(Press-News.org) Buprenorphine, an evidence-based treatment for opioid use disorder, is currently underprescribed because of concerns that it can cause ‘precipitated withdrawal’, in which the first dose causes sudden, intense pain and anxiety that resolves within a few hours. A new review of the best available evidence has found that the rate of buprenorphine-precipitated withdrawal in adults with opioid use disorder is low and should not be a barrier to use. The review is published in the scientific journal Addiction.
Lead author Dr Caroline Gregory, of the University of Ottawa, explains: “There is a lot of speculation that buprenorphine-precipitated withdrawal is a widespread problem. This had led both doctors and patients to resist using buprenorphine to treat opioid use disorder. Until now, we haven’t known the size of the problem. Our study reviewed all of the available evidence to determine how often buprenorphine-precipitated withdrawal occurs. We found that between 0 and 13.2% of adults with opioid use disorder taking their first dose of sublingual buprenorphine experienced precipitated withdrawal. Most of the evidence was at the lower end of that range, and precipitated withdrawal symptoms were generally mild.
“This means that the best evidence we have is that buprenorphine-precipitated withdrawal is a low risk and should not stop doctors or patients from using buprenorphine.”
The review also found room for improvement. The overall quality of the studies included in this review was poor: many didn’t have a process for recording cases of precipitated withdrawal and many didn’t record the severity of withdrawal. The review also found that there is no standard definition of precipitated withdrawal. Even so, the highest-quality studies to date have consistently found low rates of precipitated withdrawal.
Dr. Gregory says, “We need better evidence to measure the true risk of precipitated withdrawal. Until those high-quality studies are conducted, doctors and patients should not resist using this highly effective treatment for opioid use disorder.”
This systematic review looked at 26 studies of buprenorphine-precipitated withdrawal, including 5 randomized trials, all conducted between 2002 and 2023 and with a total sample size of 4,497 patients.
-- Ends –
For editors:
This paper is free to read online for one month after publication on the Wiley Online Library (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/add.16646) or you may request a copy from Jean O’Reilly, Editorial Manager, Addiction, jean@addictionjournal.org.
To speak with lead author Dr. Caroline Gregory, please contact her at the University of Ottawa by e-mail (cgregory@toh.ca).
Full citation for article: Gregory C, Yadav K, Linders J, Sikora L, and Eagles D. Incidence of Buprenorphine-Precipitated Opioid Withdrawal in Adults with Opioid Use Disorder: A Systematic Review. Addiction. 2024. DOI: 10.1111/add.16646
Primary funding: No specific funding was required.
Declaration of interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Addiction is a monthly international scientific journal publishing peer-reviewed research reports on alcohol, substances, tobacco, gambling, editorials, and other debate pieces. Owned by the Society for the Study of Addiction, it has been in continuous publication since 1884.
END
Risk of buprenorphine triggering sudden opioid withdrawal is low
2024-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
FAIR Health releases interactive tool tracking opioid abuse and dependence state by state
2024-09-26
NEW YORK, NY—September 26, 2024—Today FAIR Health released the Opioid Tracker, a free, interactive tool tracking opioid abuse and dependence state by state. A brief released simultaneously offers a user’s guide to the Opioid Tracker.
Available on FAIR Health’s website fairhealth.org, the Opioid Tracker includes a heat map representing the percentage of patients with opioid abuse and dependence diagnoses compared to all patients receiving medical services in 2023 for each state. Clicking on a state displays an infographic for ...
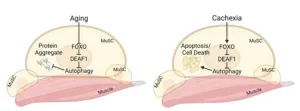
Duke-NUS discovery advances quest for treatment for age- and cancer-related muscle degeneration
2024-09-26
With the global population ageing rapidly, sarcopenia, a condition that affects millions of older adults and severely diminishes their quality of life, is emerging as an urgent public health issue. Now, a new discovery by scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School could lead to improved treatments for the condition.
In the study, published in the journal Autophagy, the scientists found that the levels of a certain type of protein, called DEAF1 (Deformed epidermal autoregulatory factor-1), need to be maintained within optimal levels ...
