(Press-News.org) The study, published in Lancet Neurology, detailed the “head-to-head” trial implemented by the researchers to test two drugs, mexiletine and lamotrigine, on people with the condition.
The trial, which was conducted at the UCL Queen Square Multidisciplinary Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases and the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCLH, involved 60 adults with confirmed non-dystrophic myotonia.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either mexiletine for eight weeks followed by lamotrigine for eight weeks, or the reverse order, with a seven-day break in between treatments. Neither the participants nor the researchers knew which treatment was being given at any time.
At the end of the trial, lamotrigine was found to reduce stiffness – the main symptom of non-dystrophic myotonia – by around the same amount as mexiletine.
Chief investigator, Dr Vino Vivekanandam (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and consultant neurologist), said: “Approximately one in 17 people in the UK have a rare disease and the majority have no treatment. Many are neurological diseases and rarity makes clinical trials to develop treatments very difficult. Head-to-head trials comparing drugs are important in order to allow us to identify which treatments are ideal.
“The trial results are very exciting and important for patients with this muscle channelopathy.”
Non-dystrophic myotonias are life-changing muscle disorders caused by problems with ion channels in the muscles. Symptoms (such as muscle stiffness, pain, weakness, and fatigue) usually start in childhood and can cause significant disability – reducing quality of life and employability. There is currently no cure.
In 2012, the same UCL team led a multi-centred international trial that repurposed mexiletine – a sodium channel blocker – and showed it was effective in treating non-dystrophic myotonia and improving quality of life.
As a result, mexiletine became the first-line treatment for non-dystrophic myotonias world-wide.
However, not all patients respond to the treatment and one third developed significant side-effects, the most common being reflux or gastrointestinal side effects. Additionally, mexiletine can’t be prescribed during pregnancy, when myotonia often worsens.
Lamotrigine provides an alternative solution, as the trial showed that the drug was well tolerated by patients, and has additional advantages as it can be used in pregnancy and is cheaper. No serious side effects were reported.
Senior author Professor Michael Hanna (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology Director and consultant neurologist) said: “Drug repurposing is an important strategy in developing treatments for rare diseases. This is the first head-to-head trial in this rare muscle disease and the results will directly inform patient care and provide more ‘real-world’ options for patients.”
This research will impact clinical practice globally as mexiletine is often not accessible in developing countries or is expensive in developed countries. The results demonstrate that lamotrigine is a comparable treatment and therefore provides an excellent treatment option for affected patients.
Dr Vivekanandam said: “Based on this trial data, we have already developed a personalised treatment algorithm for clinical practice which is already in use in our clinical service, which takes into consideration several aspects of the trial and the mechanism of actions of lamotrigine and mexiletine as well as local economic considerations.”
The research was funded by the Neuromuscular Study Group, Jon Moulton Charity Trust, and a fast track grant from the National Institute for Health and Care Research biomedical research centre at UCLH. The team are grateful to the patients involved and their families for their support throughout the trial.
END
Commonly used drug could transform treatment of rare muscle disorder
2024-09-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Michael Frumovitz, M.D., posthumously honored with Julie and Ben Rogers Award for Excellence
2024-09-27
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center has posthumously awarded Michael Frumovitz, M.D., with the Julie and Ben Rogers Award for Excellence in Patient Care. The annual award recognizes employees who consistently demonstrate excellence in their work and dedication to MD Anderson’s mission to end cancer. The award’s focus rotates among the areas of patient care, research, education, prevention and administration, with this year’s award focusing on patient care.
Frumovitz dedicated more than 20 years of service to MD Anderson, most recently as chief patient experience officer and professor in Gynecologic ...
NIH grant supports research to discover better treatments for heart failure
2024-09-27
A University of Arizona College of Medicine – Phoenix researcher was recently awarded a $1.9 million National Institutes of Health grant to study the molecular mechanisms of how dilated cardiomyopathy progresses to heart failure, which could eventually lead to better preventive and treatment options for heart failure.
Heart failure is inextricably linked with dilated cardiomyopathy, or DCM, a disease characterized by the progressive enlargement of the heart and reduced contractility reflected by reduced ejection fraction. ...
Clinical cancer research in the US is increasingly dominated by pharmaceutical industry sponsors, study finds
2024-09-27
Clinical cancer research in the U.S. is increasingly dominated by pharmaceutical industry sponsors, study finds
Study underscores need for increased investment in federally funded cancer clinical trials
SEATTLE – September 27, 2024 – Researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center identified a substantial increase over the past decade in the proportion of patients with cancer in the U.S. who participate in pharmaceutical industry sponsored clinical trials compared to those conducted with federal government support. Published in The Journal of Clinical Oncology and presented at the ASCO Quality Care Symposium, these findings reveal trends of underinvestment in federally ...
