(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, October 1, 2024 – Too warm with a jacket on but too cold without it? Athletic apparel brands boast temperature-controlling fabrics that adapt to every climate with lightweight but warm products. Yet, consider a fabric that you can adjust to fit your specific temperature needs.
Inspired by the dynamic color-changing properties of squid skin, researchers from the University of California, Irvine developed a method to manufacture a heat-adjusting material that is breathable and washable and can be integrated into flexible fabric. They published their proof-of-concept for the advanced bioinspired composites in APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing.
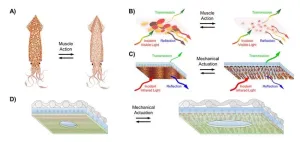
“Squid skin is complex, consisting of multiple layers that work together to manipulate light and change the animal’s overall coloration and patterning,” said author Alon Gorodetsky. “Some of the layers contain organs called chromatophores, which transition between expanded and contracted states (upon muscle action) to change how the skin transmits and reflects visible light.”
Instead of manipulating visible light, the team engineered a composite material that operates in the infrared spectrum. As people heat up, they emit some of their heat as invisible, infrared radiation (this is how thermal cameras work). Clothing that manipulates and adapts to this emission and is fitted with thermoregulatory features can finely adjust to the desired temperature of the wearer. The material consists of a polymer covered with copper islands, and stretching it separates the islands and changes how it transmits and reflects infrared light. This innovation creates the possibility of controlling the temperature of a garment.
In a prior publication in APL Bioengineering, the team modeled their composite material’s adaptive infrared properties. Here, they built upon the material to increase its functionality by making it washable, breathable, and integrated into fabric.
The team layered a thin film onto the composite to enable easy washing without degradation — a practical consideration for any fabric. To make the composite material breathable, the team perforated it, producing an array of holes. The resulting product exhibited air and water vapor permeability similar to cotton fabrics. The team then adhered the material to a mesh to demonstrate straightforward fabric integration.
Using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, the team tested the material’s adaptive infrared properties and used a sweating guarded hot plate to test the dynamic thermoregulatory properties. Even with simultaneous thin-film layering, perforations, and fabric integration, the materials’ heat-managing performance did not suffer.
“Our advanced composite material now opens opportunities for most wearable applications but may be particularly suited for cold weather clothing like ski jackets, thermal socks, insulated gloves, and winter hats,” said Gorodetsky.
In addition to the possible applications for the fabric, the manufacturing process the team used to develop the fabric is also full of potential.
“The strategies used for endowing our materials with breathability, washability, and fabric compatibility could be translated to several other types of wearable systems, such as washable organic electronics, stretchable e-textiles, and energy-harvesting triboelectric materials,” said Gorodetsky.
###
The article “Manufacturing of breathable, washable, and fabric-integrated squid skin-inspired thermoregulatory materials” is authored by Sanghoon Lee, Erica M. Leung, Mohsin Ali Badshah, Aleksandra Anna Strzelecka, and Alon Gorodetsky. It will appear in APL Bioengineering on Oct. 1, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0169558). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0169558.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
###
END
Squid-inspired fabric for temperature-controlled clothing
New fabric allows for user-adjusted warmth, breathability, and washability.
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using antimatter to detect nuclear radiation
2024-10-01
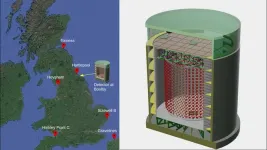
WASHINGTON, Oct. 1, 2024 – Nuclear fission reactors act as a key power source for many parts of the world and worldwide power capacity is expected to nearly double by 2050. One issue, however, is the difficulty of discerning whether a nuclear reactor is being used to also create material for nuclear weapons. Capturing and analyzing antimatter particles has shown promise for monitoring what specific reactor operations are occurring, even from hundreds of miles away.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Sheffield and the University of Hawaii developed ...
Modeling the minutia of motor manipulation with AI
2024-10-01
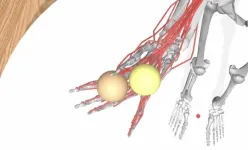
In neuroscience and biomedical engineering, accurately modeling the complex movements of the human hand has long been a significant challenge. Current models often struggle to capture the intricate interplay between the brain's motor commands and the physical actions of muscles and tendons. This gap not only hinders scientific progress but also limits the development of effective neuroprosthetics aimed at restoring hand function for those with limb loss or paralysis.
EPFL professor Alexander Mathis and his team have developed an AI-driven approach that ...
