(Press-News.org) Climate change and economic inequality are deeply interconnected, with the potential to exacerbate each other if left unchecked. A new study published in Nature Climate Change sheds light on this critical relationship using data from eight large-scale Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) to examine the distributional impacts of climate policies and climate risks. The study provides robust evidence that climate policies aligned with the Paris Agreement can mitigate long-term inequality while addressing climate change.
Led by Johannes Emmerling, Senior Scientist at the Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change (CMCC), the study assesses how climate change is projected to increase inequality within countries, with the Gini index increasing by an average of 1.4 points by 2100. However, implementing ambitious climate policies—such as carbon pricing—can significantly reduce this inequality increase in the long term. The study finds that redistributing carbon revenues equally among citizens can not only offset short-term economic costs but also reduce inequality, lowering the Gini index by nearly 2 points.
“This research demonstrates that with careful policy design, we can address both climate change and economic inequality—two of the most pressing challenges of our time,” says Emmerling. “By showing how redistributing carbon revenues can lead to immediate benefits for lower-income households while setting us on a path to a stable climate, we hope to provide policymakers with a roadmap for more equitable and politically feasible climate action.”
The innovative multi-model comparison highlights that, while climate policies may result in a short-term rise in inequality, well-designed redistribution mechanisms can reverse this trend and contribute to greater social justice.
“As countries around the world look for ways to meet climate goals without exacerbating inequality, this paper comes as especially timely, highlighting the importance of smart policy design to ensure that the benefits of climate action are shared equitably,” said Emmerling.
“This research highlights the need and the possibility to align climate safety and climate justice. This is a research topic of high importance for our institute, and this international collaboration is a testament to the capacity of community research to inform high-stakes issues”, concludes Massimo Tavoni, author of the study and director of the European Institute on Economics and the Environment at CMCC.
END
Addressing climate change and inequality: A win-win policy solution
2024-10-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
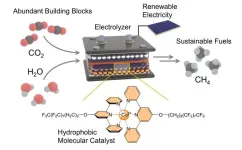
Innovative catalyst produces methane using electricity
2024-10-04
Researchers at the University of Bonn and University of Montreal have developed a new type of catalyst and used it in their study to produce methane out of carbon dioxide and water in a highly efficient way using electricity. Methane can be used, for example, to heat apartments or as a starting material in the chemical industry. It is also the main component of natural gas. If it is produced using green electricity, however, it is largely climate neutral. The insights gained from the model system studied by the researchers can be transferred to large-scale technical ...
Liver X receptor beta: a new frontier in treating depression and anxiety
2024-10-04
Houston, Texas – In a state-of-the-art Bench to Bedside review published in the journal Brain Medicine (Genomic Press), researchers Dr. Xiaoyu Song and Professor Jan-Åke Gustafsson from the University of Houston and Karolinska Institutet (Sweden) shed light on the therapeutic potential of liver X receptor beta (LXRβ) in treating depression and anxiety. This comprehensive analysis marks a significant step forward in understanding the molecular underpinnings of mental health disorders and potentially revolutionizing their treatment.
LXRβ, a nuclear receptor initially known for its role in cholesterol metabolism and inflammation, is now emerging as a crucial ...
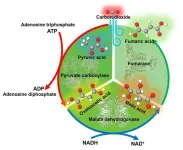
Improving fumaric acid production efficiency through a ‘more haste, less speed’ strategy
2024-10-04
As plastic waste continues to build up faster than it can decompose, the need for biodegradable solutions is evident.
Previously, Professor Yutaka Amao and his team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis succeeded in synthesizing fumaric acid, a raw material for biodegradable plastics from biomass-derived pyruvic acid and carbon dioxide. However, the fumaric acid production process reported earlier has a problem with producing undesirable substances as byproducts in addition to L-malic acid, which is ...
How future heatwaves at sea could devastate UK marine ecosystems and fisheries
2024-10-04
The oceans are warming at an alarming rate. 2023 shattered records across the world’s oceans, and was the first time that ocean temperatures exceeded 1oC over pre-industrial levels. This led to the emergence of a series of marine heatwave events across both hemispheres, from the waters around Japan, around South America, and across the wider North Atlantic. Marine heatwaves are periods of extremely warm sea temperatures that can form in quite localized hot spots but also span large parts of ocean ...
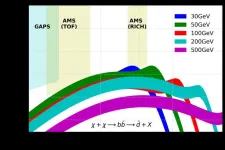
Glimmers of antimatter to explain the "dark" part of the universe
2024-10-04
One of the great challenges of modern cosmology is to reveal the nature of dark matter. We know it exists (it constitutes over 85% of the matter in the Universe), but we have never seen it directly and still do not know what it is. A new study published in JCAP has examined traces of antimatter in the cosmos that could reveal a new class of never-before-observed particles, called WIMP (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles), which could make up dark matter. The study suggests that some recent observations ...
Kids miss out on learning to swim during pandemic, widening racial and ethnic disparities
2024-10-04
Nearly three out of four kids in Chicago had no swimming lessons in summer of 2022, with significant racial and ethnic differences, according to a parent survey from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago published in Pediatrics. Black and Hispanic/Latine kids were disproportionately affected (85 percent and 82 percent, respectively), compared to white kids (64 percent).
The most common reasons for not getting swimming lessons also differed among racial and ethnic groups. Parents of White kids reported they ...
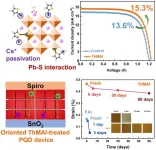
DGIST restores the performance of quantum dot solar cells as if “flattening crumpled paper!”
2024-10-04
□ Professor Jongmin Choi’s team from the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee) conducted joint research with Materials Engineering and Convergence Technology Professor Tae Kyung Lee from Gyeongsang National University and Applied Chemistry Professor Younghoon Kim from Kookmin University. The researchers developed a new method to improve both the performance and the stability of solar cells using “perovskite quantum dots.” They developed longer-lasting solar cells by addressing the issue of distortions on the surface of quantum dots, which deteriorate the ...
Hoarding disorder: ‘sensory CBT’ treatment strategy shows promise
2024-10-04
Rehearsing alternative outcomes of discarding through imagery rescripting shows promise as a treatment strategy for people who hoard, a study by UNSW psychology researchers has shown.
Hoarding disorder is a highly debilitating condition that worsens with age. People who hoard form intense emotional attachments to objects, accumulate excessive clutter, and have difficulty discarding possessions. Many avoid treatment.
People who hoard also experience more frequent, intrusive and distressing mental images in their daily lives, says Mr Isaac Sabel from the Grisham Research Lab, an experimental clinical psychology research group at UNSW Sydney.
“Negative ...
Water fluoridation less effective now than in past
2024-10-04
The dental health benefits of adding fluoride to drinking water may be smaller now than before fluoride toothpaste was widely available, an updated Cochrane review has found.
The team of researchers from the Universities of Manchester, Dundee and Aberdeen reviewed the evidence from 157 studies which compared communities that had fluoride added to their water supplies with communities that had no additional fluoride in their water. They found that the benefit of fluoridation has declined since the 1970s, when fluoride toothpaste became more widely available.
The contemporary studies were conducted in high-income countries. The impact of community water fluoridation ...
Toddlers get nearly half their calories from ultra-processed foods
2024-10-04
Toddlers in the UK obtain nearly half (47%) of their calories from ultra-processed foods (UPFs), and this rises to 59% by the age of seven, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in the European Journal of Nutrition, looked at data from 2,591 children born in the UK in 2007 and 2008 whose parents recorded what their children ate and drank over three days.
The most common UPFs consumed by the toddlers – who were 21 months when their parents recorded their diets – were flavoured ...