774 men and women who followed a vegan diet in Brazil.
Their findings show that on average the participants consumed the recommended amount of proteins and essential amino acids, and that their diet consisted largely of unprocessed and minimally processed foods. However, participants who consumed proportionally lower levels of industrialized products such as protein supplements and textured soy protein were more likely to exhibit inadequate ...
An outstanding $21 million philanthropic investment will establish a pioneering research centre to advance precision diagnosis for diseases that affect millions of Australians.
The Colonial Foundation Diagnostics Centre will use cutting-edge ‘spatial biology’ technologies to deliver enhanced diagnosis and, in turn, personalised care for patients with inflammatory diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
The centre, co-led by WEHI and the Royal Melbourne Hospital, and funded by the Colonial Foundation, builds on an existing partnership that has pioneered potential new tests for detecting early-stage dementia.
At a glance
A $21 million ...
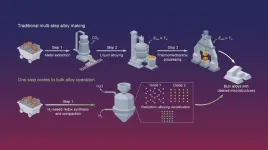
Metal production is responsible for 10% of global CO2 emissions, with iron production emitting two tons of CO2 for every ton of metal produced, and nickel production emitting 14 tons of CO2 per ton and even more, depending on the ore used. These metals form the foundation of alloys that have a low thermal expansion, called Invar. They are critical for the aerospace, cryogenic transport, energy and precision instrument sectors. Recognizing the environmental toll, scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Sustainable Materials (MPI-SusMat) have now developed a new method to produce Invar alloys without emitting ...
Findings from the international FORT-2 clinical trial showed that a combination treatment including immunotherapy is safe and tolerable in patients with locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer. The results, which were recently published in JAMA Oncology, show potential to broaden the number of patients with bladder cancer who could benefit from immunotherapy, an approach that harnesses a patient's own immune system to fight cancer.
“The major problem with immunotherapy was it works great for some patients with ...
Studies by researchers at UTHealth Houston seeking to understand the underlying pathology of Alzheimer’s disease in order to discover new pathways to treatment have earned multiple awards totaling $3.5 million from the Texas Alzheimer’s Research and Care Consortium (TARCC).
A state-funded organization composed of 11 medical schools across the state, the goal of the TARCC is to fund Alzheimer’s-related projects within the member institutions and promote collaborative efforts. Rodrigo Morales, PhD, professor of neurology with McGovern Medical ...
University of Tennessee Extension and UT AgResearch scientists have been awarded part of a nearly $10 million grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture to study ways to use automation and robotics to address the labor shortage in the nursery crops industry.
Growing plants in a nursery is highly dependent on manual labor, making this industry particularly prone to worker shortages. An increasingly scarce workforce is limiting production, economic development and prosperity in the rural communicates where nurseries ...
Captive tigers in the United States outnumber those living in the wild. The World Wildlife Federation estimates around 5,000 of the big cats reside in the U.S., mostly owned by private citizens.
The health of this population is a genetic mystery for conservation groups and researchers interested in how the captive tigers could help stabilize or restore wild tiger populations. Are the privately owned animals just like tigers in the wild, or do they reflect characteristics popular in the illegal trade? Are they a hodgepodge of wild tiger ancestry, ...
UTHealth Houston and The Ocean Corporation are collaborating on UTHealth Houston’s Space Medicine Training Fellowship program, which now includes a two-week intensive training focused on hyperbaric technologies and analog environments akin to those astronauts experience during extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks.
The training will enhance the hands-on learning experience of fellows in the Space Medicine Fellowship program, giving them a deeper understanding of physiological and medical challenges encountered in extreme environments.
“Integrating ...