Survival gap eliminated for Black cord blood recipients with blood cancers, study finds
2024-10-01
Patients who receive umbilical cord blood transplants for blood cancers now live equally long regardless of their race, new research from UVA Cancer Center shows.
The findings, from UVA Health’s Karen Ballen, MD, and collaborators, suggests that a previously identified survival gap for Black recipients has closed and that overall survival for all recipients has increased.
The retrospective analysis looked at more than 2,600 adults and children with blood cancers who received cord blood between 2007 and 2017 ...
Nominate a stroke hero today: 2025 Stroke Hero Awards open for submissions
2024-10-01
DALLAS, Oct. 1, 2024 – Strokes can strike at any age, challenging survivors to overcome physical, emotional and cognitive changes. Nominations are open now for the 2025 Stroke Hero Awards from the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, which is celebrating a century of lifesaving impact this year. The awards recognize stroke survivors, caregivers, advocates and experts making a difference in the stroke community.
Every 40 seconds someone in the U.S. has a stroke[1], according to the American Heart Association’s 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistical Update. Nearly 1 in 4 stroke survivors face the ...
Seven years on, INSEAD study reveals #MeToo's unexpected impact
2024-10-01
Seven years after actor Alyssa Milano’s tweet launched the #MeToo movement into the global consciousness, attitudes towards sexual harassment and assault have shifted in many countries. A new study shows that the movement’s impact doesn’t stop there.
INSEAD professors Frédéric Godart and David Dubois, alongside Clément Bellet of Erasmus University Rotterdam, found that #MeToo triggered far-reaching changes in consumer behaviour. Sales of stereotypically feminine shoes like high heels dropped significantly weeks after the #MeToo movement swept the media ...
Addressing the geriatric healthcare workforce shortage
2024-10-01
INDIANAPOLIS – The pandemic has highlighted the acute shortage of nurses and nursing assistants needed to care for the growing number of older adults in long-term care facilities. Yet getting nursing students excited, engaged and feeling competent to take on the challenges of caring for nursing home patients has proved elusive.
To address this critical workforce gap, researchers from Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University School of Medicine have developed and tested an innovative curriculum for nursing students, exposing ...
Age trumps gender, income and postcode for consumers' clothing habits
2024-10-01
The first-ever nationwide study into how Australians use and dispose of clothing has revealed people are buying too many clothes and are unsure how to discard them responsibly.
Conducted by RMIT University and commissioned by the Kmart Group and the Queensland Government, a study of 3,080 Australians explored how they acquired, used and disposed of their clothing.
Australians are among the world’s biggest clothing consumers, importing 1.4 billion units or over 383,000 tonnes annually.
But each year, more than 200,000 tonnes of clothing is sent to landfill.
The authors recommend establishing a national textile collection program for unwearable clothing that ...
Researchers develop method to obtain fine spatial and temporal resolution land surface temperature data
2024-10-01
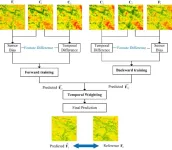
Scientists need fine spatial and temporal resolution land surface temperature (LST) data for many types of research and applications. Spatio-temporal fusion, a technique that combines data from multiple sources to create high-resolution images with both spatial (space) and temporal (time) details, is an important solution for researchers needing fine spatio-temporal resolution LST data. A team of researchers propose a new spatio-temporal fusion method based on Restormer (RES-STF).
Their work is published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on August 21, 2024.
LST data, the measurement ...
Feet first: AI reveals how infants connect with their world
2024-10-01
Recent advances in computing and artificial intelligence, along with insights into infant learning, suggest that machine and deep learning techniques can help us study how infants transition from random exploratory movements to purposeful actions. Most research has focused on babies’ spontaneous movements, distinguishing between fidgety and non-fidgety behaviors.
While early movements may seem chaotic, they reveal meaningful patterns as infants interact with their environment. However, we still lack understanding of how infants intentionally engage with their surroundings and the principles guiding their ...
Addressing health equity in childhood asthma requires engaging affected communities
2024-10-01
NEW YORK, NY (Oct. 1, 2024) – Systemic racism remains a significant challenge in efforts to address health disparities in childhood asthma. A new American Thoracic Society report provides practical frameworks to begin the research necessary to make real progress in treating asthma in Black and Latino children, who are more likely than their white counterparts to report to emergency rooms in the U.S.
Stephanie Lovinsky-Desir, MD, and a diverse group of researchers, clinicians, social scientists and community health workers shared their findings in the report published online this week in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
[Press-News.org] Squid-inspired fabric for temperature-controlled clothingNew fabric allows for user-adjusted warmth, breathability, and washability.