Honey, I shrunk the city: What should declining Japanese cities do?
A study on factors that contribute to population changes based on city size
2024-09-30
(Press-News.org)
Aging societies and population decline have been on the rise globally, but in Japan, the situation has exasperated tenfold. A staggering 36.21 million people, or 28.9% of the populace, are 65 and over. Further, 74.6% of Japan’s 1,747 cities are categorized as shrinking, with urban policies struggling to keep up with the decline. However, the factors that correlate with population changes in cities of varying sizes have not been clarified.
Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, examined these multidimensional factors using the Economic, Social, and Educational (ESE) dataset, which is a cross-sectional dataset of 270 indicators of each Japanese city. This study used the machine-learning algorithm XGBoost, which analyzed the nonlinear relationships between the population change from 2005 to 2010 and the other 269 indicators.
The results revealed that most shrinking cities in Japan are medium-sized or small. Regarding the multidimensional factors, the rate of population change is strongly correlated with social-related indicators, such as changes among persons ages 0-14 in small cities, natural population change in medium-sized cities, and migration rates in large cities. Additionally, population changes correlated with the financial strength index as an economic-related factor in medium-sized cities. Furthermore, population changes correlated with the designation of underpopulated areas as an urban-planning-related factor in small cities.
“These results imply that urban policies should be designed according to the size of the city,” said Dr. Kato. “Medium-sized cities should effectively formulate policies other than urban planning, such as childcare initiatives that would contribute to improvements in natural population change and the financial strength index. Meanwhile, small cities need to consider designating underpopulated areas.”
The findings were published in Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through the “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-30
A research team led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) Brain Disease Research Group, in collaboration with Director Justin C. Lee of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, President Do-Young Noh) and Professor Junghee Lee from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has uncovered a new mechanism involving astrocytes for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and proposed a novel therapeutic target. In this study, the researchers revealed that autophagy pathway ...
2024-09-30
Media contacts:
Lisa Robinson, lrobinson@aap.org
Alex Hulvalchick, ahulvalchick@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Announces its First Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Prescriptions
Pediatricians should prescribe opioids for pain when necessary, with recommended precautions in place to increase safety, according to a clinical practice guideline released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics has published its first clinical ...
2024-09-30
Drivers of electric vehicles (EVs) are more likely to be involved in at-fault road traffic accidents than drivers of petrol and diesel cars, research by Lero, the Research Ireland Centre for Software, at University of Limerick and Universitat de Barcelona, reveals.
In the analysis of insurance claims and data from onboard sensors, due to be published in the November issue of the journal Accident Analysis & Prevention, the Lero researchers reveal a number of key findings:
Electric and hybrid drivers exhibit different behaviours ...
2024-09-30
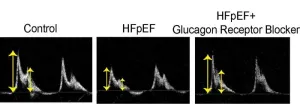
Duke-NUS scientists and their collaborators have discovered a potential new treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a type of heart disease that is notoriously difficult to treat. The team discovered that the diseased heart cells had high levels of glucagon activity, a pancreatic hormone that raises blood sugar (glucose) levels. Armed with this novel insight, the scientists demonstrated that a drug that blocks the hormone’s activity, can significantly improve heart ...
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A substantial number of patients with brain metastases who experience cognitive side effects following radiation therapy may fully regain cognitive function, according to a pooled analysis of three large, phase III clinical trials. Recovery was more likely for people treated with conformal, or highly targeted, radiation techniques, compared to standard whole-brain treatment. The findings will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) ...
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A radiopharmaceutical therapy that has successfully extended progression-free survival for patients with neuroendocrine tumors shows early promise for delivering similar benefits to patients with difficult-to-treat meningioma, a type of brain tumor. Findings of the nonrandomized phase II study will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
“We’ve found a therapy with a meaningful signal for effectiveness and safety for people with refractory meningioma, a condition with no ...
2024-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics encourages parents and caregivers to read aloud with their newborns and young children as an opportunity to foster loving, nurturing relationships during a critical time of brain development, and recommends that pediatricians support families with guidance and books at well-child visits, according to an updated policy statement.
The policy statement, “Literacy Promotion: An Essential Component of Primary Care Pediatric Practice,” marks the first update in AAP recommendations since 2014. Given the extraordinary amount of research in this area, an accompanying ...
2024-09-28
The study also examined the impact of different game structures, such as simultaneous versus alternating decision-making, and the option of voluntary participation. The results showed that these variations significantly influence participants' cooperation rate.
The research reveals that people tend to cooperate even after being defected, which contradicts many traditional game theory models. "This finding is particularly fascinating because it suggests that humans are more forgiving and cooperative than previously thought," said Dr. Hitoshi Yamamoto, the study's lead researcher.
The ...
2024-09-27
An innovative analysis of shared segments within the genome — an indication of distant “relatedness” — has identified undiagnosed cases of Long QT syndrome, a rare disorder that can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, fainting and sudden cardiac death.
The findings, reported in the journal Nature Communications, illustrate the feasibility of the new approach developed by researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center to detect undiagnosed carriers of rare ...
2024-09-27
UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers and physicians who specialize in treating patients with radiation therapies will present data on the latest radiation oncology research and clinical trial results at the 66th annual American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) meeting in Washington D.C., Sept. 29 to Oct. 2.
The annual meeting, which is the leading meeting in radiation oncology, will feature 23 abstracts from UCLA investigators that highlight key areas of radiation oncology, including new research in subspecialties ranging from survivorship, lung cancer/thoracic malignancies, physics, sarcoma, gastrointestinal cancer, genitourinary cancer, gynecological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Honey, I shrunk the city: What should declining Japanese cities do?
A study on factors that contribute to population changes based on city size