Discovery of 3,775-year-old preserved log supports ‘wood vaulting’ as a climate solution
2024-09-27
A new study published in the journal Science suggests that an ordinary old log could help refine strategies to tackle climate change.
A team of researchers led by University of Maryland Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Professor Ning Zeng analyzed a 3,775-year-old log and the soil it was excavated from. Their analysis, published on September 27, 2024, revealed that the log had lost less than 5% carbon dioxide from its original state thanks to the low-permeability clay soil that covered it.
“The wood is nice and solid—you could probably make a piece of furniture out of it,” Zeng noted.
Understanding the ...
Preterm births are on the rise, with ongoing racial and economic gaps
2024-09-27
Preterm births have increased by more than 10 percent over the past decade, with racial and socioeconomic disparities persisting over time, according to a new study analyzing more than five million births.
The study, published in the journal JAMA Network Open, also found that some factors that increase the risk for preterm birth—such as diabetes, sexually transmitted infections, and mental health conditions—became much more common over the past decade, while other factors that protect against preterm birth declined.
“Our findings not only show that preterm births are on the rise, but provide clues as ...
Menopausal hormone therapy use among postmenopausal women
2024-09-27
About The Study: The results of this cross-sectional study show that over the past 2 decades, menopausal hormone therapy use declined among U.S. postmenopausal women of all age and racial and ethnic groups. Women of racial and ethnic minority groups had lower prevalence of menopausal hormone therapy use compared to non-Hispanic white women.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Lin Yang, PhD, (lin.yang@ahs.ca) and Adetunji T. Toriola, MD, PhD, MPH, (a.toriola@wustl.edu).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3128)
Editor’s ...
Breaking the chain of intergenerational violence
2024-09-27
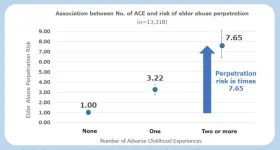
New research shows the connection between adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), such as physical or emotional abuse, and an increased risk of people growing up to be abusive against older generations. While generational trauma is known to be passed down from parent to child, the study showed that it can also reverberate upwards from parent to older generations. A survey of over 13,000 people in Japan found that about half had one or more ACEs. Of these, 8.5% self-reported committing some form of physical or verbal abuse against people aged over 65. An important contributing factor was the person’s mental and physical health, both of which are known to be affected by ...
Unraveling the role of macrophages in regulating inflammatory lipids during acute kidney injury
2024-09-27
Tsukuba, Japan—Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with a poor prognosis, and no effective treatment has been established to date. Understanding the mechanisms that prevent the progression of AKI is crucial. In AKI, immune cells known as macrophages produce lipid mediators (LMs), which are lipids with significant physiological activity and play a pivotal role in promoting and suppressing inflammation. Thus, elucidating their function is of paramount importance.
In this study, researchers focused ...
Deep underground flooding beneath arima hot springs: A potential trigger for the 1995 Kobe (Hyogo-Ken Nanbu) earthquake
2024-09-27
Tsukuba, Japan—Hot springs frequently contain water that originates from rocks within the Earth's crust. This can be confirmed through isotopic analysis. Arima Hot Springs, located in Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan, exhibit unique characteristics, including salinity that is more than twice that of seawater, indicating that their water likely originates from the Philippine Sea Plate. However, a direct evidence supporting this connection is lacking.
In this study, researchers confirmed that the isotopic ratios of plate-derived water beneath Arima Hot Springs, as predicted by a numerical model, agreed with those of nonmeteoric water components found ...
Sharing biosignals with online gaming partners to enhance a mutual sense of social presence between complete strangers
2024-09-27
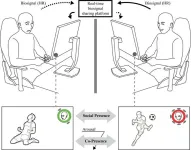
Tsukuba, Japan—Online communication tools are intended to bring people closer together. However, they often fail to sufficiently meet the human need for fulfilling social interactions. What is missing is a sense of social presence, that is, a "sense of being present with another person." This sense of social presence can be felt during mediated interactions, such as when using web conferencing tools or playing video games.
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba have identified a method for augmenting the sense of social presence in online interactions through the sharing of biosignals. Biosignals such as heart rate can ...