Women with premature ovarian insufficiency are at greater risk of severe autoimmune diseases
2024-09-26
Severe autoimmune conditions such Type I diabetes, Addison’s disease, lupus and inflammatory bowel disease, are between two to three times more common in women who have been diagnosed with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) compared to the general population.
The research, published today (Thursday) in Human Reproduction, one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, is the largest to investigate the link between autoimmune conditions and POI, has followed nearly 20,000 women for ...
Remote video consultations linked to reduced depression and anxiety
2024-09-25
Remote video consultations between patients and mental health specialists show a small but significant improvement on symptoms of depression and anxiety, finds a trial published by The BMJ today.
Although the effect size is small, the researchers say the effect is still meaningful given the high levels of these disorders in the community.
Globally, depression and anxiety disorders are among the top leading causes of years lived with disability, but most people with depression and anxiety ...
Questions over safety and effectiveness of new Alzheimer’s drug
2024-09-25
The safety and effectiveness of donanemab - an Alzheimer’s drug recently approved by the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) - is called into question in an investigation published by The BMJ today.
Journalists Jeanne Lenzer and Shannon Brownlee explore concerns not only about its effectiveness and the number of deaths among patients taking the drug, but also about financial ties to drug makers among the “independent” advisory panellists who recommended approval.
Donanemab, developed by Eli Lilly, is the latest in a new class ...
Additional GP funding has been squeezed this year, finds BMJ investigation
2024-09-25
Budgetary decisions by commissioners across England are affecting GPs’ ability to offer their patients what most people regard as essential services and forcing some practices to close, an investigation by The BMJ has found.
This year, eight in 10 Integrated Care Boards (ICBs) - responsible for planning health services for their local population - either reduced or froze discretionary funding for general practices as a proportion of their overall budget for services such as taking blood, wound care, ...
AI could predict breast cancer risk via ‘zombie cells’
2024-09-25
Women worldwide could see better treatment with new AI technology which enables better detection of damaged cells and more precisely predict the risk of getting breast cancer, shows new research from the University of Copenhagen.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. In 2022, the disease caused 670,000 deaths worldwide. Now, a new study from the University of Copenhagen shows that AI can help women with improved treatment by scanning for irregular-looking cells to give better risk assessment.
The study, published in The Lancet Digital Health, found that the AI technology was far better at predicting risk of cancer ...
Breakthrough research identifies new targets for wound healing
2024-09-25
(Thursday, 26 September 2024) Novel research, presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2024, has identified key molecular targets that could significantly enhance the healing of both acute and chronic wounds.1
These findings represent a crucial advancement in wound care, paving the way for more effective treatment options and improved patient outcomes.
Globally, acute and chronic wounds affect nearly one billion people.2 In particular, chronic wounds pose a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems and severely impact ...
Are branch faults the “on-ramps” that lead to great continental transform earthquakes?
2024-09-25
The five largest continental transform earthquakes since 2000 all originated on a branch of the main fault—and two researchers predict that the next great earthquake of this type will also get its start on a branch or splay fault.
Last year’s magnitude 7.8 Pazarcık earthquake in Türkiye was one of these large and damaging earthquakes, where two continental tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally. That earthquake began on a branch fault, as did the 2001 magnitude 7.8 Kokoxili earthquake in northern Tibet, the 2002 magnitude 7.9 Denali earthquake in Alaska, the 2008 magnitude 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in China, and the 2016 ...
Tumour-specific antibodies able to detect melanoma in its earliest stages, new study shows
2024-09-25
(Thursday, 26 September 2024, Amsterdam, Netherlands) Innovative research has unveiled promising advancements in melanoma detection, which could significantly enhance diagnosis and prognosis by identifying the disease at its earliest, most treatable stages.1
This new method, presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2024, uses tumour-specific profiling to detect antibodies unique to stage I and II melanoma patients.
Melanoma, a skin cancer with a high mutation rate,2 ...